Embed Amazon Quick Sight visual components into web applications by using Amazon Cognito and IaC automation
Ishita Gupta, Saurabh Singh, and Srishti Wadhwa, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern delivers a specialized approach for embedding Amazon Quick Sight visual components into React applications by using registered user embedding with streamlined Amazon Cognito authentication. These resources are then deployed through an infrastructure as code (IaC) template. Unlike traditional dashboard embedding, this solution isolates specific charts and graphs for direct integration into React applications, which dramatically improves both performance and the user experience.
The architecture establishes an efficient authentication flow between Amazon Cognito user management and Quick Sight permissions: Users authenticate through Amazon Cognito and access their authorized visualizations based on the dashboard sharing rules in Quick Sight. This streamlined approach eliminates the need for direct Quick Sight console access while maintaining robust security controls.
The complete environment is deployed through a single AWS CloudFormation template that provisions all the necessary infrastructure components, including:
A serverless backend that uses AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway
Secure frontend hosting through Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and AWS WAF
Identity management by using Amazon Cognito
All components are configured by following security best practices with least-privilege AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, AWS WAF protection, and end-to-end encryption.
This solution is ideal for development teams and organizations that want to integrate secure, interactive analytics into their applications while maintaining fine-grained control over user access. The solution uses AWS managed services and automation to simplify the embedding process, enhance security, and ensure scalability to meet evolving business needs.
Target audience and use cases:
Frontend developers who want to embed analytics into React apps
Software as a service (SaaS) product teams that want to offer per-user or role-based data visualizations
Solutions architects who are interested in integrating AWS analytics into custom portals
Business intelligence (BI) developers who want to expose visuals to authenticated users without requiring full dashboard access
Enterprise teams that want to embed interactive Quick Sight charts within internal tools
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
To successfully implement this pattern, make sure that the following are in place:
Active AWS account – An AWS account with permissions to deploy CloudFormation stacks and create Lambda, API Gateway, Amazon Cognito, CloudFront, and Amazon S3 resources.
Amazon Quick Sight account – An active Quick Sight account with at least one dashboard that contains visuals. For setup instructions, see Tutorial: Create an Amazon Quick Sight dashboard using sample data in the Amazon Quick Suite documentation.
A development environment that consists of:
Node.js (version 16 or later)
npm or yarn installed
Vite as the React build tool
React (version 19.1.1)
Dashboard sharing – Dashboards must be shared in Quick Sight and the implementer must log in to access the embedded visuals or dashboards.
Limitations
This pattern uses the registered user embedding method, which requires implementers to have an active Quick Sight account.
Access is restricted to the dashboards and visuals that are explicitly shared with the authenticated Quick Sight user who is implementing this pattern. If the implementer doesn’t have the correct access rights, the embed URL generation will fail and visuals won’t load.
The CloudFormation stack must be deployed in an AWS Region where Quick Sight, API Gateway, and Amazon Cognito are supported. For Region availability, see AWS services by Region
.
Product versions
Quick Sight Embedding SDK
version 2.10.1 React
version 19.1.1 Node.js
version 16 or later to ensure compatibility with the latest React and Vite versions used in this solution
Architecture
Target architecture
The following diagram shows the architecture and workflow for this pattern.
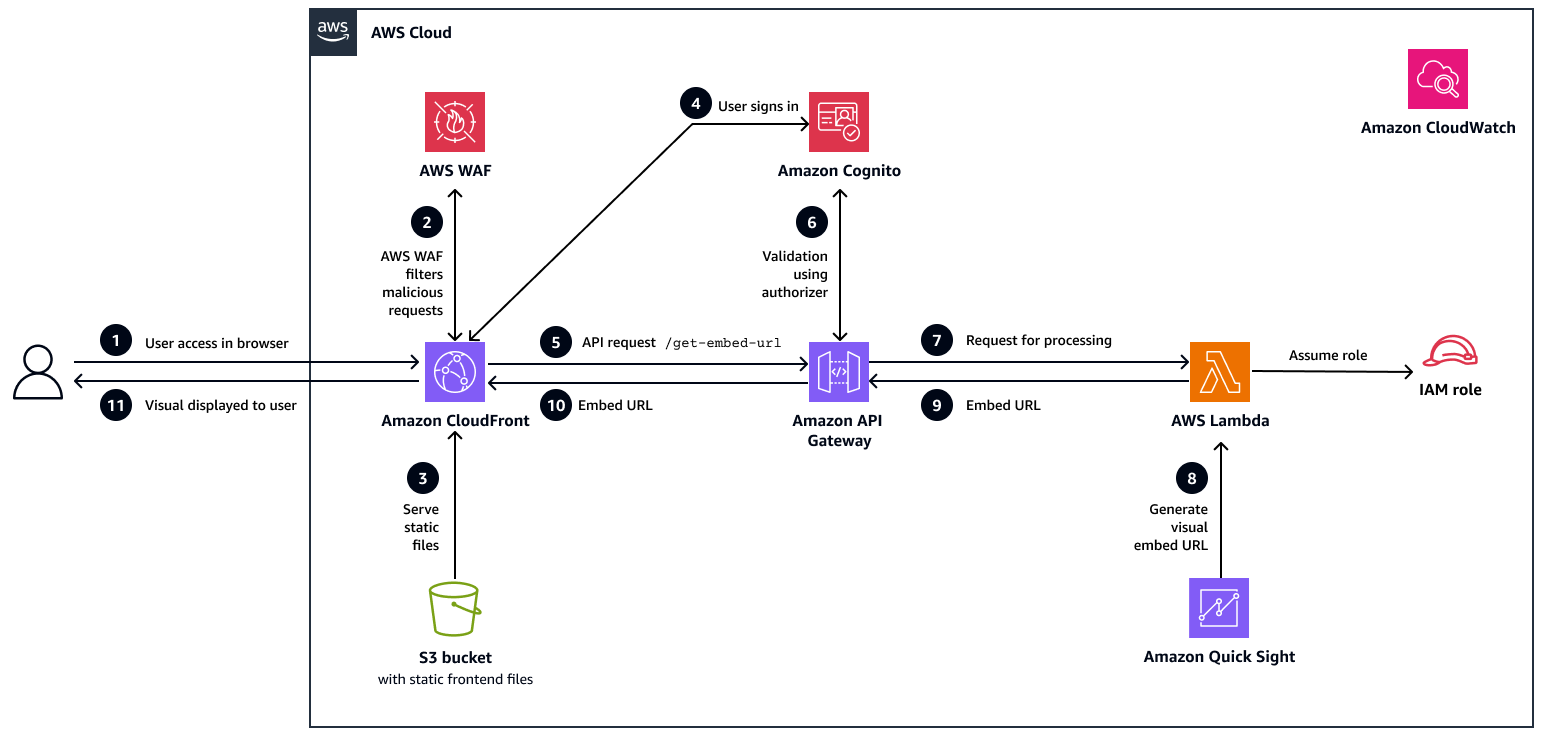
In this workflow:
The user accesses the application. The user opens the React web application by using a browser. The request is routed to a CloudFront distribution, which acts as a content delivery network for the application.
AWS WAF filters malicious requests. Before the request reaches CloudFront, it passes through AWS WAF. AWS WAF inspects the traffic and blocks any malicious or suspicious requests based on security rules.
Amazon S3 serves static files. If the request is clean, CloudFront retrieves the static frontend assets (HTML, JS, CSS) from a private S3 bucket by using origin access control (OAC) and delivers them to the browser.
The user signs in. After the application is loaded, the user signs in through Amazon Cognito, which authenticates the user and returns a secure JSON web token (JWT) for authorized API access.
The application makes an API request. After login, the React application makes a secure call to the
/get-embed-urlendpoint on API Gateway, and passes the JWT token in the request header for authentication.The token is validated. API Gateway validates the token by using an Amazon Cognito authorizer. If the token is valid, the request proceeds; otherwise, it is denied with a 401 (unauthorized) response.
The request is directed to Lambda for processing. The validated request is then forwarded to a backend Lambda function. This function is responsible for generating the embed URL for the requested Quick Sight visual.
Lambda generates the embed URL from Quick Sight. IAM uses an IAM role with appropriate permissions to call the Quick Sight
GenerateEmbedUrlForRegisteredUserAPI to generate a secure, user-scoped visual URL.Lambda returns the embed URL to API Gateway. Lambda sends the generated embed URL back to API Gateway as part of a JSON response. This response is then prepared for delivery to the frontend.
The embed URL is sent to the browser. The embed URL is returned to the browser as the API response.
The visual is displayed to the user. The React application receives the response and uses the Quick Sight Embedding SDK to render the specific visual to the user.
Automation and scale
Backend and frontend deployments are fully automated by using CloudFormation, which provisions all required AWS resources, including Amazon Cognito, Lambda, API Gateway, Amazon S3, CloudFront, AWS WAF, IAM roles, and Amazon CloudWatch in a single deployment.
This automation ensures consistent and repeatable infrastructure across all environments. All components scale automatically: Lambda adjusts to function invocations, CloudFront serves cached content globally, and API Gateway scales with incoming requests.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon Quick Sight
is a cloud-native business intelligence service that helps you create, manage, and embed interactive dashboards and visuals. Amazon API Gateway
manages APIs that act as the bridge between the React application and backend services. AWS Lambda
is a serverless compute service that this pattern uses to generate secure Quick Sight embed URLs dynamically, and scales automatically based on requests. Amazon Cognito
provides authentication and authorization for users, and issues secure tokens for API access. Amazon S3
hosts static frontend assets for this pattern, and serves them securely through CloudFront. Amazon CloudFront
delivers frontend content globally with low latency and integrates with AWS WAF for traffic filtering. AWS WAF
protects the web application from malicious traffic by applying security rules and rate limiting. AWS CloudFormationautomates the provisioning and configuration of all application resources in a single deployment.
Amazon CloudWatch
collects logs and metrics from Lambda, API Gateway, and AWS WAF for monitoring and troubleshooting.
Development tools
React JS
is a frontend framework that this pattern uses to build the web application and integrate embedded Quick Sight visuals. Vite
is a build tool used for fast development and optimized production builds of the React application. Quick Sight Embedding SDK
facilitates embedding Quick Sight visuals into the React application and enables seamless interaction between the application and visuals.
Code repository
The code for this pattern is available in the GitHub Amazon Quick Sight Visual Embedding in React
Best practices
This pattern automatically implements the following security best practices:
Uses Amazon Cognito user pools for JWT-based authentication, with optional multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Secures APIs with Amazon Cognito authorizers and enforces least-privilege IAM policies across all services.
Implements Quick Sight registered user embedding and auto-provisions users with the reader role.
Enforces encryption in transit that supports TLS 1.2 and later versions through CloudFront and HTTPS.
Encrypts data at rest by using AES-256 for Amazon S3 with versioning and OAC.
Configures API Gateway usage plans with throttling and quotas.
Secures Lambda with reserved concurrency and environment variable protection.
Enables logging for Amazon S3, CloudFront, Lambda, and API Gateway; monitors services by using CloudWatch.
Encrypts logs, applies access controls, and enforces deny policies for non-HTTPS or unencrypted uploads.
In addition, we recommend the following:
Use CloudFormation to automate deployments and maintain consistent configurations across environments.
Make sure that each user has the correct Quick Sight permissions to access embedded visuals.
Protect API Gateway endpoints with Amazon Cognito authorizers and enforce the principle of least privilege for all IAM roles.
Store sensitive information such as Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) and IDs in environment variables instead of hardcoding them.
Optimize Lambda functions by reducing dependencies and improving cold-start performance. For more information, see the AWS blog post Optimizing cold start performance of AWS Lambda using advanced priming strategies with SnapStart
. Add your CloudFront domain to the Quick Sight allowlist to enable secure visual embedding.
Monitor performance and security by using CloudWatch and AWS WAF for logging, alerts, and traffic protection.
Other recommended best practices
Use custom domains with SSL certificates from AWS Certificate Manager to provide a secure and branded user experience.
Encrypt Amazon S3 data and CloudWatch logs by using customer managed AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys for greater control over encryption.
Extend AWS WAF rules with geo-blocking, SQL injection (SQLi), cross-site scripting (XSS) protection, and custom filters for enhanced threat prevention.
Enable CloudWatch alarms, AWS Config, and AWS CloudTrail for real-time monitoring, auditing, and configuration compliance.
Apply granular IAM policies, enforce API key rotation, and allow cross-account access only when absolutely necessary.
Perform regular security assessments to ensure alignment with compliance frameworks such as System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC 2), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Clone the repository. | Clone the GitHub repository for this solution to your local system and navigate to the project directory:
This repository contains the CloudFormation template and React source code required to deploy the solution. | App developer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Deploy the template. |
For more information, see Creating and managing stacks in the CloudFormation documentation. | AWS administrator |
Monitor stack creation. | Monitor the stack in the Events tab until its status is CREATE_COMPLETE. | AWS administrator |
Retrieve stack outputs. |
| AWS administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Retrieve Quick Sight visual identifiers. |
| Quick Sight administrator |
Configure your local React environment. | To set up your local React environment and link it to AWS resources, create an
Here’s an example
| App developer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create or Manage Users in Cognito | To enable authenticated user access to embedded Quick Sight visuals, you first create users in Amazon Cognito:
| AWS administrator |
Provide Quick Sight dashboard access | To provide access to Quick Sight visuals, provide Viewer permission access to authenticated users:
Each user will receive an email with a link to the dashboard. You can modify permissions at any time through the Share menu. For more information, see Granting individual Amazon Quick Sight users and groups access to a dashboard in Amazon Quick Sight in the Amazon Quick Suite documentation. | Quick Sight administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Install dependencies and build the project. | In the React application directory, run the following commands to generate optimized production files:
| App developer |
Upload the build files to Amazon S3. | Upload all the files from the | App developer |
Create a CloudFront invalidation. | On the CloudFront console | AWS administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Add the CloudFront domain to the Quick Sight allowlist. | To enable your CloudFront domain to securely embed Quick Sight visuals:
| Quick Sight administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Open the React application. | Use the CloudFront domain (from CloudFormation outputs) to open the deployed React web application in a browser. | App owner |
Verify authentication. | Sign in to the application by using Amazon Cognito credentials to verify the authentication flow and JWT validation through API Gateway. | App owner |
Verify embedded visuals. | Confirm that Quick Sight visuals load properly within the application based on user-specific access permissions. | App owner |
Validate API and Lambda connectivity. | Confirm that the application can successfully call the | App owner |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Monitor by using CloudWatch. | You can use AWS observability tools to monitor the application and to maintain secure, scalable performance in production. Review Lambda logs, API Gateway metrics and Amazon Cognito authentication events in CloudWatch to ensure application health and to detect anomalies. | AWS administrator |
Track AWS WAF and CloudFront logs. | Inspect AWS WAF logs for blocked or suspicious requests and CloudFront access logs for performance and caching metrics. | AWS administrator |
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
"Domain not allowed" error |
|
Authentication errors | Possible causes:
Solutions:
|
API Gateway errors | Possible causes:
Solutions:
|
Quick Sight visuals don’t load | Possible causes:
Solutions:
|
"User does not have access" error | Possible causes:
Solution:
|
Related resources
AWS documentation
Tutorials and videos