Deploy a CockroachDB cluster in Amazon EKS by using Terraform
Sandip Gangapadhyay and Kalyan Senthilnathan, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern provides a HashiCorp Terraform module for deploying a multi-node CockroachDB
Intended audience
To implement this pattern, we recommend that you are familiar with the following:
HashiCorp Terraform concepts and infrastructure as code (IaC) practices
AWS services, particularly Amazon EKS
Kubernetes fundamentals, including StatefulSets, operators, and service configurations
Distributed SQL databases
Security concepts, such as TLS certificate management.
DevOps practices, CI/CD workflows, and infrastructure automation
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account
Permissions to deploy resources in an Amazon EKS cluster
An Amazon EKS cluster version v1.23 or later, with nodes labeled
node=cockroachdbAmazon Elastic Block Store Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver
version 1.19.0 or later, installed in the Amazon EKS cluster Terraform CLI version 1.0.0 or later, installed
kubectl, installed
Git, installed
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) version 2.9.18 or later, installed and configured
Limitations
The CockroachDB Kubernetes operator does not support multiple Kubernetes clusters for multi-Region deployments. For more limitation, see Orchestrate CockroachDB Across Multiple Kubernetes Clusters
(CockroachDB documentation) and CockroachDB Kubernetes Operator (GitHub). Automatic pruning of persistent volume claims (PVCs) is currently disabled by default. This means that after decommissioning and removing a node, the operator will not remove the persistent volume that was mounted to its pod. For more information, see Automatic PVC pruning
in the CockroachDB documentation.
Product versions
CockroachDB version 22.2.2
Architecture
Target architecture
The following diagram shows a highly available CockroachDB deployment across three AWS Availability Zones within a virtual private cloud (VPC). The CockroachDB pods are managed through Amazon EKS. The architecture illustrates how users access the database through a Network Load Balancer, which distributes traffic to the CockroachDB pods. The pods run on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances in each Availability Zone, which provides resilience and fault tolerance.
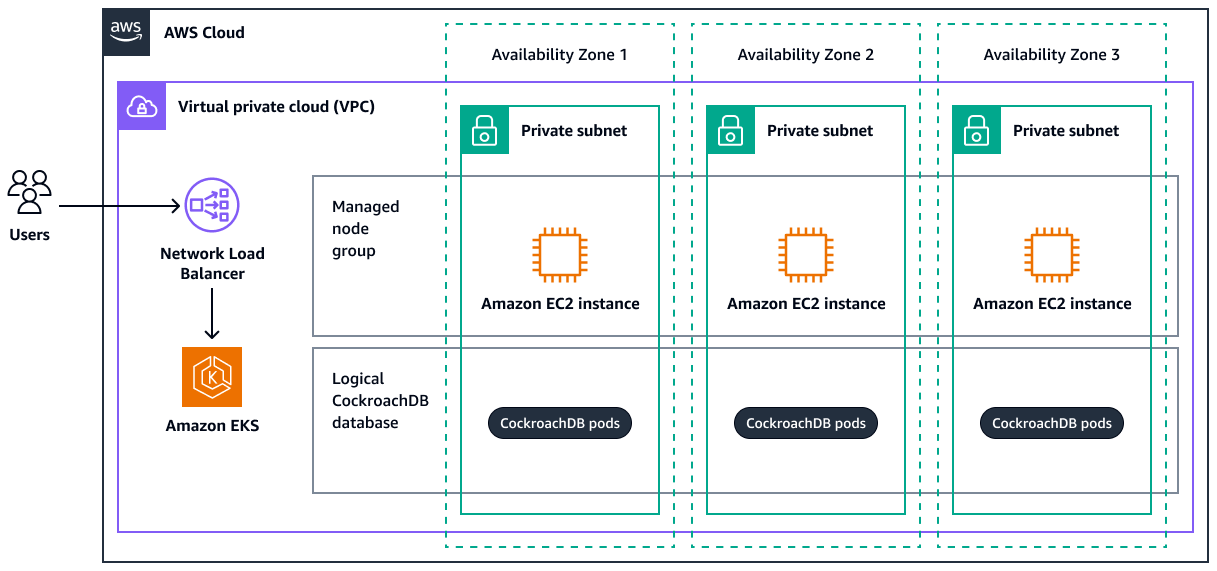
Resources created
Deploying the Terraform module used in this pattern creates the following resources:
Network Load Balancer – This resource serves as the entry point for client requests and evenly distributes traffic across the CockroachDB instances.
CockroachDB StatefulSet – The StatefulSet defines the desired state of the CockroachDB deployment within the Amazon EKS cluster. It manages the ordered deployment, scaling, and updates of CockroachDB pods.
CockroachDB pods – These pods are instances of CockroachDB running as containers within Kubernetes pods. These pods store and manage the data across the distributed cluster.
CockroachDB database – This is the distributed database that is managed by CockroachDB, spanning multiple pods. It replicates data for high availability, fault tolerance, and performance.
Tools
AWS services
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) is an open source tool that helps you interact with AWS services through commands in your command-line shell.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) helps you run Kubernetes on AWS without needing to install or maintain your own Kubernetes control plane or nodes.
Other tools
HashiCorp Terraform
is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that helps you use code to provision and manage cloud infrastructure and resources. kubectl
is a command-line interface that helps you run commands against Kubernetes clusters.
Code repository
The code for this pattern is available in the GitHub Deploy a CockroachDB cluster in Amazon EKS using Terraform
modulesfolder – This folder contains the Terraform module for CockroachDBmainfolder – This folder contains the root module that calls CockroachDB child module to create the CockroachDB database cluster.
Best practices
Do not scale down to fewer than three nodes. This is considered an anti-pattern on CockroachDB and can cause errors. For more information, see Cluster Scaling
in the CockroachDB documentation. Implement Amazon EKS autoscaling by using Karpernter or Cluster Autoscaler. This allows the CockroachDB cluster to scale horizontally and new nodes automatically. For more information, see Scale cluster compute with Karpenter and Cluster Autoscaler in the Amazon EKS documentation.
Note
Due to the
podAntiAffinityKubernetes scheduling rule, only one CockroachDB pod can be schedule in one Amazon EKS node.For Amazon EKS security best practices, see Best Practices for Security in the Amazon EKS documentation.
For SQL performance best practices for CockroachDB, see SQL Performance Best Practices
in the CockroachDB documentation. For more information about setting up an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) remote backend for the Terraform state file, see Amazon S3
in the Terraform documentation.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Clone the code repository. | Enter the following command to clone the repository:
| DevOps engineer, Git |
Update the Terraform variables. |
| DevOps engineer, Terraform |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Deploy the infrastructure. |
| DevOps engineer, Terraform |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Verify resource creation. |
| DevOps engineer |
(Optional) Scale up or down. |
| DevOps engineer, Terraform |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Delete the infrastructure. | Scaling nodes to
| Terraform |
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
Error validating provider credentials | When you run the Terraform
This error is caused by the expiration of the security token for the credentials used in your local machine’s configuration. For instructions on how to resolve the error, see Set and view configuration settings in the AWS CLI documentation. |
CockroachDB pods in pending state |
|
Related resources
Deploy CockroachDB in a Single Kubernetes Cluster
(CockroachDB documentation) Orchestrate CockroachDB Across Multiple Kubernetes Clusters
(CockroachDB documentation) AWS Provider
(Terraform documentation)
Attachments
To access additional content that is associated with this document, unzip the following file: attachment.zip