Set up queued callback by creating flows, queues, and routing profiles in Amazon Connect
You can allow your customers to maintain their position in queue without requiring them to stay on the call during high wait times, and get a callback from an available agent when it's their turn.
Contents
How callbacks keep their place in queue
You can configure callbacks to remain in the same queue as the original inbound call or to be placed in a separate dedicated queue that you create. This separate queue enables you to get a clearer delineation between active inbound calls and callbacks in real time reports.
You can ensure that the callback maintains its position in queue even when you place it in a dedicated queue by configuring it at the same priority as the original inbound queue in the routing profile. This configuration ensures that Amazon Connect continues to look at the original start time of the inbound call to maintain order, regardless of whether the customer opted for a callback or to stay on the call for the next available agent.
Amazon Connect evaluates the routing profiles first so if the two queues have the same priority, the oldest call is pushed first across all queues with the same priorities. For example, if your original call arrived at 10:00 and left a callback request at 10:05, Amazon Connect looks for the call start time of 10:00, not 10:05.
Steps to set up queued callbacks
Use the steps provided in the following overview to set up queued callback.
-
Set up a queue specifically for callbacks. In your real-time metrics reports, you can look at that queue and see how many customers are waiting for callbacks.
-
Set up caller ID. When setting your callback queue, specify the caller ID name and phone number that appears to customers when you call back.
-
Add the callback queue to a routing profile. Set this up so that contacts waiting for a call are routed to agents.
-
Create a flow for queued callbacks. Set this up to offer the option for a callback to the customer.
-
(Optional) Create a callback creation flow. When a callback is created, this flow is run. The contact is enqueued only when there is a Transfer to queue set on this flow. You can use the callback creation flow to Check contact attributes to see if the callback is a duplicate or if the customer issue is resolved before queuing the contact for an agent. This flow also allows you to set a customer queue flow by adding a Set customer queue flow block.
-
(Optional) Create a customer queue flow for callback. This flow is run if you choose a Set customer queue flow block for the Set creation flow option. You can use a Set customer queue flow block to add logic to transfer a contact from one queue to another. Or, you can manually remove a callback from the queue by using the StopContact API.
-
(Optional) Create an outbound whisper flow. When a queued call is placed, the customer hears this message after they pick up and before they connect to the agent. For example, "Hello, this is your scheduled callback..."
-
(Optional) Create an agent whisper flow. This is what the agent hears right after they accept the contact, before they are joined to the customer. For example, "You're about to be connected to Customer John, who requested a refund for..."
-
(Optional) Provide a caller ID. This is what the customer sees when dialed. Must be a valid phone number claimed in your Amazon Connect instance. This field is reflected as the system endpoint in contact records. The number set here takes precedence over the outbound phone number set on the queue.
-
Choose a dial mode between agent first and customer first.
Important
-
This option is available only when Next Generation Amazon Connect is enabled for your Amazon Connect instance.
-
If you disable Next Generation Amazon Connect after you've already activated and started using customer first callback, customer first callback is also disabled. It is not available in the pay-per-feature pricing model.
-
The routing process
-
When a customer leaves their number it's put in a queue and then routed to the next available agent.
-
After an agent accepts the callback in the CCP, Amazon Connect calls the customer.
If no agents are available to work on callbacks, the callbacks can stay in queue for up to 7 days after they are created before Amazon Connect automatically removes them.
Tip
To manually remove a callback from the queue, use the StopContact API.
-
If there is no answer when the Amazon Connect calls the customer, it retries based on the number of times you've specified.
-
If the call goes to voicemail, it's considered connected.
-
If the customer calls again while in the callback queue, it's treated as a new call and will be handled as usual. To avoid duplicate callback requests in a callback queue, see this blog: Preventing duplicate callback requests in Amazon Connect
.
How queued callbacks affect queue limits
-
Queued callbacks count towards the queue size limit, but they are routed to the error branch. For example, if you have a queue that handles callbacks and incoming calls, and that queue reaches the size limit:
-
The next callback is routed to the error branch.
-
The next incoming call gets a reorder tone (also known as a fast busy tone), which indicates no transmission path to the called number is available.
-
-
Consider setting up your queued callbacks to be lower priority than your queue for incoming calls. This way, your agents only work on queued callbacks when the incoming call volume is low.
Create a flow for queued callbacks
To see what a flow looks like with queued callback, in new Amazon Connect instances see Sample queue configurations flow in Amazon Connect. In previous instances, see Sample queued callback flow in Amazon Connect.
The following procedure shows how to:
-
Request a callback number from a customer.
-
Store the callback number in an attribute.
-
Reference the attribute in a Set callback number block to set the number to dial the customer.
-
Transfer the customer to the callback queue.
At the basic level, here's what this queued callback flow looks like, without any of the alternative branches or error handling configured. The following image shows a flow with the following blocks: Get customer input, Store customer input, Set callback number, Play prompt, Transfer to queue, and Disconnect/hang up.
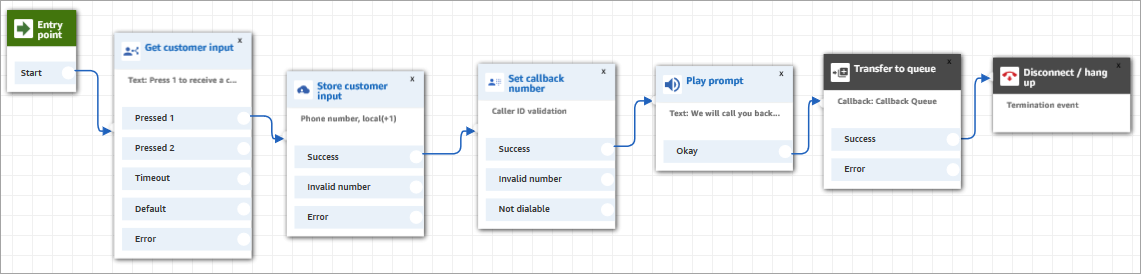
Following are the steps to create this flow.
To create a flow for queued callbacks
-
In Amazon Connect, choose Routing, Contact flows.
-
Select an existing flow, or choose Create flow to create a new one.
Tip
You can create this flow using different flow types: Customer queue flow, Transfer to agent, Transfer to queue.
-
Add a Get customer input block.
-
Configure the block to prompt the customer for a callback. The following image shows a message in the Text-to-speech box: Press 1 to receive a callback. Press 2 to stay in queue.

-
At the bottom of the block, choose Add another condition, and add options 1 and 2, as shown in the following image.
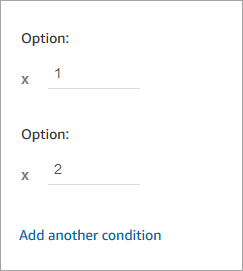
-
Add a Store customer input block.
-
Configure the block to prompt customers for their callback number, such as "Please enter your phone number." The following image shows the Properties page of the Store customer input block.

-
In the Customer input section, select Phone number, and then choose one of the following:
-
Local format: Your customers are calling from phone numbers that are in the same country as the AWS Region where you created your Amazon Connect instance.
-
International format/Enforce E.164: Your customers are calling from phone numbers in countries or regions other than the one where you created your instance.
-
-
Add a Set callback number block to your flow.
-
Configure the block to set Type to System, as shown in the following image. For Attribute, choose Store customer input. This attribute stores the customer's phone number.

-
Add a Transfer to queue block.
-
In the Transfer to queue block, configure the Transfer to callback queue tab as shown in the following image. Set Initial delay to 99. Set Max number of retries to 2. Set Minimum time between attempts to 10 minutes.
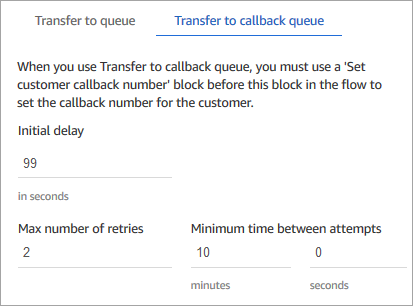
The following properties are available:
-
Initial delay: Specify how much time has to pass between a callback contact being initiated in the flow, and the customer is put in queue for the next available agent. In the previous example, the time is 99 seconds.
-
Maximum number of retries: If this is set to 2, then Amazon Connect tries to call back the customer a maximum of three times: the initial callback, and two retries.
A retry only happens if it rings but there's no answer. If the callback goes to voicemail, it's considered connected and Amazon Connect does not retry again.
Tip
We strongly recommend that you double-check the number entered in Maximum number of retries. If you accidentally enter a high number, such as 20, it's going to result in unnecessary work for the agent and too many calls for the customer.
-
Minimum time between attempts: If the customer doesn't answer the phone, this is how long to wait until trying again. In the previous example, we wait 10 minutes between attempts.
-
-
In the Optional parameters section, choose Set working queue if you want to transfer the contact to a queue that you set up specifically for callbacks. This option is shown in the following image.

Creating a queue just for callbacks lets you view in your real-time metrics reports how many customers are waiting for callbacks.
If you don't set a working queue, Amazon Connect uses the queue that was set previously in the flow.
-
You can optionally specify the caller ID that customers see when they receive the callback by configuring the Caller ID number to display option in the Transfer to queue block, as shown in the following image.

-
The callback contact is a new contact separate from the inbound voice contact. You can optionally control the experience of this callback contact when it is created by configuring the Set creation flow option in the Transfer to queue block, as shown in the following image.

-
If Next Generation Amazon Connect is enabled for your Amazon Connect instance (learn how to check whether it's enabled), you can choose either agent first callback mode (the default) or customer first callback mode. For more information about these options, see Use customer first callback mode.
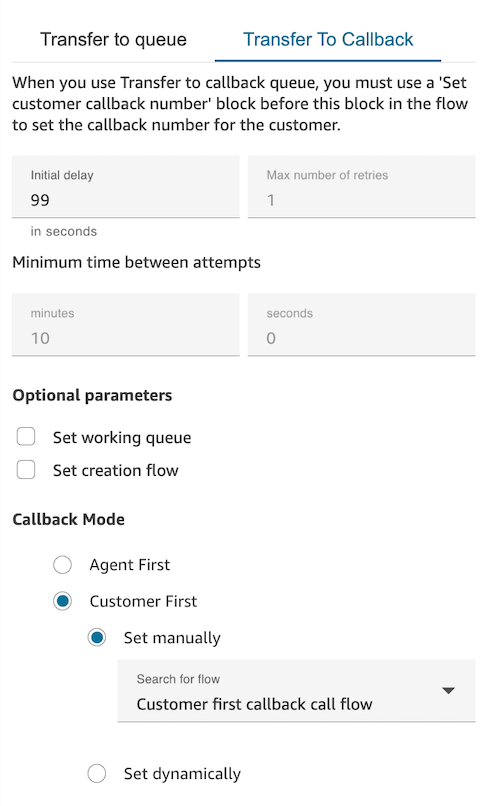
-
(Optional) Create a callback creation flow. Use the Set creation flow dropdown menu to select the flow to be run when a callback contact is created.
The callback creation flow that you select must meet the following requirements:
-
The flow type must be the default flow type, Contact flow (inbound). For information about flow types, see Choose a flow type.
-
You need to configure a Transfer to queue block to queue the contact in the queue of your choice.
Following are additional options for how you can configure your callback creation flow:
-
You can evaluate contact attributes (including customer profiles) by using a Check contact attributes block to see if the callback should be terminated because it is a duplicate or the customer issue has already been resolved.
-
You can add a Set customer queue flow block and use it to specify the flow to run when a customer is transferred to a queue. This flow is called a customer queue flow.
-
In the customer queue flow, you can evaluate the contact's wait time in queue by using a combination of the Get metrics block and GetCurrentMetricData to send an advance SMS to customers, notifying them to expect a callback in the near future from the specific contact center number.
-
-
-
-
To save and test this flow, configure the other branches and add error handling. To see an example of how this is done, see Sample queue configurations flow in Amazon Connect. For previous instances, see Sample queued callback flow in Amazon Connect.
-
For information about how callbacks appear in real-time metrics reports and contact records, see Queued callbacks in real-time metrics in Amazon Connect.
Callbacks from a chat, task, or email contact
You can also configure the Transfer to Callback option in the Transfer to queue block to support callbacks when a customer contacts you from a chat, task, or email contact. For example, if a customer reaches out after hours when no agent is available, they can request a voice callback by sending a chat message or completing a webform request (which uses tasks).
The following video shows how to use Contact Lens to allow customers who contact you through Amazon Connect chat to request a callback. This creates a more personalized customer experience. It shows how to configure this capability that allows customers to request callbacks from any channel, not just voice calls.
Learn more about queued callbacks
See the following topics to learn more about queued callbacks: