Automate the deployment of AWS Supply Chain data lakes in a multi-repository setup by using GitHub Actions, Artifactory, and Terraform
Keshav Ganesh, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern provides an automated approach for deploying and managing AWS Supply Chain data lakes using a multi-repository continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline. It demonstrates two deployment methods: automated deployment using GitHub Actions workflows, or manual deployment using Terraform directly. Both approaches use Terraform for infrastructure as code (IaC), with the automated method adding GitHub Actions and JFrog Artifactory for enhanced CI/CD capabilities.
The solution leverages AWS Supply Chain, AWS Lambda, and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) to establish the data lake infrastructure, while using either deployment method to automate configuration and resource creation. This automation eliminates manual configuration steps and ensures consistent deployments across environments. In addition, AWS Supply Chain eliminates the need for deep expertise in extract, transform, and load (ETL) and can provide insights and analytics powered by Amazon Quick Sight.
By implementing this pattern, organizations can reduce deployment time, maintain infrastructure as code, and manage supply chain data lakes through a version-controlled, automated process. The multi-repository approach provides fine-grained access control and supports independent deployment of different components. Teams can choose the deployment method that best fits their existing tools and processes.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
Ensure the following are installed on your local machine:
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) version 2
Python
v3.13 Terraform
v1.12 or later
Ensure the following are in place before deployment:
An active AWS account.
A virtual private cloud (VPC) with two private subnets in your AWS account in the AWS Region of your choice.
Sufficient permissions for the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role used for deployment to the following services:
AWS Supply Chain – Full Access preferred for deploying its components like datasets and integration flows, along with accessing it from the AWS Management Console.
Amazon CloudWatch Logs – For creating and managing CloudWatch log groups.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) – For Amazon EC2 security groups and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) endpoints.
Amazon EventBridge – For use by AWS Supply Chain.
IAM – For creating AWS Lambda service roles.
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) – For access to the AWS KMS keys used for the Amazon S3 artifacts bucket and the Amazon S3 AWS Supply Chain staging bucket.
AWS Lambda – For creating the Lambda functions that deploy the AWS Supply Chain components.
Amazon S3 – For access to the Amazon S3 artifacts bucket, server access logging bucket, and AWS Supply Chain staging bucket. If you’re using manual deployment, permissions for the Amazon S3 Terraform artifacts bucket are also required.
Amazon VPC – For creating and managing a VPC.
If you prefer to use GitHub Actions workflows for deployment, do the following:
Set up OpenID Connect (OIDC)
for the IAM role with the permissions mentioned earlier. Create an IAM role with similar permissions to access the AWS Management Console. For more information, see Create a role to give permissions to an IAM user in the IAM documentation.
If you prefer to do a manual deployment, do the following:
Create an IAM user to assume the IAM role with the permissions mentioned earlier. For more information, see Create a role to give permissions to an IAM user in the IAM documentation.
Assume the role in your local terminal.
If you prefer to use GitHub Actions workflows for deployment, set up the following:
A JFrog Artifactory account
to get the host name, login username, and login access token. A JFrog project key and repository
for storing artifacts.
Limitations
The AWS Supply Chain instance doesn’t support complex data transformation techniques.
AWS Supply Chain is most suited for supply chain domains because it provides built-in analytics and insights. For any other domain, AWS Supply Chain can be used as a data store as part of the data lake architecture.
Lambda functions used in this solution might need to be enhanced to handle API retries and memory management in a production scale deployment.
Some AWS services aren’t available in all AWS Regions. For Region availability, see AWS Services by Region
. For specific endpoints, see Service endpoints and quotas, and choose the link for the service.
Architecture
You can deploy this solution either by using automated GitHub Actions workflows or manually using Terraform.
Automated deployment with GitHub Actions
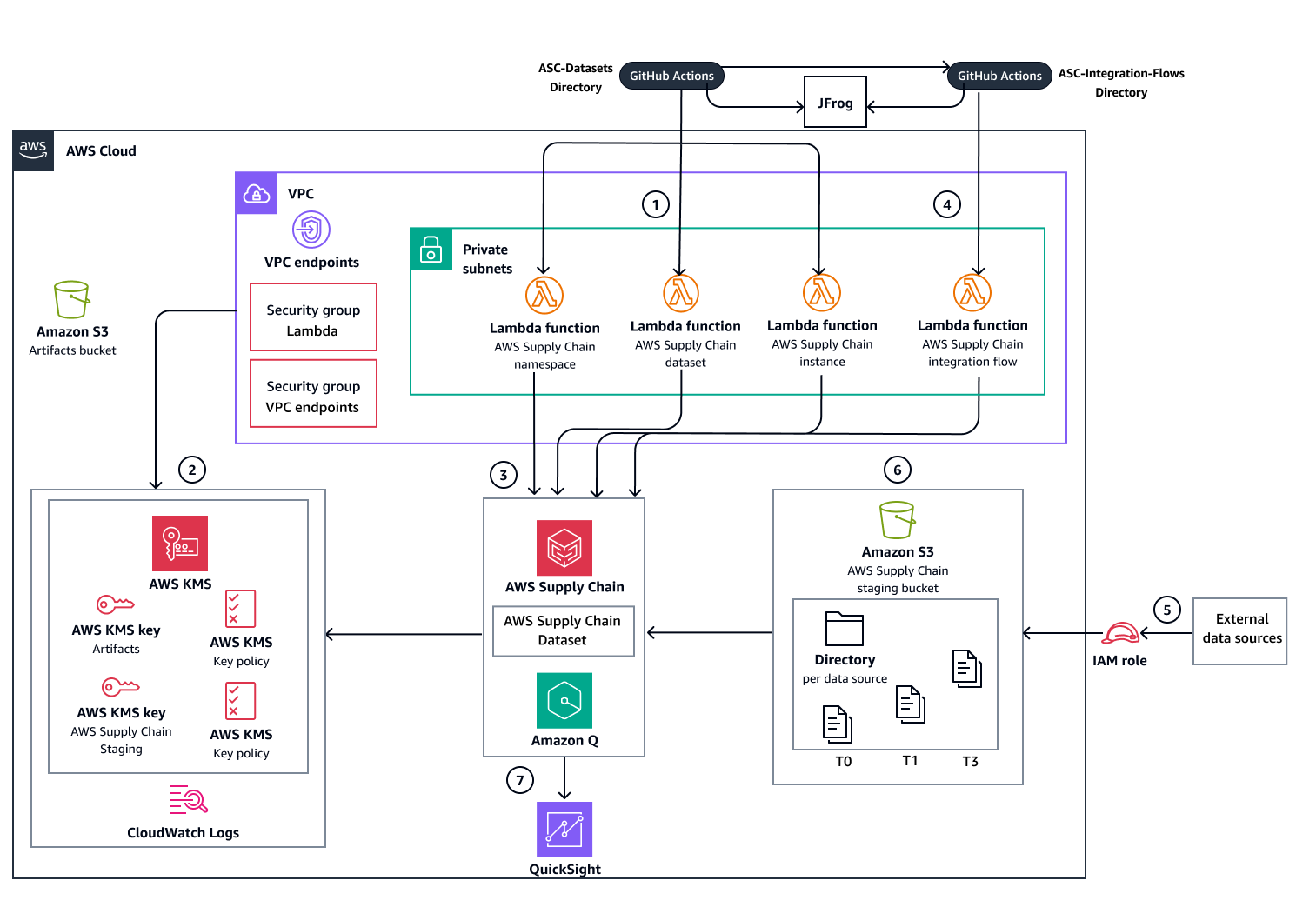
The following diagram shows the automated deployment option that uses GitHub Actions workflows. JFrog Artifactory is used for artifacts management. It stores resource information and outputs for use in a multi-repository deployment.
Manual deployment with Terraform
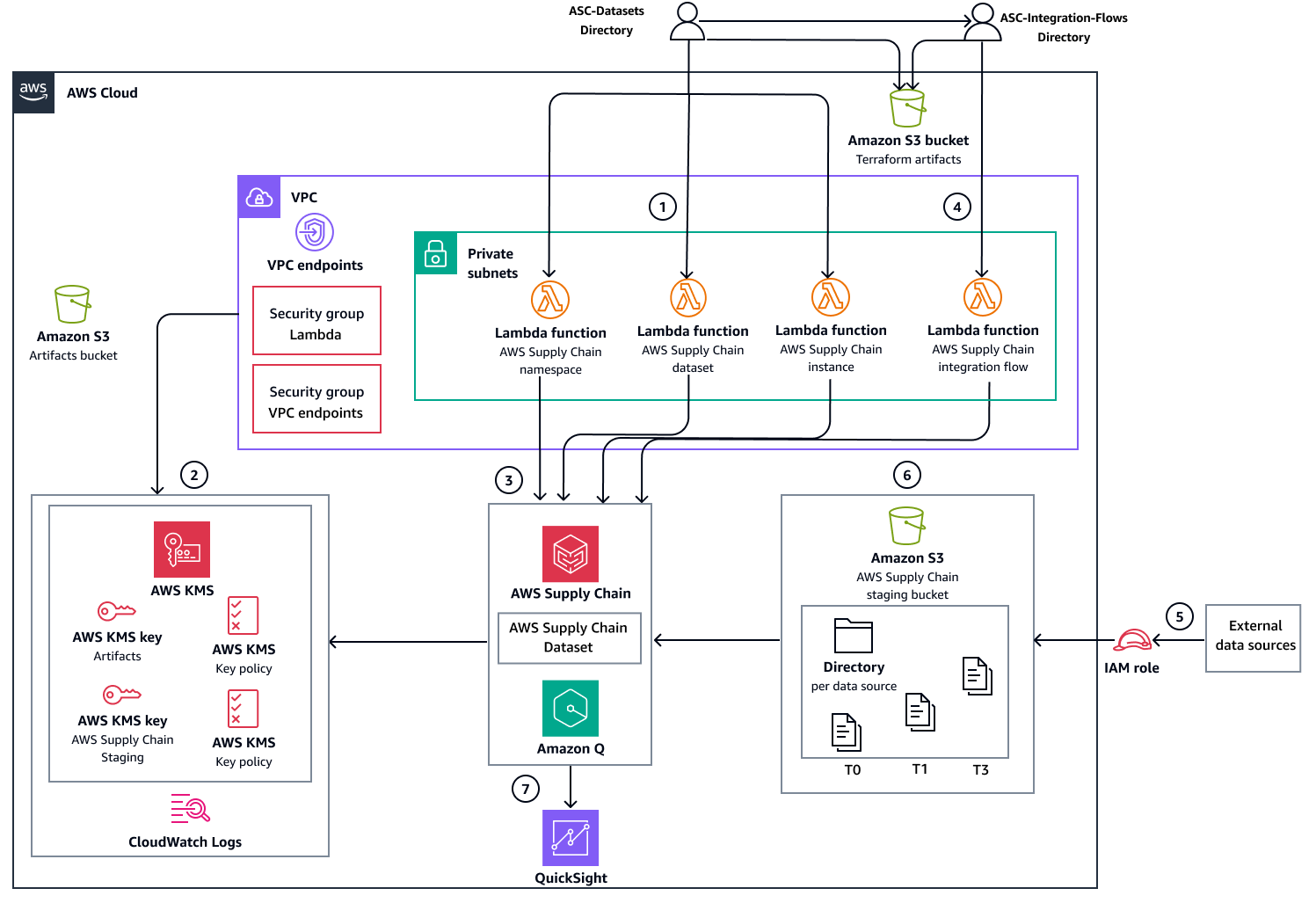
The following diagram shows the manual deployment option through Terraform. Instead of JFrog Artifactory, Amazon S3 is used for artifacts management.
Deployment workflow
The diagrams show the following workflow:
Deploy AWS Supply Chain service datasets infrastructure and databases using one of the following deployment methods:
Automated deployment – Uses GitHub Actions workflows to orchestrate all deployment steps and uses JFrog Artifactory for artifacts management.
Manual deployment – Executes Terraform commands directly for each deployment step and uses Amazon S3 for artifacts management.
Create the supporting AWS resources that are required for AWS Supply Chain service operation:
Amazon VPC endpoints and security groups
AWS KMS keys
CloudWatch Logs log groups
Create and deploy the following infrastructure resources:
Lambda functions that manage (create, update, and delete) the AWS Supply Chain service instance, namespaces, and datasets.
AWS Supply Chain staging Amazon S3 bucket for data ingestion
Deploy the Lambda function that manages integration flows between the staging bucket and AWS Supply Chain datasets. After deployment is complete, the remaining workflow steps manage data ingestion and analysis.
Configure source data ingestion to the AWS Supply Chain staging Amazon S3 bucket.
After data is added to the AWS Supply Chain staging Amazon S3 bucket, the service automatically triggers the integration flow to the AWS Supply Chain datasets.
AWS Supply Chain integrates with Quick Sight Analytics to produce dashboards based on the ingested data.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon CloudWatch Logs helps you centralize the logs from all your systems, applications, and AWS services so you can monitor them and archive them securely.
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) is an open source tool that helps you interact with AWS services through commands in your command-line shell.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) provides scalable computing capacity in the AWS Cloud. You can launch as many virtual servers as you need and quickly scale them up or down.
Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that helps you connect your applications with real-time data from a variety of sources. For example, AWS Lambda functions, HTTP invocation endpoints using API destinations, or event buses in other AWS accounts.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) helps you securely manage access to your AWS resources by controlling who is authenticated and authorized to use them.
AWS IAM Identity Center helps you centrally manage single sign-on (SSO) access to all of your AWS accounts and cloud applications.
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) helps you create and control cryptographic keys to help protect your data.
AWS Lambda is a compute service that helps you run code without needing to provision or manage servers. It runs your code only when needed and scales automatically, so you pay only for the compute time that you use.
Amazon Q in AWS Supply Chain is an interactive generative AI assistant that helps you operate your supply chain more efficiently by analyzing the data in your AWS Supply Chain data lake.
Amazon Quick Sight is a cloud-scale business intelligence (BI) service that helps you visualize, analyze, and report your data in a single dashboard.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is a cloud-based object storage service that helps you store, protect, and retrieve any amount of data.
AWS Supply Chain is a cloud-based managed application that can be used as a data store in organizations for supply chain domains, which can be used to generate insights and perform analysis on the ingested data.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) helps you launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS. An Amazon VPC endpoint is a virtual device that helps you privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection.
Other tools
GitHub Actions
is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that’s tightly integrated with GitHub repositories. You can use GitHub Actions to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline. HashiCorp Terraform
is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that helps you create and manage cloud and on-premises resources. JFrog Artifactory
provides end-to-end automation and management of binaries and artifacts through the application delivery process. Python
is a general-purpose computer programming language. This pattern uses Python for the AWS function’s code to interact with AWS Supply Chain .
Best practices
Maintain the highest possible security when implementing this pattern. As stated in Prerequisites, make sure a virtual private cloud (VPC) with two private subnets is in your AWS account in the AWS Region of your choice.
Use AWS KMS customer managed keys wherever possible, and grant limited access permissions to them.
To set up IAM roles with the least access required for ingesting data for this pattern, see Secure Data Ingestion from Source Systems to Amazon S3
in this pattern’s repository.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Clone the repository. | To clone this pattern’s repository, run the following command in your local workstation:
| AWS DevOps |
(Automated option) Verify prerequisites for deployment. | Make sure that the Prerequisites are complete for the automated deployment. | App owner |
(Manual option) Prepare for deployment of AWS Supply Chain datasets. | To go to the
To assume the role ARN that was created in the Prerequisites, run the following command:
To configure and export the environment variables, run the following commands:
| AWS DevOps |
(Manual option) Prepare for managing AWS Supply Chain integration flows in deployment. | To go to the
To assume the role ARN that was created earlier, run the following command:
To configure and export the environment variables, run the following commands:
| App owner |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Copy the | To copy the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the | To set up
| AWS DevOps |
Configure the branch name in the .github workflow file. | Set up the branch name in the deployment
| App owner |
Set up GitHub environments and configure environment values. | To set up GitHub environments in your GitHub organization, use the instructions in Setup GitHub environments To configure environment values | App owner |
Trigger the workflow. | To push your changes to your GitHub organization and trigger the deployment workflow, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Copy the | To copy the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the | To set up the
| AWS DevOps |
Configure the branch name in the .github workflow file. | Set up the branch name in the deployment
| App owner |
Set up GitHub environments and configure environment values. | To set up GitHub environments in your GitHub organization, use the instructions in Setup GitHub environments To configure environment values | App owner |
Trigger the workflow. | To push your changes to your GitHub organization and trigger the deployment workflow, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Navigate to the | To go to the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform state Amazon S3 bucket. | To set up the Terraform state Amazon S3 bucket, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform artifacts Amazon S3 bucket. | To set up the Terraform artifacts Amazon S3 bucket, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration. | To set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Generate a deployment plan. | To generate a deployment plan, run the following commands:
| AWS DevOps |
Deploy the configurations. | To deploy the configurations, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
Update other configurations and store outputs. | To update AWS KMS key policies and store the applied configurations outputs in the Terraform artifacts Amazon S3 bucket, run the following commands:
| AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Navigate to the | To go to the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration. | To set up the Terraform backend and provider configurations, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Generate a deployment plan. | To generate a deployment plan, run the following commands. These commands initialize your Terraform environment, merge configuration variables from
| AWS DevOps |
Deploy the configurations. | To deploy the configurations, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
Update other configurations. | To update AWS KMS key policies and store the applied configurations outputs in the Terraform artifacts Amazon S3 bucket, run the following commands:
| AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Upload sample CSV files. | To upload sample CSV files for the datasets, use the following steps:
| Data engineer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Set up AWS Supply Chain access. | To set up AWS Supply Chain access from the AWS Management Console, use the following steps:
| App owner |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Trigger the destroy workflow for integration flows resources. | Trigger the destroy workflow | AWS DevOps |
Trigger the destroy workflow for datasets resources. | Trigger the destroy workflow | AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Navigate to the | To go to the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration. | To set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Generate infrastructure destruction plan. | To prepare for the controlled destruction of your AWS infrastructure by generating a detailed teardown plan, run the following commands. The process initializes Terraform, incorporates AWS Supply Chain dataset configurations, and creates a destruction plan that you can review before executing.
| AWS DevOps |
Execute infrastructure destruction plan. | To execute the planned destruction of your infrastructure, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
Remove Terraform outputs from Amazon S3 bucket. | To remove the outputs file that was uploaded during the deployment of
| AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Navigate to the | To go to the
| AWS DevOps |
Set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration. | To set up the Terraform backend and providers configuration, use the following script:
| AWS DevOps |
Generate infrastructure destruction plan. | To create a plan for destroying AWS Supply Chain dataset resources, run the following commands:
| AWS DevOps |
Empty Amazon S3 buckets. | To empty all Amazon S3 buckets (except the server access logging bucket, which is configured for
| AWS DevOps |
Execute infrastructure destruction plan. | To execute the planned destruction of your AWS Supply Chain dataset infrastructure using the generated plan, run the following command:
| AWS DevOps |
Remove Terraform outputs from the Amazon S3 Terraform artifacts bucket. | To complete the cleanup process, remove the outputs file that was uploaded during the deployment of
| AWS DevOps |
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
An AWS Supply Chain dataset or integration flow did not deploy correctly because of AWS Supply Chain internal errors or insufficient IAM permissions for the service role. | First, clean up all resources. Then, redeploy the AWS Supply Chain dataset resources |
The AWS Supply Chain integration flow doesn’t fetch the new data files uploaded for the AWS Supply Chain datasets. |
|
Related resources
AWS documentation
Other resources
Understanding GitHub Actions workflows
(GitHub documentation)
Additional information
This solution can be replicated for more datasets and can be queried for further analysis, through prebuilt dashboards provided with AWS Supply Chain or custom integration with Amazon Quick Sight. In addition, you can use Amazon Q to ask questions related to your AWS Supply Chain instance.
Analyze data with AWS Supply Chain Analytics
For instructions to set up AWS Supply Chain Analytics, see Setting AWS Supply Chain Analytics in the AWS Supply Chain documentation.
This pattern demonstrated the creation of Calendar and Outbound_Order_Line datasets. To create an analysis that uses these datasets, use the following steps:
To analyze the datasets, use the Seasonality Analysis dashboard. To add the dashboard, follow the steps in Prebuilt dashboards in the AWS Supply Chain documentation.
Choose the dashboard to see its analysis that is based on sample CSV files for Calendar data and Outbound Order Line data.
The dashboard provides insights on demand over the years based on the ingested data for the datasets. You can further specify the ProductID, CustomerID, years, and other parameters for analysis.
Use Amazon Q to ask questions related to your AWS Supply Chain instance
Amazon Q in AWS Supply Chain is an interactive generative AI assistant that helps you operate your supply chain more efficiently. Amazon Q can do the following:
Analyze the data in your AWS Supply Chain data lake.
Provide operational and financial insights.
Answer your immediate supply chain questions.
For more information about using Amazon Q, see Enabling Amazon Q in AWS Supply Chain and Using Amazon Q in AWS Supply Chain in the AWS Supply Chain documentation.