Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Emulieren Sie PL/SQL assoziative Oracle-Arrays in Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL und Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
Rajkumar Raghuwanshi, Bhanu Ganesh Gudivada und Sachin Khanna, Amazon Web Services
Übersicht
Dieses Muster beschreibt, wie PL/SQL assoziative Oracle-Arrays mit leeren Indexpositionen in Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL- und Amazon
Wir bieten eine PostgreSQL-Alternative zur Verwendung von aws_oracle_ext Funktionen zur Behandlung leerer Indexpositionen bei der Migration einer Oracle-Datenbank. Dieses Muster verwendet eine zusätzliche Spalte, um Indexpositionen zu speichern, und es behält den Umgang von Oracle mit spärlichen Arrays bei und integriert gleichzeitig native PostgreSQL-Funktionen.
Oracle
In Oracle können Sammlungen als leer initialisiert und mit der EXTEND Collection-Methode aufgefüllt werden, bei der Elemente an das Array angehängt werden. NULL Bei der Arbeit mit PL/SQL assoziativen Arrays, die mit indexiert sindPLS_INTEGER, fügt die EXTEND Methode Elemente sequentiell hinzu. NULL Elemente können aber auch an nicht sequentiellen Indexpositionen initialisiert werden. Jede Indexposition, die nicht explizit initialisiert wurde, bleibt leer.
Diese Flexibilität ermöglicht spärliche Array-Strukturen, in denen Elemente an beliebigen Positionen aufgefüllt werden können. Bei der Iteration durch Sammlungen mit einem FOR LOOP mit FIRST und LAST Grenzen werden nur die initialisierten Elemente (unabhängig davon, ob NULL oder mit einem definierten Wert) verarbeitet, während leere Positionen übersprungen werden.
PostgreSQL (Amazon Aurora und Amazon RDS)
PostgreSQL behandelt leere Werte anders NULL als Werte. Es speichert leere Werte als unterschiedliche Entitäten, die ein Byte Speicherplatz verwenden. Wenn ein Array leere Werte enthält, weist PostgreSQL sequentielle Indexpositionen genau wie nicht leere Werte zu. Die sequentielle Indizierung erfordert jedoch zusätzliche Verarbeitung, da das System alle indizierten Positionen durchlaufen muss, einschließlich der leeren. Dies macht die herkömmliche Array-Erstellung für spärliche Datensätze ineffizient.
AWS Schema Conversion Tool
The AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) verarbeitet Oracle-to-PostgreSQL Migrationen in der Regel mithilfe von Funktionen. aws_oracle_ext In diesem Muster schlagen wir einen alternativen Ansatz vor, der native PostgreSQL-Funktionen verwendet und PostgreSQL-Arraytypen mit einer zusätzlichen Spalte zum Speichern von Indexpositionen kombiniert. Das System kann dann durch Arrays iterieren, indem es nur die Indexspalte verwendet.
Voraussetzungen und Einschränkungen
Voraussetzungen
Ein aktiver. AWS-Konto
Ein AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM-) Benutzer mit Administratorrechten.
Eine Instance, die mit Amazon RDS oder Aurora PostgreSQL kompatibel ist.
Ein grundlegendes Verständnis von relationalen Datenbanken.
Einschränkungen
Einige AWS-Services sind nicht in allen AWS-Regionen verfügbar. Informationen zur Verfügbarkeit in den einzelnen Regionen finden Sie AWS-Services unter Nach Regionen
. Informationen zu bestimmten Endpunkten finden Sie auf der Seite Dienstendpunkte und Kontingente. Wählen Sie dort den Link für den Dienst aus.
Produktversionen
Dieses Muster wurde mit den folgenden Versionen getestet:
Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL 13.3
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL 13.3
AWS SCT 1.0.674
Oracle 12c EE 12.2
Architektur
Quelltechnologie-Stack
Lokale Oracle-Datenbank
Zieltechnologie-Stack
Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
Amazon RDS für PostgreSQL
Zielarchitektur
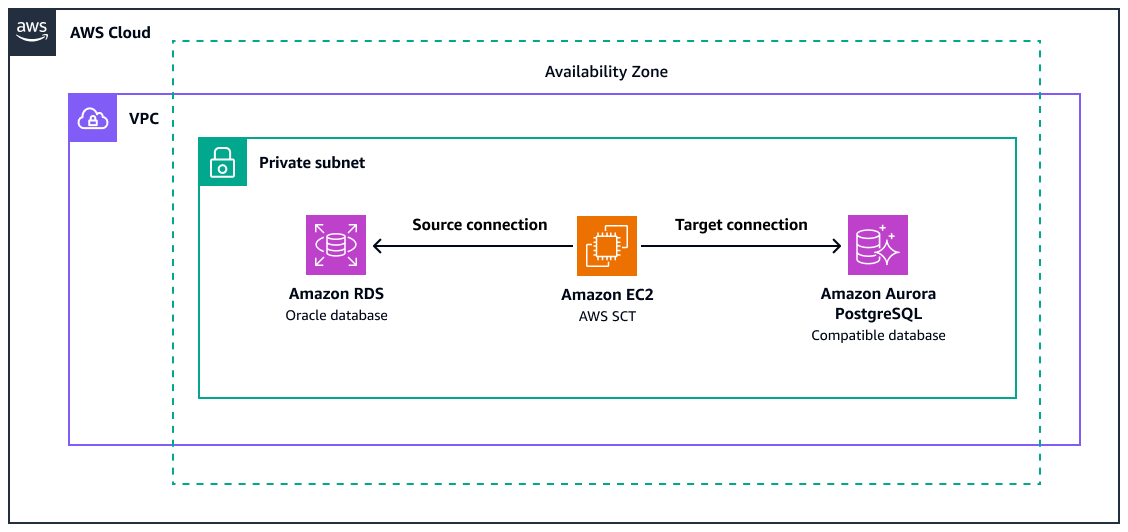
Das Diagramm zeigt Folgendes:
Eine Amazon RDS for Oracle-Quelldatenbank-Instance
Eine EC2 Amazon-Instance mit AWS SCT zur Konvertierung von Oracle-Funktionen in das PostgreSQL-Äquivalent
Eine Zieldatenbank, die mit Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL kompatibel ist
Tools
AWS-Services
Amazon Aurora ist eine vollständig verwaltete relationale Datenbank-Engine, die für die Cloud entwickelt wurde und mit MySQL und PostgreSQL kompatibel ist.
Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition ist eine vollständig verwaltete, ACID-konforme relationale Datenbank-Engine, die Sie bei der Einrichtung, dem Betrieb und der Skalierung von PostgreSQL-Bereitstellungen unterstützt.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) bietet skalierbare Rechenkapazität in der AWS Cloud. Sie können so viele virtuelle Server wie nötig nutzen und sie schnell nach oben oder unten skalieren.
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) unterstützt Sie bei der Einrichtung, dem Betrieb und der Skalierung einer relationalen Datenbank in der. AWS Cloud
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) für Oracle unterstützt Sie bei der Einrichtung, dem Betrieb und der Skalierung einer relationalen Oracle-Datenbank in der. AWS Cloud
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) für PostgreSQL unterstützt Sie bei der Einrichtung, dem Betrieb und der Skalierung einer relationalen PostgreSQL-Datenbank in der. AWS Cloud
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) unterstützt heterogene Datenbankmigrationen, indem das Quelldatenbankschema und ein Großteil des benutzerdefinierten Codes automatisch in ein Format konvertiert werden, das mit der Zieldatenbank kompatibel ist.
Andere Tools
Oracle SQL Developer
ist eine integrierte Entwicklungsumgebung, die die Entwicklung und Verwaltung von Oracle-Datenbanken sowohl in herkömmlichen als auch in Cloud-basierten Bereitstellungen vereinfacht. pgAdmin
ist ein Open-Source-Verwaltungstool für PostgreSQL. Es bietet eine grafische Oberfläche, mit der Sie Datenbankobjekte erstellen, verwalten und verwenden können. In diesem Muster stellt pgAdmin eine Verbindung zur Datenbankinstanz RDS for PostgreSQL her und fragt die Daten ab. Alternativ können Sie den psql-Befehlszeilenclient verwenden.
Bewährte Methoden
Testen Sie Datensatzgrenzen und Edge-Szenarien.
Erwägen Sie die Implementierung einer Fehlerbehandlung für out-of-bounds Indexbedingungen.
Optimieren Sie Abfragen, um das Scannen spärlicher Datensätze zu vermeiden.
Epen
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Erstellen Sie einen PL/SQL Quellblock in Oracle. | Erstellen Sie in Oracle einen PL/SQL Quellblock, der das folgende assoziative Array verwendet:
| DBA |
Lass den PL/SQL Block laufen. | Führen Sie den PL/SQL Quellblock in Oracle aus. Wenn zwischen den Indexwerten eines assoziativen Arrays Lücken bestehen, werden in diesen Lücken keine Daten gespeichert. Dadurch kann die Oracle-Schleife nur durch die Indexpositionen iterieren. | DBA |
Überprüfen Sie die Ausgabe. | Fünf Elemente wurden in nicht aufeinanderfolgenden Intervallen in das Array (
| DBA |
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Erstellen Sie einen PL/pgSQL Zielblock in PostgreSQL. | Erstellen Sie einen PL/pgSQL Zielblock in PostgreSQL, der das folgende assoziative Array verwendet:
| DBA |
Lass den PL/pgSQL Block laufen. | Führen Sie den PL/pgSQL Zielblock in PostgreSQL aus. Wenn zwischen den Indexwerten eines assoziativen Arrays Lücken bestehen, werden in diesen Lücken keine Daten gespeichert. Dadurch kann die Oracle-Schleife nur durch die Indexpositionen iterieren. | DBA |
Überprüfen Sie die Ausgabe. | Die Array-Länge ist größer als 5, weil sie in den Lücken zwischen den Indexpositionen gespeichert
| DBA |
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Erstellen Sie einen PL/pgSQL Zielblock mit einem Array und einem benutzerdefinierten Typ. | Um die Leistung zu optimieren und der Funktionalität von Oracle zu entsprechen, können wir einen benutzerdefinierten Typ erstellen, der sowohl Indexpositionen als auch die entsprechenden Daten speichert. Dieser Ansatz reduziert unnötige Iterationen, indem direkte Verknüpfungen zwischen Indizes und Werten beibehalten werden.
| DBA |
Lass den PL/pgSQL Block laufen. | Führen Sie den PL/pgSQL Zielblock aus. Wenn zwischen den Indexwerten eines assoziativen Arrays Lücken bestehen, werden in diesen Lücken keine Daten gespeichert. Dadurch kann die Oracle-Schleife nur durch die Indexpositionen iterieren. | DBA |
Überprüfen Sie die Ausgabe. | Wie in der folgenden Ausgabe gezeigt, speichert der benutzerdefinierte Typ nur aufgefüllte Datenelemente, was bedeutet, dass die Länge des Arrays der Anzahl der Werte entspricht. Daher sind
| DBA |
Zugehörige Ressourcen
AWS Dokumentation
Weitere Dokumentation