The .vectors.distance.byEmbedding algorithm
The .vectors.distance.byEmbedding algorithm computes the distance between an embedding vector and the
embedding of an input node. The default distance is the squared L2 norm of the input embedding vector and the embedding
vector of the input node.
.vectors.distance.byEmbedding syntax
MATCH( n {`~id`: "the ID of the input node(s)"} ) CALL neptune.algo.vectors.distance.byEmbedding(n, { metric: The distance computation metric (optional), embedding: [*an embedding*] (required) } ) YIELD distance RETURN n, distance
.vectors.distance.byEmbedding inputs
-
an input node list (required) – type:
node[]orNodeId[]; default: none.The result of a `MATCH` statement from which you want get the input nodes of the distance computations.
-
embedding (required) – type:
float[]ordouble[];.The input embedding vector from which you want to use for the distance computations. The dimension of the embedding must match the declared dimension of the associated vector index.
The embedding may or may not exist in the database. If not, it can be any vector of the same dimension as is declared in the associated vector index.
-
metric (optional) – type:
stringdefault: L2Squared.The distance metric to use for distance computation.
-
Must be one of [L2Squared, L2, CosineSimilarity, CosineDistance, DotProduct].
-
Case-insensitive.
-
The descriptions for the metrics, where x and y are vectors, x_i and y_i are the components of x and y vectors, θ is the angle between the x and y vectors, ||x|| denotes the magnitude (length, l2-norm, norm2) of vector x, ∑ denotes summation:
-
L2-Squared: Squared Euclidean distance between two vectors:

For more information on L2-Squared, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance#Squared_Euclidean_distance
. -
L2: Euclidean distance (L2 norm) between two vectors:
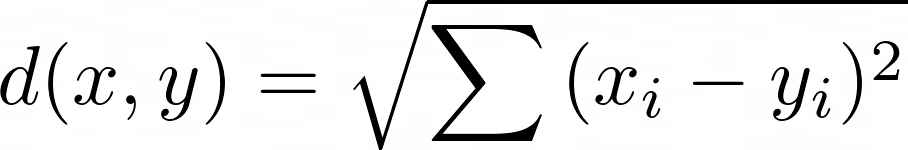
For more information on L2, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance
. -
Dot Product: Inner dot product of two vectors:

For more information on Dot Product, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product
. -
Cosine Similarity: Measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors (higher value means more similar):

Range: [-1, 1]
For more information on Cosine Similarity, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity
. -
Cosine Distance: Opposite of cosine similarity (lower value means more similar):

Range: [0, 2]
For more information on Cosine Distance, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity#Cosine_distance
.
-
-
.vectors.distance.byEmbedding outputs
For every target node:
-
target – The target node.
-
distance – The distance between the source embedding and the embedding of the target node.
.vectors.distance.byEmbedding query examples
MATCH (n) WHERE id(n)="v1" CALL neptune.algo.vectors.distance.byEmbedding(n, {embedding: [1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4], metric: "L2Squared"}) YIELD distance RETURN n, distance
MATCH (n:person) WHERE id(n)=entry.id WITH n CALL neptune.algo.vectors.distance.byEmbedding(n, {embedding: [1,2,3,4], metric: "CosineSimilarity"}) YIELD distance RETURN n, distance
Sample .vectors.distance.byEmbedding output
Here is an example of the output returned by .vectors.distance.byEmbedding when run against
a sample Wikipedia dataset using the following query:
aws neptune-graph execute-query \ --graph-identifier ${graphIdentifier} \ --query-string "MATCH (n{`~id`: '1'}) CALL neptune.algo.vectors.distance.byEmbedding(n, {embedding: [*an embedding*]}) YIELD distance RETURN n, distance" \ --language open_cypher \ /tmp/out.txt { "results": [ { "n": { "~id": "1", "~entityType": "node", "~labels": [], "~properties": { "title": "24-hour clock", "views": 2450.62548828125, "wiki_id": 9985, "paragraph_id": 1, "url": "https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki?curid=9985", "langs": 30, "text": "A time in the 24-hour clock is written in the form hours:minutes (for example\\, 01:23)\\, or hours:minutes:seconds (01:23:45). Numbers under 10 have a zero in front (called a leading zero); e.g. 09:07. Under the 24-hour clock system\\, the day begins at midnight\\, 00:00\\, and the last minute of the day begins at 23:59 and ends at 24:00\\, which is identical to 00:00 of the following day. 12:00 can only be mid-day. Midnight is called 24:00 and is used to mean the end of the day and 00:00 is used to mean the beginning of the day. For example\\, you would say \"Tuesday at 24:00\" and \"Wednesday at 00:00\" to mean exactly the same time." } }, "distance": 27.762847900390626 } ] }