기계 번역으로 제공되는 번역입니다. 제공된 번역과 원본 영어의 내용이 상충하는 경우에는 영어 버전이 우선합니다.
Azure DevOps 파이프라인에서 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터로 워크로드 배포
Mahendra Revanasiddappa, Amazon Web Services
요약
이 패턴은 Azure DevOps 파이프라인에서 프라이빗 Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service(Amazon EKS) 클러스터로 지속적 통합 및 지속적 전달(CI/CD)을 구현하는 방법을 보여줍니다. Amazon EKS 클러스터의 프라이빗 API 서버 엔드포인트로 전환하여 보안 태세를 강화하고 있는 조직이 직면한 중요한 문제를 해결합니다.
퍼블릭 엔드포인트는 Kubernetes API 서버를 인터넷에 직접 노출하여 악의적인 공격자가 잠재적으로 대상으로 삼을 수 있는 더 큰 공격 표면을 생성합니다. 프라이빗 엔드포인트로 전환하면 클러스터의 컨트롤 플레인에 대한 액세스가 고객의 Virtual Private Cloud(VPC) 내에서 로 제한됩니다.
Amazon EKS 클러스터를 프라이빗 API 엔드포인트로 전환하면 보안이 크게 향상되지만 Azure DevOps와 같은 외부 CI/CD 플랫폼에 연결 문제가 발생합니다. 프라이빗 엔드포인트는 클러스터의 VPC 또는 피어링된 네트워크 내에서만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 따라서 AWS 프라이빗 네트워크 외부에서 작동하는 표준 Microsoft 호스팅 Azure DevOps 에이전트는 Kubernetes API 서버에 직접 연결할 수 없습니다. 이렇게 하면 클러스터에 대한 연결을 설정하지 못하기 때문에 이러한 에이전트에서 실행되는 kubectl 또는 Helm과 같은 도구에 의존하는 일반적인 배포 워크플로가 중단됩니다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위해이 패턴은 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터 내에서 자체 호스팅된 Azure DevOps 에이전트를 사용하여 효율적인 접근 방식을 보여줍니다. 이 솔루션은 보안 요구 사항을 유지하면서 우수한 비용 최적화, 운영 효율성 및 확장성을 제공합니다. 이 접근 방식은 성능 또는 보안을 손상시키지 않고 멀티 클라우드 DevOps 프로세스를 간소화하려는 기업에 특히 유용합니다.
사전 조건 및 제한 사항
사전 조건
활성. AWS 계정
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) 버전 2.13.17 이상, 설치됨.
kubectl 버전 1.25.1 이상이 설치되었습니다.
네임스페이스, 보안 암호 및 배포를 생성할 수 있는 권한이 있는 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터 버전 1.24 이상이 생성되었습니다.
Amazon EKS 클러스터의 작업자 노드를 인터넷에 아웃바운드로 연결하여 해당 노드에서 실행되는 Azure DevOps 에이전트가 Azure DevOps 에이전트 풀에 연결할 수 있도록 합니다.
GitHub 계정이 생성되었습니다.
Azure Pipelines과 외부 또는 원격 서비스 간의 인증된 연결인 서비스 연결을 구성할 수 있는 액세스 권한이 있는 Azure DevOps 프로젝트가 생성됩니다.
이전 포인트에서 설명한 Azure DevOps 프로젝트를 위해 설치된 AWS Toolkit for Azure DevOps 버전 1.15 이상입니다. 설치 지침은 Visual Studio MarketplaceAWS Toolkit for Azure DevOps의 섹션을 참조하세요.
제한 사항
아키텍처
이 패턴은 다음을 생성합니다.
Amazon ECR 리포지토리 - Amazon Elastic Container Registry(Amazon ECR) 리포지토리는 Azure DevOps 에이전트 및 배포된 샘플 앱과 함께 Docker 이미지를 저장합니다.
Azure DevOps 에이전트 풀 - Azure DevOps 자체 호스팅 에이전트 풀은 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 실행되는 에이전트를 등록합니다.
IAM 역할 - 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 실행 중인 에이전트에 필요한 액세스를 제공하는 Azure 서비스 연결을 위한 AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) 역할입니다.
Azure DevOps 서비스 연결 - 파이프라인 작업이 액세스하는 데 필요한 액세스를 제공하는 IAM 역할을 사용하기 위한 Azure DevOps 계정의 서비스 연결입니다 AWS 서비스.
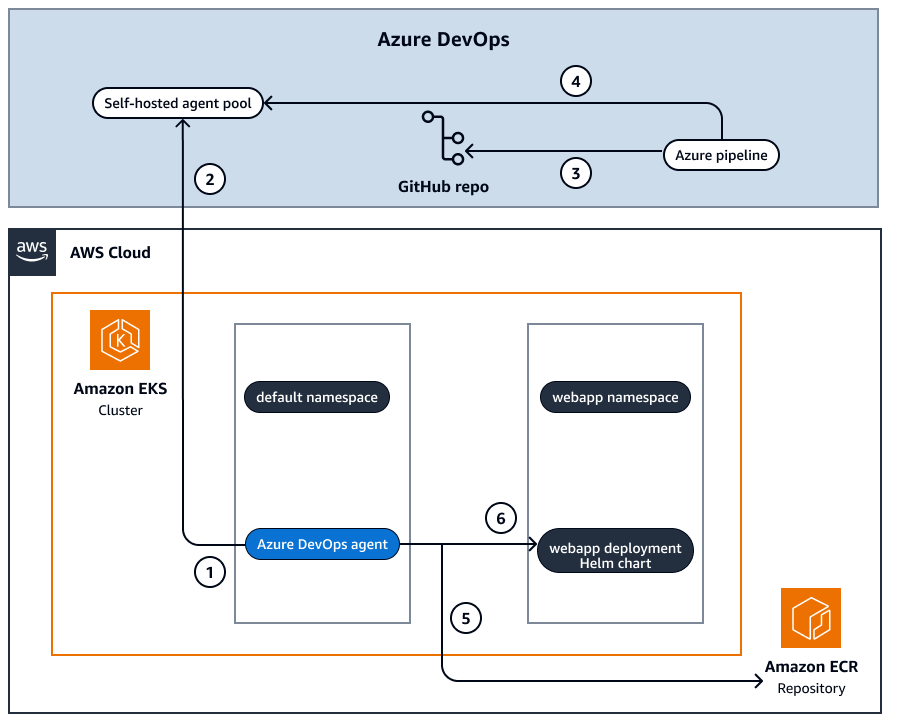
다음 다이어그램은 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 자체 호스팅된 Azure DevOps 에이전트를 배포하고 동일한 클러스터에 샘플 애플리케이션을 배포하는 아키텍처를 보여줍니다.
이 다이어그램은 다음 워크플로를 보여줍니다.
자체 호스팅 Azure DevOps 에이전트를 Amazon EKS 클러스터 내에 배포로 배포합니다.
Azure DevOps 에이전트는 인증을 위한 개인 액세스 토큰(PAT)을 사용하여 Azure DevOps 계정의 에이전트 풀에 연결합니다.
Azure Pipelines은 GitHub 리포지토리의 코드를 사용하여 배포하도록 파이프라인을 구성합니다.
파이프라인은 파이프라인 구성에 구성된 에이전트 풀의 에이전트에서 실행됩니다. Azure DevOps 에이전트는 Azure DevOps 계정으로 지속적으로 폴링하여 파이프라인의 작업 정보를 가져옵니다.
Azure DevOps 에이전트는 파이프라인 작업의 일부로 Docker 이미지를 빌드하고 이미지를 Amazon ECR 리포지토리로 푸시합니다.
Azure DevOps 에이전트는 샘플 애플리케이션을 라는 네임스페이스의 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 배포합니다webapp.
도구
기타 도구
코드 리포지토리
모범 사례
에픽
| 작업 | 설명 | 필요한 기술 |
|---|
Azure DevOps 조직 GUID를 찾습니다. | Azure DevOps 계정에 로그인한 다음 다음 URL을 사용하여 조직 GUID를 찾습니다. URLhttps://dev.azure.com/{DevOps_Org_ID}/_apis/projectCollections?api-version=6.0에서를 Azure DevOps 조직 ID{DevOps_org_ID}로 바꿉니다. | DevOps |
에서 IdP를 구성합니다 AWS 계정. | Azure 서비스 연결을 AWS 계정 위해에서 ID 제공업체(IdP)를 구성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. 에 로그인 AWS Management 콘솔하고 https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/ IAM 콘솔을 엽니다. 왼쪽 창에서 자격 증명 공급자를 선택합니다. [공급자 추가(Add Provider)]를 선택합니다. 공급자 유형으로 OpenID Connect를 선택합니다. 공급자 URL에 Azure DevOps 발급자 URL을 입력합니다. Azure DevOps의 각 테넌트에는 일반적으로 다음 형식을 사용하는 고유한 OrganizationGUID가 있습니다.를 Azure DevOps 조직 ID{OrganizationGUID}로 https://vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID} 바꿉니다. 대상에 api://AzureADTokenExchange를 입력합니다. Azure DevOps의 고정 값입니다. [공급자 추가(Add Provider)]를 선택합니다. 다음 작업에 사용할 새로 생성된 공급자의 ARN을 기록해 둡니다.
자세한 내용은 OpenID Connect를 사용하여 Azure DevOps AWS 에서 로 페더레이션하는 방법을 참조하세요. | DevOps |
에서 IAM 정책을 생성합니다 AWS 계정. | Azure DevOps 파이프라인에서 사용하는 IAM 역할에 필요한 권한을 제공하는 IAM 정책을 생성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. IAM 콘솔의 왼쪽 창에서 정책을 선택합니다. 정책 생성을 선택하세요. 권한 지정의 정책 편집기에서 JSON을 선택합니다. 기본 JSON 정책을 다음 JSON으로 바꿉니다.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Statement1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:*",
"eks:DescribeCluster",
"eks:ListClusters"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
다음을 선택합니다. 정책 이름에 IAM 정책의 이름을 입력합니다. 이 패턴은 ADO-policy라는 이름을 사용합니다. 정책 생성을 선택합니다.
| DevOps |
에서 IAM 역할을 생성합니다 AWS 계정. | Azure 서비스 연결을 AWS 계정 위해에서 IAM 역할을 구성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. IAM 콘솔의 왼쪽 창에서 역할을 선택합니다. 역할 생성을 선택합니다. 신뢰할 수 있는 엔터티 유형에서 웹 자격 증명을 선택합니다. 드롭다운 목록에서 올바른 IdP를 선택합니다. IdP 이름은 로 시작합니다vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID}. 대상 드롭다운 목록에서 api://AzureADTokenExchange를 선택합니다. 이 역할을 하나의 서비스 연결로만 제한하려면 조건을 추가합니다. 조건에서 조건 추가를 선택하고 키에서 vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID}:sub를 선택합니다. 조건에서 StringEquals 선택합니다. 값에는 형식을 사용합니다sc://{OrganizationName}/{ProjectName}/{ServiceConnectionName}. 의 경우 aws-sc를 ServiceConnectionName사용합니다. 다음 작업에서이 서비스 연결을 생성합니다. 다음을 선택합니다. 권한 추가에서 이전 작업에서 생성한 정책인 ADO 정책을 선택합니다. 다음을 선택하고 역할 이름에 ado-role을 입력합니다. 신뢰할 수 있는 개체 선택에서 다음 신뢰 정책을 사용합니다.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::{account_id}:oidc-provider/vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID}"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID}:aud": "api://AzureADTokenExchange",
"vstoken.dev.azure.com/{OrganizationGUID}:sub": "sc://{OrganizationName}/{ProjectName}/{ServiceConnectionName}"
}
}
}
]
}
정책에서 다음 자리 표시자에 대한 정보를 제공합니다. {account_id} - AWS 계정 ID
{OrganizationGUID} - Azure DevOps 조직 GUID
{OrganizationName} - Azure DevOps 조직 이름
{ProjectName} - Azure DevOps 프로젝트 이름
{ServiceConnectionName} - Azure DevOps 서비스 연결 이름입니다. aws-sc를 사용합니다. 다음 작업에서이 서비스 연결을 생성합니다.
| DevOps |
Azure DevOps 계정에서 서비스 연결을 생성합니다. | Azure 서비스 연결을 구성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. Azure DevOps 프로젝트에서 프로젝트 설정, 서비스 연결을 선택합니다. 새 서비스 연결을 선택하고 서비스 연결 유형을 로 선택한 다음 다음을 aws선택합니다. 수임할 역할에 IAM 역할 ado-role의 arn을 입력합니다. 이전 작업에서 ado-role을 생성했습니다. 에서 IAM 역할을 생성합니다 AWS 계정. OIDC 사용 확인란을 선택합니다. 서비스 연결 이름에 작업 속성에 aws-sc를 입력합니다. 저장을 선택합니다.
자세한 내용은 Microsoft 설명서의 서비스 연결 생성을 참조하세요. | DevOps |
Amazon EKS 구성 파일에 IAM 역할을 추가합니다. | IAM 역할에는 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 필요한 작업을 수행하는 데 필요한 권한이 있어야 합니다. 파이프라인 역할이므로 IAM 역할은 클러스터에서 거의 모든 유형의 리소스를 관리할 수 있어야 합니다. 따라서 system:masters 그룹 권한은이 역할에 적합합니다. Kubernetes aws-auth ConfigMap 내의에 필요한 구성을 추가하려면 다음 코드를 사용합니다. - groups:
- system:masters
rolearn: arn:aws:iam::{account_id}:role/ADO-role
username: ADO-role
를 AWS 계정 ID{account_id}로 바꿉니다. 자세한 내용은 Amazon EKS 설명서의 Amazon EKS에서 IAM을 사용하는 방법을 참조하세요. | DevOps |
| 작업 | 설명 | 필요한 기술 |
|---|
자체 호스팅 에이전트 풀을 생성합니다. | Azure DevOps 계정에서 자체 호스팅 에이전트 풀을 구성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. Azure DevOps 계정 조직에 로그인합니다. Azure DevOps 조직을 선택합니다. Azure DevOps 프로젝트를 선택합니다. 프로젝트 설정을 선택하세요. 에이전트 풀을 선택합니다. 풀 추가를 선택합니다. 자체 호스팅을 선택합니다. 이름에 eks-agent를 입력합니다. 모든 파이프라인에 액세스 권한 부여 확인란을 선택합니다. 생성(Create)을 선택합니다.
자세한 내용은 Microsoft 설명서의 에이전트 풀 생성 및 관리를 참조하세요. | |
| 작업 | 설명 | 필요한 기술 |
|---|
Amazon ECR 리포지토리를 생성합니다. | 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 Azure DevOps 에이전트 및 샘플 애플리케이션(webapp)을 배포하는 데 사용되는 Docker 이미지는 Amazon ECR 리포지토리에 저장되어야 합니다. Amazon ECR 리포지토리를 생성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. 자세한 내용은 Amazon ECR 설명서의 이미지를 저장할 Amazon ECR 프라이빗 리포지토리 생성을 참조하세요. | DevOps |
Dockerfile을 생성하여 Azure DevOps 에이전트를 빌드합니다. | Dockerfile을 생성하여 Azure DevOps 에이전트가 설치된 Docker 이미지를 빌드합니다. 다음 콘텐츠를 라는 파일에 저장합니다Dockerfile.
FROM ubuntu:22.04
ENV TARGETARCH="linux-x64"
RUN apt update && apt upgrade -y && apt install -y curl git jq libicu70 unzip wget
RUN curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
RUN unzip awscliv2.zip
RUN ./aws/install
RUN rm -rf aws awscliv2.zip
RUN curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
RUN curl -sL https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | bash
RUN mkdir -p azp
WORKDIR /azp/
COPY ./start.sh ./
RUN chmod +x ./start.sh
RUN useradd -m -d /home/agent agent
RUN chown -R agent:agent /azp /home/agent
RUN groupadd -f docker
RUN usermod -aG docker agent
USER agent
ENTRYPOINT [ "./start.sh" ]
| DevOps |
Azure DevOps 에이전트용 스크립트를 생성합니다. | start.sh 스크립트를 생성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다.
Microsoft 설명서의 Dockerfile 생성 및 빌드 절차로 이동하여 5단계로 스크롤합니다. 다음 콘텐츠를에 저장~/azp-agent-in-docker/start.sh하고 Unix 스타일(LF) 줄 끝을 사용해야 합니다. 스크립트의 콘텐츠를 복사하여 Dockerfile과 동일한 디렉터리start.sh의 파일에 저장합니다.
| DevOps |
Azure DevOps 에이전트를 사용하여 Docker 이미지를 빌드합니다. | Azure DevOps 에이전트를 설치할 Docker 이미지를 생성하려면 이전에 생성한 Dockerfile을 사용하여 이미지를 빌드합니다. Dockerfile이 저장된 디렉터리와 동일한 디렉터리에서 다음 명령을 실행합니다. aws ecr get-login-password --region region | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com
docker build --platform linux/amd64 -t ado-agent:latest .
docker tag ado-agent:latest aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/webapp:latest
docker push aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/webapp:latest
aws_account_id 및를 AWS 계정 ID 및 region 로 바꿉니다 AWS 리전.
| DevOps |
| 작업 | 설명 | 필요한 기술 |
|---|
Azure 개인 액세스 토큰을 생성합니다. | 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 실행되는 에이전트는 Azure DevOps 계정으로 인증할 수 있도록 개인 액세스 토큰(PAT)이 필요합니다. PAT를 생성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. Azure DevOps 조직()에서 사용하려는 사용자 계정으로 로그인합니다https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization}.
홈 페이지에서 사용자 설정을 연 다음 개인 액세스 토큰을 선택합니다. 새 토큰을 선택합니다. 토큰의 이름을 입력합니다. 모든 범위 표시를 선택합니다. 에이전트 풀에서 읽기 및 관리 확인란을 선택합니다. 생성(Create)을 선택합니다. 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 보안 암호를 생성하려면 다음 구성을 사용합니다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: azdevops-pat
namespace: default
type: Opaque
stringData:
AZP_TOKEN: <PAT Token>
구성을 라는 파일에 저장합니다ado-secret.yaml. 를 방금 생성한 개인 액세스 토큰<PAT Token>으로 바꿉니다. 보안 암호를 생성하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
kubectl create -f ado-secret.yaml
자세한 내용은 Microsoft 설명서의 개인 액세스 토큰(PAT)을 사용하여 에이전트 등록을 참조하세요. | DevOps |
에이전트 배포에 Kubernetes 매니페스트 파일을 사용합니다. | 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 Azure DevOps 에이전트를 배포하려면 다음 매니페스트 파일을 복사하고 파일을 로 저장합니다. agent-deployment.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: azure-pipelines-agent-eks
labels:
app: azure-pipelines-agent
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: azure-pipelines-agent
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: azure-pipelines-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: docker
image: docker:dind
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: shared-workspace
mountPath: /workspace
- name: dind-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/docker
env:
- name: DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR
value: ""
- name: azure-pipelines-agent
image: aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.region.amazonaws.com/webapp:latest
env:
- name: AZP_URL
value: "<Azure account URL>"
- name: AZP_POOL
value: "eks-agent"
- name: AZP_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: azdevops-pat
key: AZP_TOKEN
- name: AZP_AGENT_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: DOCKER_HOST
value: tcp://localhost:2375
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /workspace
name: shared-workspace
volumes:
- name: dind-storage
emptyDir: {}
- name: shared-workspace
emptyDir: {}
aws_account_id 및를 AWS 계정 ID 및 Azure DevOps 계정 URL<Azure account URL>로 바꿉니다.
| DevOps |
프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 에이전트를 배포합니다. | 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 Azure Devops 에이전트를 배포하려면 다음 명령을 사용합니다. kubectl create -f agent-deployment.tf
| DevOps |
에이전트가 실행 중인지 확인합니다. | Azure DevOps 에이전트가 실행 중인지 확인하려면 다음 명령을 사용합니다. kubectl get deploy azure-pipelines-agent-eks
예상 출력은 다음과 유사해야 합니다.
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
azure-pipelines-agent-eks 1/1 1 1 58s
READY 열에가 표시되는지 확인합니다1/1.
| DevOps |
에이전트가 Azure DevOps 에이전트 풀에 등록되어 있는지 확인합니다. | 에이전트가 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에 배포되고 에이전트 풀에 등록되었는지 확인하려면 다음 단계를 eks-agent사용합니다. Azure DevOps 조직(https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization})에 로그인합니다. 프로젝트 설정을 선택하세요. 에이전트 풀을 선택합니다. eks-agent 풀을 선택한 다음 에이전트 탭을 확인합니다.
하나의 에이전트가 온라인 상태로 나열되고 에이전트 이름이 azure-pipelines-agent-eks-*로 시작해야 합니다. | DevOps |
| 작업 | 설명 | 필요한 기술 |
|---|
샘플 애플리케이션 리포지토리를 GitHub 계정으로 포크합니다. | GitHub 계정에 다음 AWS 샘플 리포지토리를 포크합니다. https://github.com/aws-samples/deploy-kubernetes-resources-to-amazon-eks-using-azure-devops | DevOps |
파이프라인 생성. | Azure DevOps 계정에서 파이프라인을 생성하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. Azure DevOps 조직()에서 사용하려는 사용자 계정으로 로그인합니다https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization}. 프로젝트 및 파이프라인 콘솔로 이동합니다. 새 파이프라인을 선택합니다. 코드가 있는 위치의 경우 GitHub를 선택합니다. 파이프라인이 GitHub 계정에 연결하는 데 필요한 자격 증명을 제공합니다. 리포지토리 deploy-kubernetes-resources-to-amazon-eks-using-azure-devops를 선택합니다. 파이프라인 구성에서 기존 Azure Pipelines YAML 파일을 선택합니다. 기존 YAML 파일 선택에서 브랜치의 경우 기본을 선택하고 경로의 경우 azure_pipelines.yaml을 선택합니다. 계속을 선택합니다. 파이프라인 YAML 검토에서 awsRegion 및에 대한 입력 파라미터 값을 정보로 바꿉니다awsEKSClusterName.
pool:
name: eks-agent
#pool: self-hosted # If you are running self-hosted Azure DevOps Agents
stages:
# Refering the pipeline template, input parameter that are not specified will be added with defaults
- template: ./pipeline_templates/main_template.yaml
parameters:
serviceConnectionName: aws-sc
awsRegion: <your region>
awsEKSClusterName: <name of your EKS cluster>
projectName: webapp
| DevOps |
샘플 애플리케이션이 배포되었는지 확인합니다. | 파이프라인이 완료되면 Amazon ECR 리포지토리와 Amazon EKS 클러스터를 모두 확인하여 샘플 애플리케이션의 성공적인 배포를 확인합니다. Amazon ECR 리포지토리에서 아티팩트를 확인하려면 다음 단계를 사용합니다. webapp Amazon ECR 리포지토리로 이동합니다.
다음과 같은 새 아티팩트가 있는지 확인합니다.
예: 20250501.1-image 및 20250501.1-helm. 네임스페이스의 프라이빗 Amazon EKS 클러스터에서 배포를 확인하려면 다음 명령을 webapp사용합니다. kubectl get deploy -n webapp
예상 출력은 다음과 같습니다.
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE
webapp 1/1 1 1
참고: 첫 번째 파이프라인 실행인 경우 서비스 연결 및 에이전트 풀을 승인해야 할 수 있습니다. Azure DevOps 파이프라인 인터페이스에서 권한 요청을 찾아 계속 진행하도록 승인합니다. | DevOps |
문제 해결
| 문제 | Solution |
|---|
Amazon ECR 리포지토리 이름이 일치하지 않으면 파이프라인이 실패합니다. webapp | 샘플 애플리케이션은 Amazon ECR 리포지토리 이름이의 projectName: webapp 파라미터와 일치할 것으로 예상합니다azure_pipeline.yml. 이 문제를 해결하려면 Amazon ECR 리포지토리의 이름을 로 바꾸webapp거나 다음을 업데이트합니다. |
오류: Kubernetes 클러스터에 연결할 수 없음: 서버가 클라이언트에 자격 증명을 제공하도록 요청했습니다. | Azure 파이프라인의 "Helm 차트 풀 및 배포" 단계에서이 오류가 발생하는 경우 근본 원인은 일반적으로 Amazon EKS 클러스터의에서 잘못된 IAM 역할 구성으로 인해 발생합니다aws-auth ConfigMap. 이 문제를 해결하려면 다음을 확인하세요. aws-auth ConfigMap 구성을 확인합니다.
Amazon EKS 클러스터의 인증 설정 확인: Amazon EKS 콘솔, 클러스터 세부 정보, 액세스 구성을 엽니다. 인증 모드가 EKS API 및 ConfigMap(EKS API뿐만 아니라)으로 설정되어 있는지 확인합니다.
|
관련 리소스
AWS 블로그
AWS 서비스 설명서
Microsoft 설명서