As traduções são geradas por tradução automática. Em caso de conflito entre o conteúdo da tradução e da versão original em inglês, a versão em inglês prevalecerá.
Entenda a arquitetura de inserção de anúncios para CDN e integrações MediaTailor
Esta seção explica os conceitos e a arquitetura da inserção de anúncios no lado do servidor (SSAI) com redes de entrega de conteúdo () para. CDNs AWS Elemental MediaTailor Você aprenderá como a inserção dinâmica de anúncios e a manipulação de manifestos funcionam juntas para permitir uma monetização eficaz de vídeos.
A inserção de anúncios no lado do servidor (SSAI) permite que você: MediaTailor
-
Insira publicidade personalizada em seus streams de vídeo em pontos de interrupção de anúncios definidos
-
Segmente anúncios com precisão com base nos dados do espectador
-
Elimine a necessidade de tecnologia de inserção de anúncios do lado do cliente
Quando combinado com uma CDN, você pode fornecer esses streams personalizados aos espectadores com melhor desempenho e escalabilidade, aprimorando sua estratégia de monetização de vídeos.
A arquitetura recomendada para inserção de anúncios com uma CDN posiciona a CDN entre os visualizadores e a inserção de anúncios, com a inserção de anúncios acessando o conteúdo diretamente de sua origem. Essa arquitetura oferece os seguintes benefícios tanto para a entrega de conteúdo quanto para a monetização de vídeos:
-
Armazenamento efetivo de conteúdo e segmentos de anúncios
-
Carga de solicitações reduzida em MediaTailor
-
Velocidade de entrega aprimorada para os espectadores
-
Gerenciamento simplificado de URL
-
Entrega consistente de publicidade personalizada em todos os dispositivos
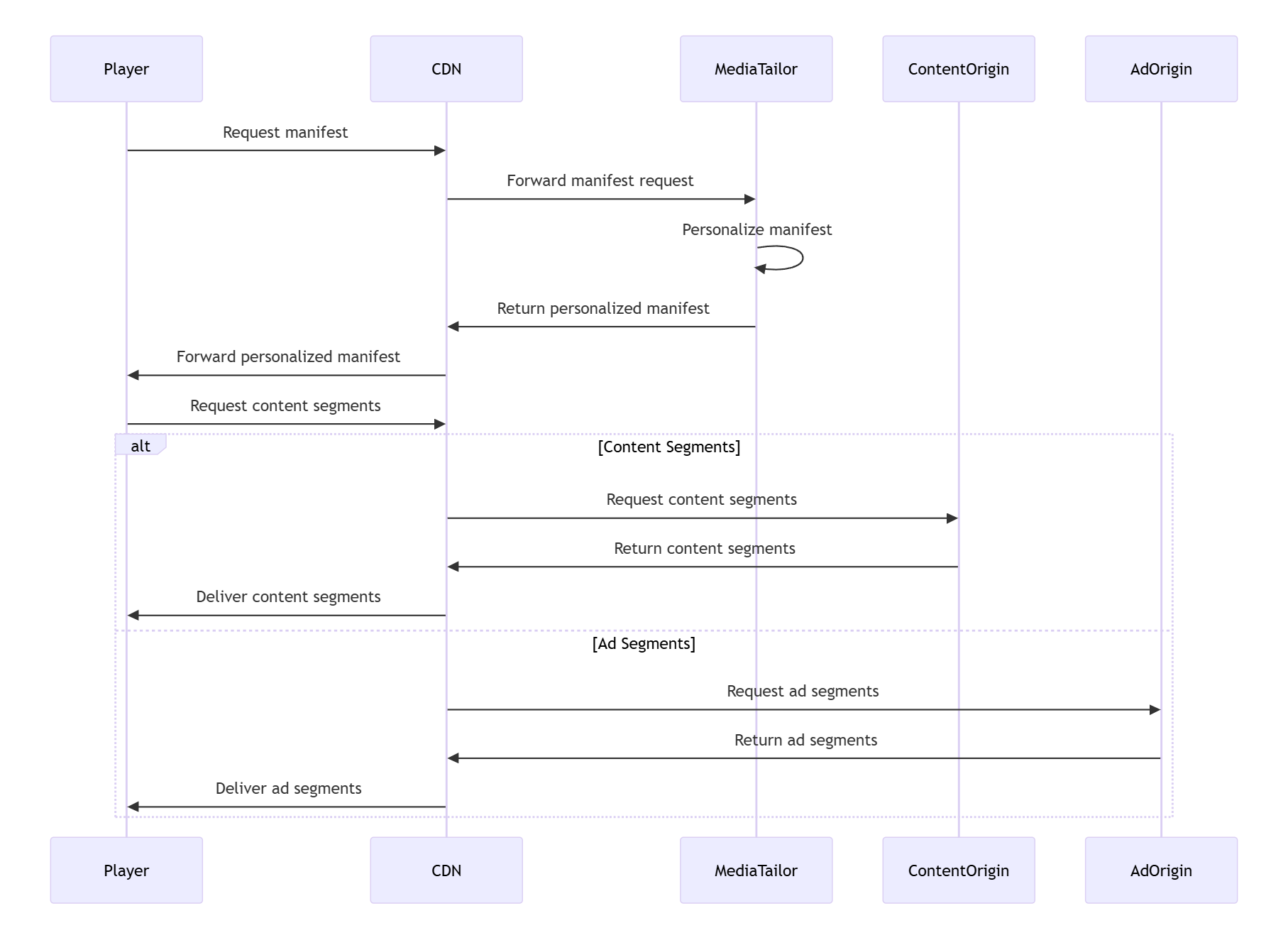
Nessa arquitetura recomendada:
-
Os espectadores solicitam manifestos da CDN
-
CDN encaminha solicitações para inserção de anúncios
-
A inserção de anúncios solicita manifestos de conteúdo da origem
-
A inserção de anúncios solicita anúncios do servidor de decisão de anúncios (ADS)
-
A inserção de anúncios personaliza os manifestos substituindo os marcadores de anúncios (do manifesto de origem) por URLs esse ponto em segmentos de anúncios segmentados para o espectador específico (do ADS)
-
A inserção de anúncios retorna os manifestos personalizados contendo segmentos de anúncios URLs para a CDN, que os encaminha para os espectadores
-
Os espectadores solicitam segmentos por meio da CDN
-
A CDN encaminha as solicitações de segmentos com base no tipo de segmento:
-
As solicitações de segmentos de conteúdo vão para a origem do conteúdo
-
As solicitações de segmentos de anúncios vão para MediaTailor
-
Essa arquitetura garante um desempenho ideal enquanto mantém os benefícios de segurança e flexibilidade do uso de uma CDN.
nota
Esse fluxo varia um pouco entre VOD e conteúdo ao vivo. Para VOD, os manifestos podem ser armazenados em cache por mais tempo, enquanto o conteúdo ao vivo exige atualizações mais frequentes dos manifestos para manter a continuidade do stream.
A principal diferença entre VOD e cache de conteúdo ao vivo:
- Conteúdo VOD
-
Defina valores de TTL mais longos (minutos a horas) para manifestos porque eles não mudam com frequência
- Conteúdo ao vivo
-
Defina valores de TTL mais curtos (segundos) para manifestos para garantir que os espectadores recebam os segmentos de transmissão mais atuais
Não recomendamos que você posicione uma CDN entre a origem do seu conteúdo e. AWS Elemental MediaTailor Fazer isso pode introduzir vários desafios técnicos:
- Colisões de chaves de cache
-
Configure sua CDN para lidar adequadamente com os parâmetros de consulta. Isso evita o recebimento MediaTailor de manifestos incorretos ao solicitar o mesmo manifesto com parâmetros de consulta diferentes.
- Problemas de compressão do Gzip
-
Se você tiver erros de análise de manifestos, certifique-se de que sua CDN entregue manifestos formatados corretamente para. MediaTailor Alguns CDNs podem fornecer cargas gzip corrompidas que podem causar falhas na análise. Se isso ocorrer, talvez seja necessário desativar a compactação entre sua CDN e, ao MediaTailor mesmo tempo, manter a compactação para reduzir custos em outras partes do fluxo de trabalho.
- Frescura manifesta
-
Para transmissões ao vivo, configure sua CDN para entregar os manifestos atuais para. MediaTailor Isso evita problemas de sincronização entre conteúdo e anúncios.
- Otimização de desempenho
-
Minimize os saltos de rede e possíveis perdas de cache para reduzir os tempos de inicialização da reprodução.
- Gerenciamento de cache
-
Implemente estratégias simplificadas de invalidação de cache, especialmente para conteúdo ativo em que os manifestos são atualizados com frequência.
Nessa arquitetura abaixo do ideal:
-
Os espectadores solicitam playlists multivariantes, playlists de mídia ou diretamente de. MPDs AWS Elemental MediaTailor
-
MediaTailor solicita manifestos de conteúdo (playlists multivariantes, playlists de mídia ou) por meio da CDN. MPDs
-
A CDN encaminha as solicitações para o servidor de origem.
-
O servidor de origem retorna playlists multivariantes, playlists de mídia ou para a CDN. MPDs
-
O CDN encaminha playlists multivariantes, playlists de mídia ou para. MPDs MediaTailor
-
MediaTailor solicita anúncios do servidor de decisão de anúncios (ADS).
-
MediaTailor personaliza manifestos inserindo anúncios em playlists multivariantes, playlists de mídia ou os entrega diretamente aos espectadores. MPDs
-
Essa arquitetura introduz latência adicional, possíveis problemas de cache e complica a solução de problemas.
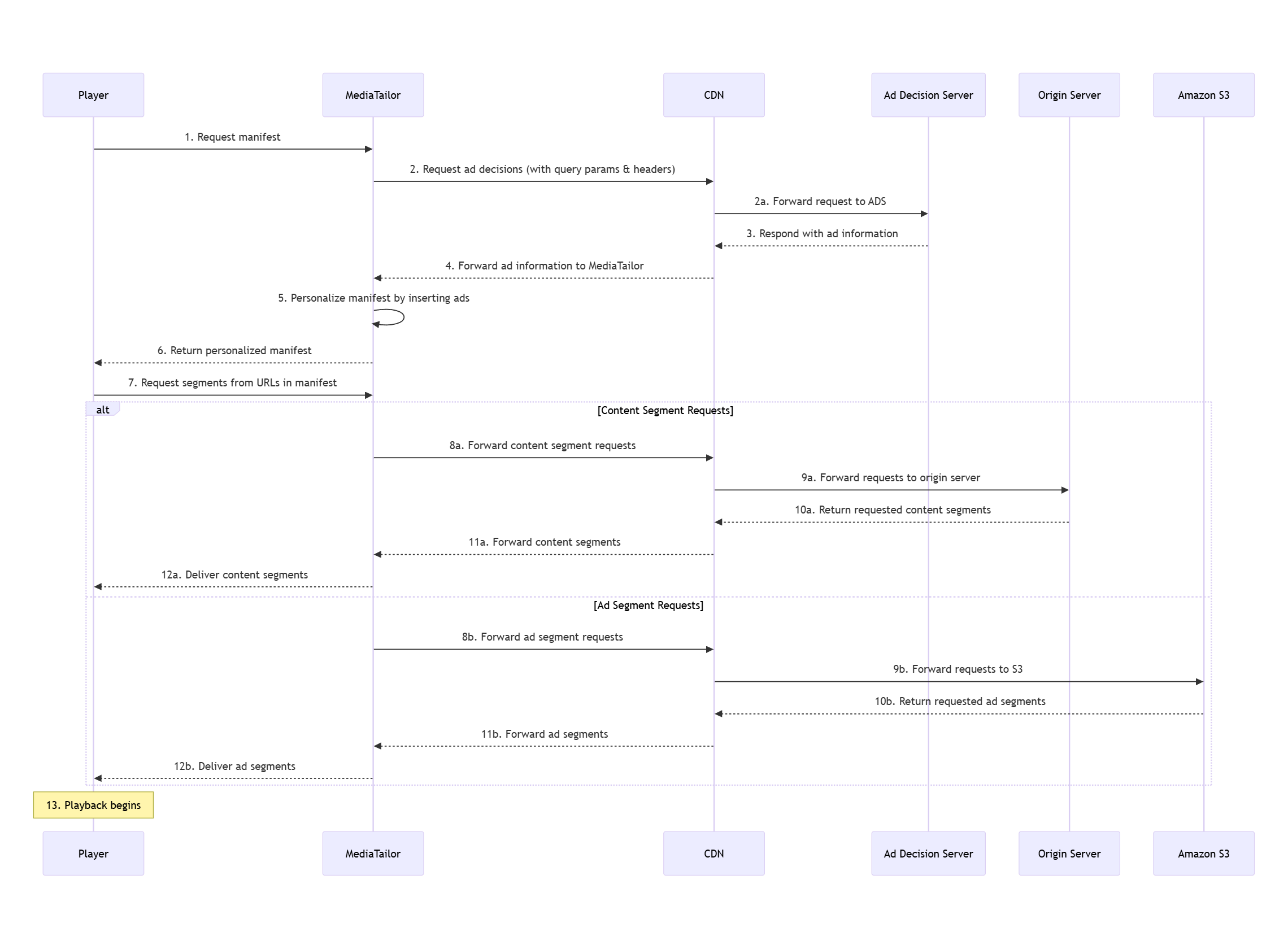
Fluxo de solicitações e respostas
Ao implementar a inserção dinâmica de anúncios com uma CDN, configure seu sistema para suportar esse fluxo de solicitação e resposta:
-
Configure seu player para solicitar playlists multivariantes (HLS) ou MPDs (DASH) do seu CDN como origem do manifesto. MediaTailor
-
Configure sua CDN para encaminhar todas as solicitações multivariadas de playlist, playlist de mídia e MPD MediaTailor, incluindo todos os parâmetros e cabeçalhos de consulta.
-
Certifique-se de MediaTailor poder se comunicar com seu servidor de decisão de anúncios (ADS), transmitindo parâmetros e cabeçalhos de consulta.
-
Configure seu ADS para usar parâmetros de consulta para determinar quais anúncios inserir.
-
Configure o prefixo CDN na configuração de MediaTailor reprodução para MediaTailor poder substituir os nomes de domínio CDN pelos prefixos de URL do conteúdo e do segmento de anúncios.
-
Configure sua CDN para encaminhar playlists multivariantes personalizadas, playlists de mídia e MPDs de para o player solicitante. MediaTailor
-
Configure sua CDN para traduzir segmentos URLs, encaminhando solicitações de segmentos de conteúdo para o servidor de origem e solicitações de anúncios para o bucket do Amazon S3, MediaTailor onde armazena anúncios transcodificados.
Terminologia CDN para inserção de anúncios
A compreensão desses termos-chave ajudará você a implementar e solucionar problemas de integração com a CDN de inserção de anúncios:
- CDN de origem e CDN de borda
-
CDN de origem: uma CDN posicionada entre MediaTailor e a origem do seu conteúdo. Ele armazena segmentos de conteúdo em cache para reduzir a carga em seus servidores de origem. Em uma arquitetura multi-CDN, essa é a primeira camada CDN que interage diretamente com a origem.
Edge CDN: Uma CDN posicionada entre visualizadores e. MediaTailor Ele oferece manifestos e conteúdo personalizados aos espectadores. Em uma arquitetura multi-CDN, essa é a camada CDN mais externa que interage diretamente com os visualizadores.
- Termos de configuração do CDN
-
Comportamento do cache: regras que determinam como uma CDN lida com diferentes tipos de solicitações. Essas regras incluem:
-
Configurações de duração do armazenamento em cache
-
Configurações de roteamento de origem
-
Parâmetros de tratamento de solicitações
TTL (Time To Live): a duração pela qual o conteúdo permanece válido em um cache CDN antes de precisar ser atualizado a partir da origem.
Chave de cache: o identificador exclusivo usado por uma CDN para armazenar e recuperar conteúdo em cache. Normalmente inclui:
-
Caminho do URL
-
Parâmetros de consulta
-
Cabeçalhos selecionados
Escudo de origem: uma camada intermediária de cache entre os pontos de borda da CDN e seu servidor de origem. Isso reduz o número de solicitações até sua origem.
Colapso da solicitação: um recurso de CDN que combina várias solicitações simultâneas para o mesmo conteúdo em uma única solicitação de origem.
-
- MediaTailor-termos específicos da CDN
-
Prefixo do segmento de conteúdo CDN: O nome de domínio CDN AWS Elemental MediaTailor usado na geração de segmentos de conteúdo em URLs manifestos.
Prefixo do segmento de anúncio CDN: o nome de domínio CDN MediaTailor usado na geração de segmentos de anúncios em URLs manifestos.
Para obter mais informações sobre a configuração de CDN com MediaTailor, consulteConfigurar a integração com a CDN.
nota
Esses termos são consistentes com aqueles usados na documentação de montagem do canal. Para a terminologia de montagem de canais, consulteTerminologia CDN para montagem de canais.