Architecture overview
This section provides a reference implementation architecture diagram for the components deployed with this guidance.
Architecture diagram
Deploying this guidance with the default parameters deploys the following components in your AWS account.
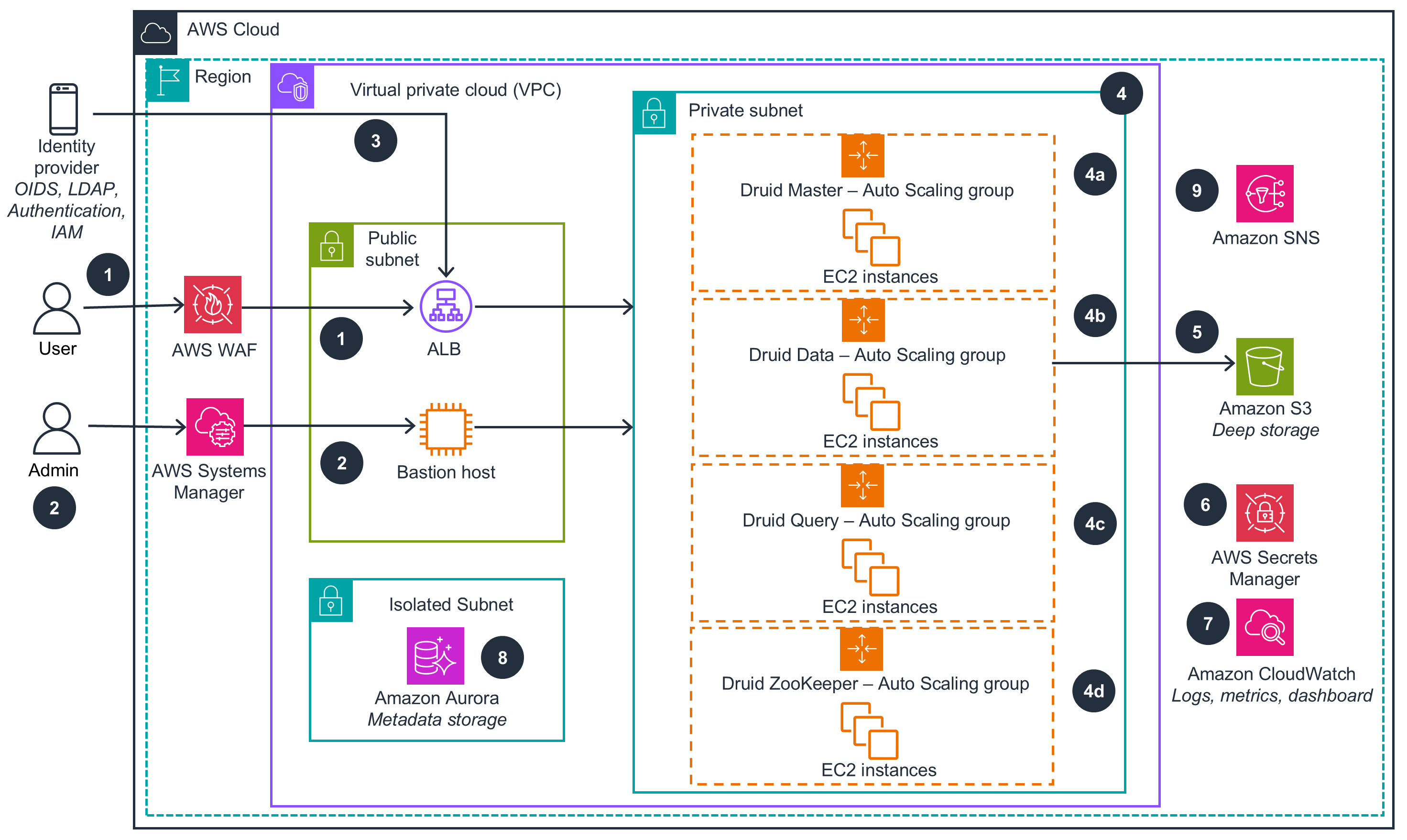
Guidance for Scalable Analytics Using Apache Druid on AWS - Architecture diagram
Note
AWS CloudFormation resources are created from AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) (AWS CDK) constructs.
The high-level process flow for the guidance components deployed with the AWS CDK constructs is as follows. The numbers and description matches the number designated in the following architecture diagram.
The guidance deploys the following components that work together to provide a production-ready Druid cluster:
-
AWS WAF protects the Druid web console and Druid API endpoints against common web exploits and bots that may affect availability, compromise security, or consume excessive resources. AWS WAF is only provisioned and deployed for internet facing clusters.
-
A security hardened Linux server (Bastion host) manages access to the Druid servers running in a private network separate from an external network. It can also be used to access the Druid web console through SSH tunneling, where a private Application Load Balancer (ALB) is deployed.
-
ALB serves as the single point of contact for clients. The load balancer distributes incoming application traffic from identity providers—such as object identifiers (OIDS) and lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP)—across multiple query servers in multiple Availability Zones.
-
The private subnet consists of the following:
-
The Druid Master Auto Scaling group contains a collection of Druid master servers. A master server manages data ingestion and availability and is responsible for starting new ingestion jobs and coordinating availability of data on the data servers. Within a master server, functionality is split between two processes: the Coordinator and Overlord.
-
The Druid Data Auto scaling group contains a collection of Druid data servers. A data server runs ingestion jobs and stores queryable data. Within a data server, functionality is split between two processes: the Historical and MiddleManager.
-
The Druid Query Auto scaling group contains a collection of Druid query servers. A query server provides the endpoints that users and client applications interact with, routing queries to data servers or other query servers. Within a query server, functionality is split between two processes; the Broker and Router.
-
The ZooKeeper Auto Scaling group contains a collection of ZooKeeper servers. Apache Druid uses Apache ZooKeeper for management of current cluster state.The ZooKeeper Auto Scaling group contains a collection of ZooKeeper servers. Apache Druid uses Apache ZooKeeper for management of current cluster state.
-
-
An Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket provides deep storage for the Apache Druid cluster. Deep storage is the location where the segments are stored.
-
AWS Secrets Manager stores the secrets used by Apache Druid, including the Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) secret and the administrator user secret. It also stores the credentials for the system account the Druid components use to authenticate with each other.
-
Amazon CloudWatch supports logs, metrics, and dashboards.
-
An Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL database provides the metadata storage for the Apache Druid cluster. Druid uses the metadata store to house only metadata about the system and does not store the actual data.
-
The notification system, powered by Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS), delivers alerts or alarms promptly when system events occur. This helps ensure immediate awareness and action when needed.