Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Integrieren Sie visuelle Komponenten von Amazon Quick Sight mithilfe von Amazon Cognito und IaC-Automatisierung in Webanwendungen
Ishita Gupta und Srishti Wadhwa, Amazon Web Services
Zusammenfassung
Dieses Muster bietet einen speziellen Ansatz für die Einbettung der visuellen Komponenten von Amazon Quick Sight in React-Anwendungen, indem die Einbettung registrierter Benutzer mit optimierter Amazon Cognito Cognito-Authentifizierung verwendet wird. Diese Ressourcen werden dann über eine IaC-Vorlage (Infrastructure as Code) bereitgestellt. Im Gegensatz zur herkömmlichen Dashboard-Einbettung isoliert diese Lösung spezifische Diagramme und Grafiken für die direkte Integration in React-Anwendungen, wodurch sowohl die Leistung als auch die Benutzererfahrung erheblich verbessert werden.
Die Architektur sorgt für einen effizienten Authentifizierungsfluss zwischen der Amazon Cognito-Benutzerverwaltung und den Quick Sight-Berechtigungen: Benutzer authentifizieren sich über Amazon Cognito und greifen auf ihre autorisierten Visualisierungen auf der Grundlage der Dashboard-Freigaberegeln in Quick Sight zu. Dieser optimierte Ansatz macht den direkten Zugriff auf die Quick Sight-Konsole überflüssig und gewährleistet gleichzeitig robuste Sicherheitskontrollen.
Die gesamte Umgebung wird über eine einzige AWS CloudFormation Vorlage bereitgestellt, die alle erforderlichen Infrastrukturkomponenten bereitstellt, darunter:
Ein serverloses Backend, das ein Amazon AWS Lambda API Gateway verwendet
Sicheres Frontend-Hosting über Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) und AWS WAF
Identitätsmanagement mithilfe von Amazon Cognito
Alle Komponenten werden gemäß den bewährten Sicherheitsmethoden mit IAM-Richtlinien AWS Identity and Access Management (Least-Privilege), AWS WAF Schutz und Verschlüsselung konfiguriert. end-to-end
Diese Lösung ist ideal für Entwicklungsteams und Unternehmen, die sichere, interaktive Analysen in ihre Anwendungen integrieren und gleichzeitig die genaue Kontrolle über den Benutzerzugriff behalten möchten. Die Lösung nutzt AWS verwaltete Dienste und Automatisierung, um den Einbettungsprozess zu vereinfachen, die Sicherheit zu erhöhen und Skalierbarkeit zu gewährleisten, um den sich ändernden Geschäftsanforderungen gerecht zu werden.
Zielgruppe und Anwendungsfälle:
Frontend-Entwickler, die Analysen in React-Apps einbetten möchten
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) -Produktteams, die benutzerspezifische oder rollenbasierte Datenvisualisierungen anbieten möchten
Lösungsarchitekten, die an der Integration von Analysen in benutzerdefinierte Portale interessiert sind AWS
Entwickler von Business Intelligence (BI), die authentifizierten Benutzern Grafiken zur Verfügung stellen möchten, ohne vollen Zugriff auf das Dashboard zu benötigen
Unternehmensteams, die interaktive Quick Sight-Diagramme in interne Tools einbetten möchten
Voraussetzungen und Einschränkungen
Voraussetzungen
Um dieses Muster erfolgreich zu implementieren, stellen Sie sicher, dass die folgenden Voraussetzungen erfüllt sind:
Aktiv AWS-Konto — Ein AWS-Konto mit Berechtigungen zum Bereitstellen von CloudFormation Stacks und zum Erstellen von Lambda-, API Gateway-, Amazon Cognito- und Amazon S3 CloudFront S3-Ressourcen.
Amazon Quick Sight-Konto — Ein aktives Quick Sight-Konto mit mindestens einem Dashboard, das Bildmaterial enthält. Anweisungen zur Einrichtung finden Sie unter Tutorial: Erstellen Sie ein Amazon Quick Sight-Dashboard mithilfe von Beispieldaten in der Amazon Quick Suite-Dokumentation.
Eine Entwicklungsumgebung, die aus folgenden Komponenten besteht:
Node.js (Version 16 oder höher)
npm oder yarn installiert
Vite als React-Build-Tool
React (Version 19.1.1)
Teilen von Dashboards — Dashboards müssen in Quick Sight geteilt werden und der Implementierer muss sich anmelden, um auf die eingebetteten Grafiken oder Dashboards zugreifen zu können.
Einschränkungen
Dieses Muster verwendet die Methode zur Einbettung registrierter Benutzer, was voraussetzt, dass Implementierer über ein aktives Quick Sight-Konto verfügen.
Der Zugriff ist auf die Dashboards und Grafiken beschränkt, die explizit mit dem authentifizierten Quick Sight-Benutzer geteilt werden, der dieses Muster implementiert. Wenn der Implementierer nicht über die richtigen Zugriffsrechte verfügt, schlägt die Generierung der Einbettungs-URL fehl und die Grafiken werden nicht geladen.
Der CloudFormation Stack muss in einem System bereitgestellt werden, in AWS-Region dem Quick Sight, API Gateway und Amazon Cognito unterstützt werden. Informationen zur Verfügbarkeit nach Regionen finden Sie unter AWS-Services Nach Regionen.
Versionen der Produkte
Version 2.10.1 des SDK zum Einbetten von Quick Sight
Node.js
Version 16 oder höher, um die Kompatibilität mit den neuesten in dieser Lösung verwendeten React- und Vite-Versionen sicherzustellen
Architektur
Zielarchitektur
Das folgende Diagramm zeigt die Architektur und den Arbeitsablauf für dieses Muster.
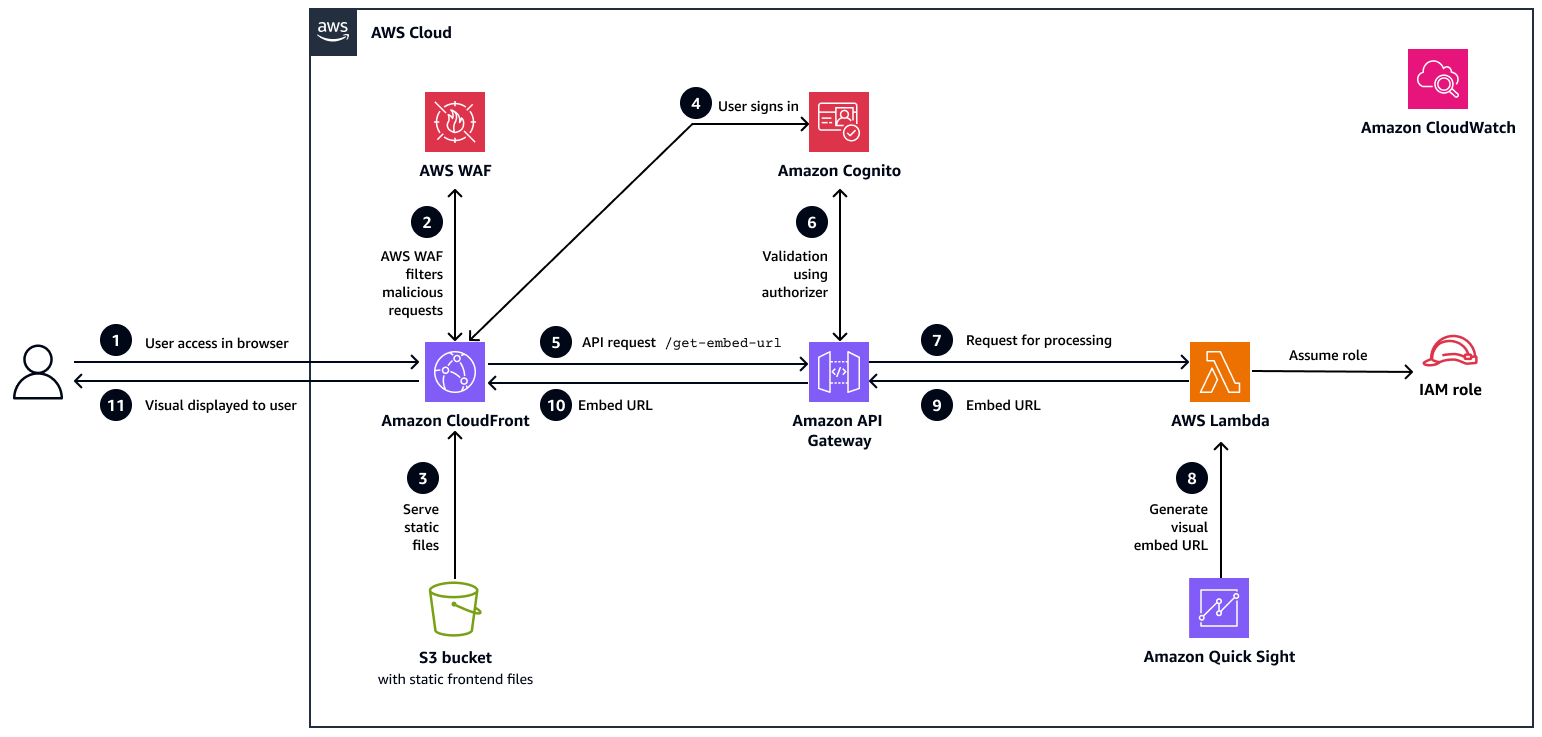
In diesem Workflow:
Der Benutzer greift auf die Anwendung zu. Der Benutzer öffnet die React-Webanwendung mit einem Browser. Die Anfrage wird an eine CloudFront Distribution weitergeleitet, die als Netzwerk zur Bereitstellung von Inhalten für die Anwendung fungiert.
AWS WAF filtert bösartige Anfragen. Bevor die Anfrage eintrifft CloudFront, wird sie weitergeleitet AWS WAF. AWS WAF untersucht den Datenverkehr und blockiert alle böswilligen oder verdächtigen Anfragen auf der Grundlage von Sicherheitsregeln.
Amazon S3 stellt statische Dateien bereit. Wenn die Anfrage sauber ist, CloudFront ruft die statischen Frontend-Assets (HTML, JS, CSS) mithilfe von Origin Access Control (OAC) aus einem privaten S3-Bucket ab und übermittelt sie an den Browser.
Der Benutzer meldet sich an. Nachdem die Anwendung geladen wurde, meldet sich der Benutzer über Amazon Cognito an, das den Benutzer authentifiziert und ein sicheres JSON-Web-Token (JWT) für den autorisierten API-Zugriff zurückgibt.
Die Anwendung stellt eine API-Anfrage. Nach der Anmeldung ruft die React-Anwendung den
/get-embed-urlEndpunkt auf API Gateway sicher auf und übergibt das JWT-Token im Anforderungsheader zur Authentifizierung.Das Token ist validiert. API Gateway validiert das Token mithilfe eines Amazon Cognito Cognito-Autorisierers. Wenn das Token gültig ist, wird die Anfrage fortgesetzt; andernfalls wird sie mit einer 401-Antwort (nicht autorisiert) abgelehnt.
Die Anfrage wird zur Bearbeitung an Lambda weitergeleitet. Die validierte Anfrage wird dann an eine Backend-Lambda-Funktion weitergeleitet. Diese Funktion ist für die Generierung der Einbettungs-URL für das angeforderte Quick Sight-Visual verantwortlich.
Lambda generiert die Einbettungs-URL aus Quick Sight. IAM verwendet eine IAM-Rolle mit den entsprechenden Berechtigungen, um die Quick
GenerateEmbedUrlForRegisteredUserSight-API aufzurufen und eine sichere, benutzerspezifische visuelle URL zu generieren.Lambda gibt die Einbettungs-URL an API Gateway zurück. Lambda sendet die generierte Einbettungs-URL als Teil einer JSON-Antwort zurück an API Gateway. Diese Antwort wird dann für die Übermittlung an das Frontend vorbereitet.
Die Einbettungs-URL wird an den Browser gesendet. Die Einbettungs-URL wird als API-Antwort an den Browser zurückgegeben.
Das Bild wird dem Benutzer angezeigt. Die React-Anwendung empfängt die Antwort und verwendet das Quick Sight Embedding SDK, um das spezifische Bild für den Benutzer zu rendern.
Automatisierung und Skalierung
Backend- und Frontend-Bereitstellungen sind vollständig automatisiert durch die Verwendung CloudFormation, wodurch alle erforderlichen AWS Ressourcen bereitgestellt werden, einschließlich Amazon Cognito, Lambda, API Gateway, Amazon S3,, CloudFront AWS WAF, IAM-Rollen und Amazon in einer einzigen Bereitstellung. CloudWatch
Diese Automatisierung gewährleistet eine konsistente und wiederholbare Infrastruktur in allen Umgebungen. Alle Komponenten werden automatisch skaliert: Lambda passt sich Funktionsaufrufen an, CloudFront stellt zwischengespeicherte Inhalte global bereit und API Gateway skaliert mit eingehenden Anfragen.
Tools
AWS-Services
Amazon Quick Sight
ist ein Cloud-nativer Business Intelligence-Service, mit dem Sie interaktive Dashboards und Grafiken erstellen, verwalten und einbetten können. Amazon API Gateway
verwaltet APIs diese Funktionen als Brücke zwischen der React-Anwendung und den Backend-Services. AWS Lambda
ist ein serverloser Rechendienst, den dieses Muster verwendet, um sichere Quick Sight-Einbettungen URLs dynamisch zu generieren, und der automatisch auf der Grundlage von Anfragen skaliert wird. Amazon Cognito
bietet Authentifizierung und Autorisierung für Benutzer und stellt sichere Token für den API-Zugriff aus. Amazon S3
hostet statische Frontend-Ressourcen für dieses Muster und stellt sie sicher bereit. CloudFront Amazon CloudFront
stellt Frontend-Inhalte weltweit mit geringer Latenz bereit und integriert sie AWS WAF zur Filterung des Datenverkehrs. AWS WAF
schützt die Webanwendung vor bösartigem Datenverkehr durch Anwendung von Sicherheitsregeln und Ratenbegrenzung. AWS CloudFormationautomatisiert die Bereitstellung und Konfiguration aller Anwendungsressourcen in einer einzigen Bereitstellung.
Amazon CloudWatch
sammelt Protokolle und Metriken von Lambda, API Gateway und AWS WAF zur Überwachung und Fehlerbehebung.
Tools für die Entwicklung
React JS
ist ein Frontend-Framework, das dieses Muster verwendet, um die Webanwendung zu erstellen und eingebettete Quick Sight-Grafiken zu integrieren. Vite
ist ein Build-Tool, das für die schnelle Entwicklung und optimierte Produktions-Builds der React-Anwendung verwendet wird. Das Quick Sight Embedding SDK
erleichtert das Einbetten von Quick Sight-Grafiken in die React-Anwendung und ermöglicht eine nahtlose Interaktion zwischen der Anwendung und den Grafiken.
Code-Repository
Der Code für dieses Muster ist im GitHub Amazon Quick Sight Visual Embedding in React-Repository
Best Practices
Dieses Muster implementiert automatisch die folgenden bewährten Sicherheitsmethoden:
Verwendet Amazon Cognito Cognito-Benutzerpools für die JWT-basierte Authentifizierung mit optionaler Multi-Faktor-Authentifizierung (MFA).
Schützt APIs mit Amazon Cognito Cognito-Autorisierern und setzt IAM-Richtlinien mit den geringsten Rechten für alle Services durch.
Implementiert die Einbettung registrierter Benutzer in Quick Sight und stellt Benutzern automatisch die Leserrolle zu.
Erzwingt eine Verschlüsselung bei der Übertragung, die TLS 1.2 und spätere Versionen über CloudFront HTTPS unterstützt.
Verschlüsselt Daten im Ruhezustand mithilfe von AES-256 für Amazon S3 mit Versionierung und OAC.
Konfiguriert API Gateway Gateway-Nutzungspläne mit Drosselung und Kontingenten.
Schützt Lambda mit reservierter Parallelität und Schutz vor Umgebungsvariablen.
Aktiviert die Protokollierung für Amazon S3 CloudFront, Lambda und API Gateway; überwacht Dienste mithilfe CloudWatch von.
Verschlüsselt Protokolle, wendet Zugriffskontrollen an und setzt Ablehnungsrichtlinien für Nicht-HTTPS-basierte oder unverschlüsselte Uploads durch.
Darüber hinaus empfehlen wir Folgendes:
Wird verwendet CloudFormation , um Bereitstellungen zu automatisieren und konsistente Konfigurationen in allen Umgebungen aufrechtzuerhalten.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass jeder Benutzer über die richtigen Quick Sight-Berechtigungen für den Zugriff auf eingebettete Grafiken verfügt.
Schützen Sie API Gateway Gateway-Endpunkte mit Amazon Cognito Cognito-Autorisierern und setzen Sie das Prinzip der geringsten Rechte für alle IAM-Rollen durch.
Speichern Sie vertrauliche Informationen wie Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) und IDs in Umgebungsvariablen, anstatt sie fest zu codieren.
Optimieren Sie Lambda-Funktionen, indem Sie Abhängigkeiten reduzieren und die Kaltstartleistung verbessern. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im AWS Blogbeitrag Optimierung der Kaltstartleistung beim AWS Lambda Einsatz fortschrittlicher Priming-Strategien
mit. SnapStart Fügen Sie Ihre CloudFront Domain zur Quick Sight-Zulassungsliste hinzu, um eine sichere visuelle Einbettung zu ermöglichen.
Überwachen Sie Leistung und Sicherheit mithilfe CloudWatch von Protokollierung, Warnmeldungen und Datenverkehrsschutz. AWS WAF
Weitere empfohlene bewährte Methoden
Verwenden Sie benutzerdefinierte Domains mit SSL-Zertifikaten von AWS Certificate Manager , um ein sicheres und markenspezifisches Benutzererlebnis zu bieten.
Verschlüsseln Sie Amazon S3 S3-Daten und CloudWatch -Protokolle mithilfe von vom Kunden verwalteten AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) Schlüsseln, um mehr Kontrolle über die Verschlüsselung zu haben.
Erweitern Sie die AWS WAF Regeln um Geoblocking, SQL-Injection (SQLi), Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) -Schutz und benutzerdefinierte Filter für eine verbesserte Bedrohungsabwehr.
Aktivieren Sie CloudWatch Alarme und sorgen Sie AWS CloudTrail für Überwachung AWS Config, Prüfung und Einhaltung von Konfigurationen in Echtzeit.
Wenden Sie detaillierte IAM-Richtlinien an, erzwingen Sie die Rotation von API-Schlüsseln und gewähren Sie kontoübergreifenden Zugriff nur dann, wenn dies unbedingt erforderlich ist.
Führen Sie regelmäßige Sicherheitsbewertungen durch, um die Einhaltung von Compliance-Rahmenbedingungen wie System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC 2), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) und Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sicherzustellen.
Epen
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Klonen Sie das Repository | Klonen Sie das GitHub Repository für diese Lösung auf Ihr lokales System und navigieren Sie zum Projektverzeichnis:
Dieses Repository enthält die CloudFormation Vorlage und den React-Quellcode, die für die Bereitstellung der Lösung erforderlich sind. | App-Developer |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Stellen Sie die Vorlage bereit. |
Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der CloudFormation Dokumentation unter Stacks erstellen und verwalten. | AWS-Administrator |
Überwachen Sie die Stack-Erstellung. | Überwachen Sie den Stack auf der Registerkarte Ereignisse, bis sein Status CREATE_COMPLETE lautet. | AWS-Administrator |
Rufen Sie die Stack-Ausgaben ab. |
| AWS-Administrator |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Rufen Sie die visuellen Kennungen von Quick Sight ab. |
| Quick Sight-Administrator |
Konfigurieren Sie Ihre lokale React-Umgebung. | Um Ihre lokale React-Umgebung einzurichten und sie mit AWS Ressourcen zu verknüpfen, erstellen Sie eine
Hier ist eine
| App-Developer |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Benutzer in Cognito erstellen oder verwalten | Um authentifizierten Benutzerzugriff auf eingebettete Quick Sight-Grafiken zu ermöglichen, erstellen Sie zunächst Benutzer in Amazon Cognito:
| AWS-Administrator |
Bieten Sie Zugriff auf das Quick Sight Dashboard | Um Zugriff auf Quick Sight-Grafiken zu gewähren, gewähren Sie authentifizierten Benutzern Viewer-Zugriffsrechte:
Jeder Benutzer erhält eine E-Mail mit einem Link zum Dashboard. Sie können die Berechtigungen jederzeit über das Menü Teilen ändern. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der Amazon Quick Suite-Dokumentation unter Gewähren einzelner Amazon Quick Sight-Benutzer und -Gruppen Zugriff auf ein Dashboard in Amazon Quick Sight. | Quick Sight-Administrator |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Installieren Sie Abhängigkeiten und erstellen Sie das Projekt. | Führen Sie im React-Anwendungsverzeichnis die folgenden Befehle aus, um optimierte Produktionsdateien zu generieren:
| App-Developer |
Laden Sie die Build-Dateien auf Amazon S3 hoch. | Laden Sie alle Dateien aus dem | App-Developer |
Erstellen Sie eine CloudFront Ungültigerklärung. | Erstellen Sie auf der CloudFront Konsole | AWS-Administrator |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Fügen Sie die CloudFront Domain zur Quick Sight-Zulassungsliste hinzu. | So ermöglichen Sie es Ihrer CloudFront Domain, Quick Sight-Grafiken sicher einzubetten:
| Quick Sight-Administrator |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Öffnen Sie die React-Anwendung. | Verwenden Sie die CloudFront Domain (aus den CloudFormation Ausgaben), um die bereitgestellte React-Webanwendung in einem Browser zu öffnen. | Besitzer der App |
Verifizieren Sie die Authentifizierung. | Melden Sie sich mit Amazon Cognito Cognito-Anmeldeinformationen bei der Anwendung an, um den Authentifizierungsablauf und die JWT-Validierung über API Gateway zu überprüfen. | Besitzer der App |
Überprüfen Sie die eingebetteten Grafiken. | Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Quick Sight-Grafiken auf der Grundlage benutzerspezifischer Zugriffsberechtigungen ordnungsgemäß in der Anwendung geladen werden. | Besitzer der App |
Validieren Sie die API- und Lambda-Konnektivität. | Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Anwendung die | Besitzer der App |
| Aufgabe | Description | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Überwachen Sie mithilfe von CloudWatch. | Sie können AWS Observability-Tools verwenden, um die Anwendung zu überwachen und eine sichere, skalierbare Leistung in der Produktion aufrechtzuerhalten. Überprüfen Sie Lambda-Protokolle, API Gateway Gateway-Metriken und Amazon Cognito Cognito-Authentifizierungsereignisse CloudWatch , um den Zustand der Anwendung sicherzustellen und Anomalien zu erkennen. | AWS-Administrator |
Nachverfolgen AWS WAF und CloudFront protokollieren. | Untersuchen Sie die AWS WAF Protokolle auf blockierte oder verdächtige Anfragen und die CloudFront Zugriffsprotokolle auf Leistungs- und Caching-Metriken. | AWS-Administrator |
Fehlerbehebung
| Problem | Lösung |
|---|---|
Fehler „Domain nicht erlaubt“ |
|
Authentifizierungsfehler | Mögliche Ursachen:
Lösungen:
|
API-Gateway-Fehler | Mögliche Ursachen:
Lösungen:
|
Die Grafiken von Quick Sight werden nicht geladen | Mögliche Ursachen:
Lösungen:
|
Fehler „Benutzer hat keinen Zugriff“ | Mögliche Ursachen:
Lösung:
|
Zugehörige Ressourcen
AWS Dokumentation
Tutorials und Videos