Create a Hybrid Job
This section shows you how to create a Hybrid Job using a Python script. Alternatively, to create a hybrid job from local Python code, such as your preferred integrated development environment (IDE) or a Braket notebook, see Run your local code as a hybrid job.
In this section:
Create and run
Once you have a role with permissions to run a hybrid job, you are ready to proceed. The key piece of your first Braket hybrid job is the algorithm script. It defines the algorithm you want to run and contains the classical logic and quantum tasks that are part of your algorithm. In addition to your algorithm script, you can provide other dependency files. The algorithm script together with its dependencies is called the source module. The entry point defines the first file or function to run in your source module when the hybrid job starts.
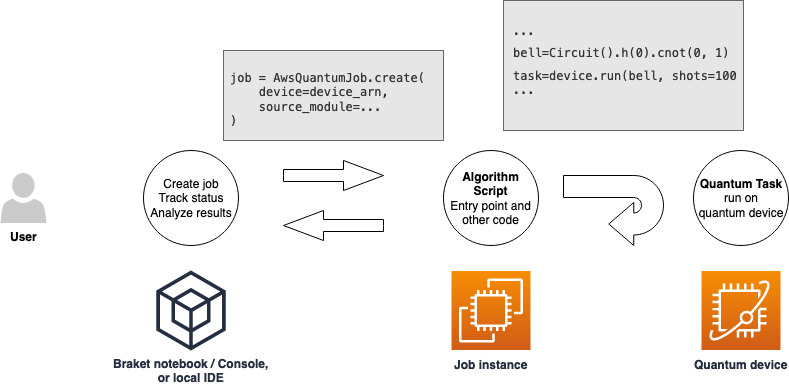
First, consider the following basic example of an algorithm script that creates five bell states and prints the corresponding measurement results.
import os from braket.aws import AwsDevice from braket.circuits import Circuit def start_here(): print("Test job started!") # Use the device declared in the job script device = AwsDevice(os.environ["AMZN_BRAKET_DEVICE_ARN"]) bell = Circuit().h(0).cnot(0, 1) for count in range(5): task = device.run(bell, shots=100) print(task.result().measurement_counts) print("Test job completed!")
Save this file with the name algorithm_script.py in your current
working directory on your Braket notebook or local environment. The algorithm_script.py
file has start_here() as the planned entry point.
Next, create a Python file or Python notebook in the same directory as the algorithm_script.py file. This script kicks off the hybrid job and handles any asynchronous processing, such as printing the status or key outcomes that we are interested in. At a minimum, this script needs to specify your hybrid job script and your primary device.
Note
For more information about how to create a Braket notebook or upload a file, such as the algorithm_script.py file, in the same directory as the notebooks, see Run your first circuit using the Amazon Braket Python SDK
For this basic first case, you target a simulator. Whichever type of quantum device you
target, a simulator or an actual quantum processing unit (QPU), the device you specify with
device in the following script is used to schedule the hybrid job and is available
to the algorithm scripts as the environment variable
AMZN_BRAKET_DEVICE_ARN.
Note
You can only use devices that are available in the AWS Region of your hybrid job. The Amazon Braket SDK auto selects this AWS Region. For example, a hybrid job in us-east-1 can use IonQ, SV1, DM1, and TN1 devices, but not Rigetti devices.
If you choose a quantum computer instead of a simulator, Braket schedules your hybrid jobs to run all of their quantum tasks with priority access.
from braket.aws import AwsQuantumJob from braket.devices import Devices job = AwsQuantumJob.create( Devices.Amazon.SV1, source_module="algorithm_script.py", entry_point="algorithm_script:start_here", wait_until_complete=True )
The parameter wait_until_complete=True sets a verbose mode so that your job
prints output from the actual job as it's running. You should see an output similar to the
following example.
Initializing Braket Job: arn:aws:braket:us-west-2:111122223333:job/braket-job-default-123456789012 Job queue position: 1 Job queue position: 1 Job queue position: 1 .............. . . . Beginning Setup Checking for Additional Requirements Additional Requirements Check Finished Running Code As Process Test job started! Counter({'00': 58, '11': 42}) Counter({'00': 55, '11': 45}) Counter({'11': 51, '00': 49}) Counter({'00': 56, '11': 44}) Counter({'11': 56, '00': 44}) Test job completed! Code Run Finished 2025-09-24 23:13:40,962 sagemaker-training-toolkit INFO Reporting training SUCCESS
Note
You can also use your custom-made module with the
AwsQuantumJob.create
Monitor your results
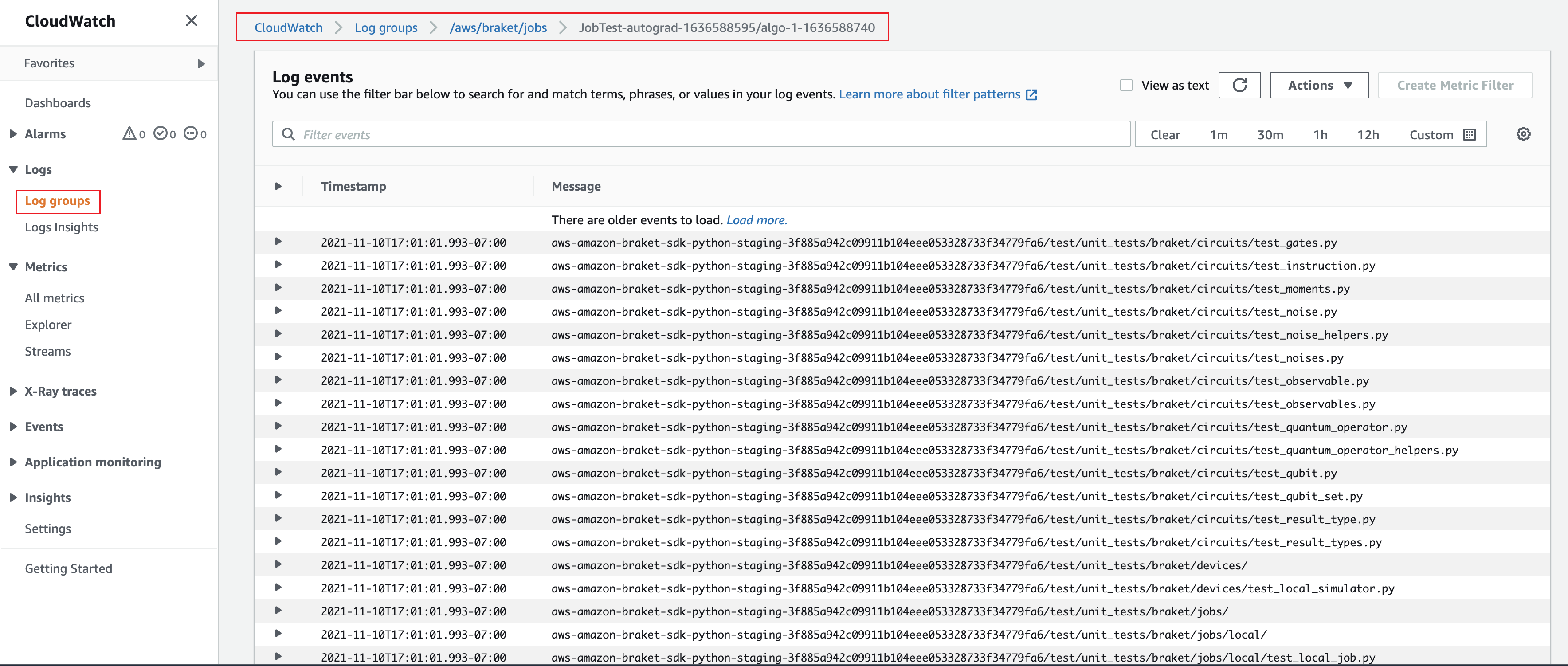
Alternatively, you can access the log output from Amazon CloudWatch. To do this, go to the
Log groups tab on the left menu of the job detail
page, select the log group aws/braket/jobs, and then choose the log stream
that contains the job name. In the example above,
this is braket-job-default-1631915042705/algo-1-1631915190.
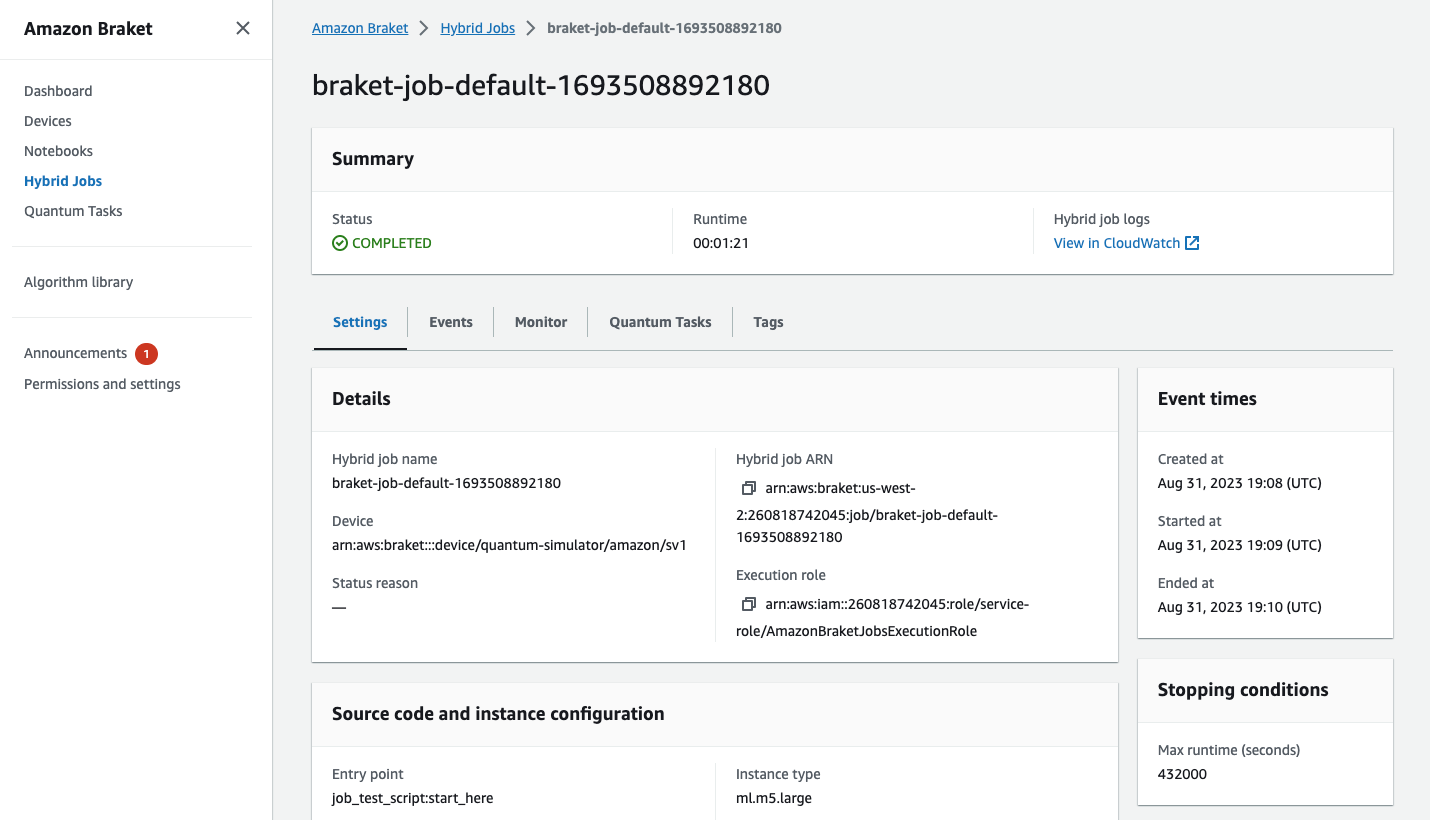
You can also view the status of the hybrid job in the console by selecting the Hybrid Jobs page and then choose Settings.
Your hybrid job produces some artifacts in Amazon S3 while it runs. The default S3 bucket name is
amazon-braket-<region>-<accountid> and the content is in the
jobs/<jobname>/<timestamp> directory. You can configure the S3 locations where
these artifacts are stored by specifying a different code_location when the
hybrid job is created with the Braket Python SDK.
Note
This S3 bucket must be located in the same AWS Region as your job script.
The jobs/<jobname>/<timestamp> directory contains a subfolder with the output
from the entry point script in a model.tar.gz file. There is also a directory called
script that contains your algorithm script artifacts in a source.tar.gz
file. The results from your actual quantum tasks are in the directory named
jobs/<jobname>/tasks.
Save your results
You can save the results generated by the algorithm script so that they are available from the hybrid job object in the hybrid job script as well as from the output folder in Amazon S3 (in a tar-zipped file named model.tar.gz).
The output must be saved in a file using a JavaScript Object
Notation (JSON) format. If the data can not be readily serialized to text, as in the case of a
numpy array, you could pass in an option to serialize using a pickled data format.
See the braket.jobs.data_persistence module
To save the results of the hybrid jobs, add the following lines commented with #ADD to the algorithm_script.py file.
import os from braket.aws import AwsDevice from braket.circuits import Circuit from braket.jobs import save_job_result # ADD def start_here(): print("Test job started!") device = AwsDevice(os.environ['AMZN_BRAKET_DEVICE_ARN']) results = [] # ADD bell = Circuit().h(0).cnot(0, 1) for count in range(5): task = device.run(bell, shots=100) print(task.result().measurement_counts) results.append(task.result().measurement_counts) # ADD save_job_result({"measurement_counts": results}) # ADD print("Test job completed!")
You can then display the results of the job from your job script by appending the line
print(job.result())
commented with #ADD.
import time from braket.aws import AwsQuantumJob job = AwsQuantumJob.create( source_module="algorithm_script.py", entry_point="algorithm_script:start_here", device="arn:aws:braket:::device/quantum-simulator/amazon/sv1", ) print(job.arn) while job.state() not in AwsQuantumJob.TERMINAL_STATES: print(job.state()) time.sleep(10) print(job.state()) print(job.result()) # ADD
In this example, we have removed wait_until_complete=True to suppress
verbose output. You can add it back in for debugging. When you run this hybrid job, it outputs the
identifier and the job-arn, followed by the state of the hybrid job every 10 seconds
until the hybrid job is COMPLETED, after which it shows you the results of the bell
circuit. See the following example.
arn:aws:braket:us-west-2:111122223333:job/braket-job-default-123456789012 INITIALIZED RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING RUNNING ... RUNNING RUNNING COMPLETED {'measurement_counts': [{'11': 53, '00': 47},..., {'00': 51, '11': 49}]}
Using checkpoints
You can save intermediate iterations of your hybrid jobs using checkpoints. In the algorithm script example from the previous section, you would add the following lines commented with #ADD to create checkpoint files.
from braket.aws import AwsDevice from braket.circuits import Circuit from braket.jobs import save_job_checkpoint # ADD import os def start_here(): print("Test job starts!") device = AwsDevice(os.environ["AMZN_BRAKET_DEVICE_ARN"]) # ADD the following code job_name = os.environ["AMZN_BRAKET_JOB_NAME"] save_job_checkpoint(checkpoint_data={"data": f"data for checkpoint from {job_name}"}, checkpoint_file_suffix="checkpoint-1") # End of ADD bell = Circuit().h(0).cnot(0, 1) for count in range(5): task = device.run(bell, shots=100) print(task.result().measurement_counts) print("Test hybrid job completed!")
When you run the hybrid job, it creates the file
<jobname>-checkpoint-1.json in your hybrid job artifacts in the
checkpoints directory with a default /opt/jobs/checkpoints path. The hybrid job
script remains unchanged unless you want to change this default path.
If you want to load a hybrid job from a checkpoint generated by a previous hybrid job, the algorithm
script uses from braket.jobs import load_job_checkpoint. The logic to load in
your algorithm script is as follows.
from braket.jobs import load_job_checkpoint checkpoint_1 = load_job_checkpoint( "previous_job_name", checkpoint_file_suffix="checkpoint-1", )
After loading this checkpoint, you can continue your logic based on the content loaded
to checkpoint-1.
Note
The checkpoint_file_suffix must match the suffix previously specified when creating the checkpoint.
Your orchestration script needs to specify the job-arn from the previous
hybrid job with the line commented with #ADD.
from braket.aws import AwsQuantumJob job = AwsQuantumJob.create( source_module="source_dir", entry_point="source_dir.algorithm_script:start_here", device="arn:aws:braket:::device/quantum-simulator/amazon/sv1", copy_checkpoints_from_job="<previous-job-ARN>", #ADD )