Edit identity provider configuration
You can change your server's identity provider type from any type to any other type. The available identity provider types are:
-
Service managed – Store user credentials within the service
-
AWS Directory Service – Use AWS Managed Microsoft AD or AWS Directory Service for Entra ID Domain Services
-
Custom – Use Lambda function or Amazon API Gateway to integrate with your existing identity provider
When changing identity provider types, you need to provide specific information depending on the transition you're making. The following sections describe the required information for each type of change.
Important
Considerations when changing identity providers:
-
User migration – When changing identity provider types, existing user configurations are not automatically migrated. You'll need to set up users in the new identity provider system.
-
Testing – Test the new identity provider configuration thoroughly before making the change in production environments.
-
Permissions – Ensure that the new identity provider has the necessary IAM permissions and roles configured before making the change.
Changing to service-managed identity provider
When changing from any other identity provider type to service-managed, you need to:
-
Select Service managed as the identity provider type
-
Create new users directly in AWS Transfer Family after the change is complete, as existing user configurations from other identity providers won't be transferred
Example: If you're changing from a custom identity provider to service-managed, you'll need to recreate all user accounts and their associated permissions within the AWS Transfer Family service.
Changing to AWS Directory Service
When changing from any other identity provider type to AWS Directory Service, you need to provide:
-
Directory – Select an existing AWS Managed Microsoft AD or AWS Directory Service for Entra ID Domain Services directory
-
Access – Choose whether to restrict access to a specific group or allow access to all users in the directory
-
Access role – An IAM role that allows AWS Transfer Family to access your directory
Example: If you're changing from service-managed to AWS Directory Service, you would
select your existing d-1234567890 directory, choose to restrict access to
the TransferUsers group, and specify the
TransferDirectoryAccessRole IAM role.
Changing to custom identity provider
When changing from any other identity provider type to a custom identity provider, you need to choose between Lambda function or Amazon API Gateway and provide the required configuration:
Using Lambda function
For Lambda function integration, provide:
-
Function – Select an existing Lambda function that handles authentication
-
Authentication method (for SFTP protocol) – Choose password, public key, or both
Example: If you're changing from AWS Directory Service to a custom Lambda
identity provider, you would select your TransferCustomAuth function
and choose Password as the authentication method.

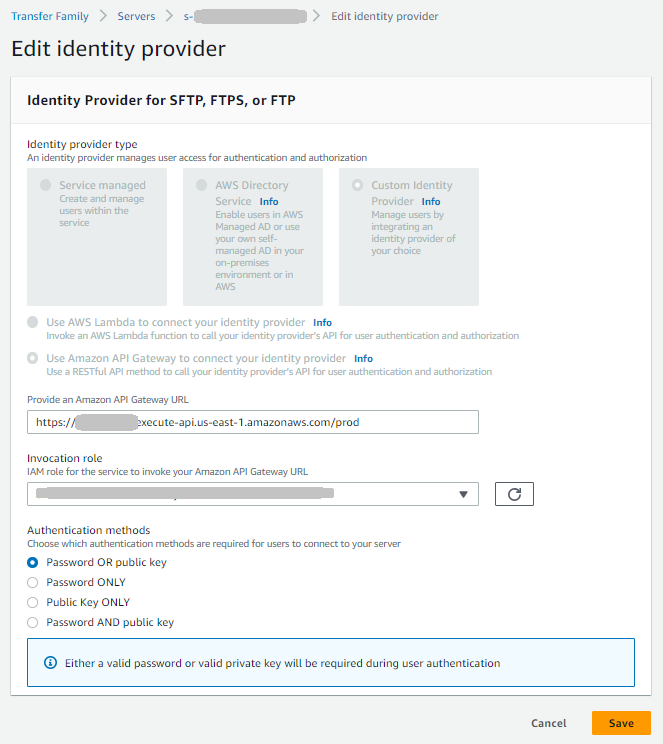
Using Amazon API Gateway
For Amazon API Gateway integration, provide:
-
API Gateway URL – The invoke URL of your API Gateway endpoint
-
Invocation role – An IAM role that allows AWS Transfer Family to invoke your API Gateway
-
Authentication method (for SFTP protocol) – Choose password, public key, or both
Example: If you're changing from service-managed to API Gateway, you would provide the
URL https://abcdef123.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod, specify
the TransferApiGatewayInvocationRole IAM role, and choose
Public key as the authentication method.
Changing from Amazon API Gateway to Lambda function
A common transition is changing from Amazon API Gateway to Lambda function for custom identity provider integration. This change allows you to simplify your architecture while maintaining the same authentication logic.
Key considerations for this transition:
-
Same function, different permissions – You can use the same Lambda function for both API Gateway and direct Lambda integration, but the resource policy must be updated.
-
Resource policy requirements – When changing to direct Lambda integration, the function's resource policy must grant
transfer.amazonaws.com.rproxy.govskope.capermission to invoke the function, in addition toapigateway.amazonaws.com.
To make this change
-
Update your Lambda function's resource policy to allow
transfer.amazonaws.com.rproxy.govskope.cato invoke the function. -
In the AWS Transfer Family console, change the identity provider from API Gateway to Lambda function.
-
Select your existing Lambda function.
-
Test the configuration to ensure authentication works correctly.
Example resource policy for direct Lambda integration:
-
{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement": [{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": [ "transfer.amazonaws.com", "apigateway.amazonaws.com" ] }, "Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction", "Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:function-name" }] }
User preservation during identity provider transitions
When changing between identity provider types, existing user configurations are preserved in specific scenarios to enable efficient rollback in case of issues:
-
Service-managed to custom identity provider and back – If you change from service-managed to a custom identity provider and then back to service-managed, all users are preserved in their last known configuration.
-
AWS Directory Service to custom identity provider and back – If you change from AWS Directory Service to a custom identity provider and then back to AWS Directory Service, all definitions for Delegated Access groups are retained in their last known configuration.
This preservation behavior allows you to safely test custom identity provider configurations and roll back to your previous setup without losing user access configurations.
Important considerations when changing identity providers
-
User migration – When changing identity provider types, existing user configurations are not automatically migrated. You'll need to set up users in the new identity provider system.
-
Testing – Test the new identity provider configuration thoroughly before making the change in production environments.
-
Permissions – Ensure that the new identity provider has the necessary IAM permissions and roles configured before making the change.