IVS Broadcast SDK: Mixed Devices
Mixed devices are audio and video devices that take multiple input sources and generate a single output. Mixing devices is a powerful feature that lets you define and manage multiple on-screen (video) elements and audio tracks. You can combine video and audio from multiple sources such as cameras, microphones, screen captures, and audio and video generated by your app. You can use transitions to move these sources around the video that you stream to IVS, and add to and remove sources mid-stream.
Mixed devices come in image and audio flavors. To create a mixed image device, call:
DeviceDiscovery.createMixedImageDevice() on Android
IVSDeviceDiscovery.createMixedImageDevice() on iOS
The returned device can be attached to a BroadcastSession (low-latency
streaming) or Stage (real-time streaming), like any other device.
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
Device |
A hardware or software component that produces audio or image input. Examples of devices are microphones, cameras, Bluetooth headsets, and virtual devices such as screen captures or custom-image inputs. |
Mixed Device |
A Mixed devices come in either audio or image flavors. |
Mixed device configuration |
A configuration object for the mixed device. For mixed image devices, this configures properties like dimensions and framerate. For mixed audio devices, this configures the channel count. |
|
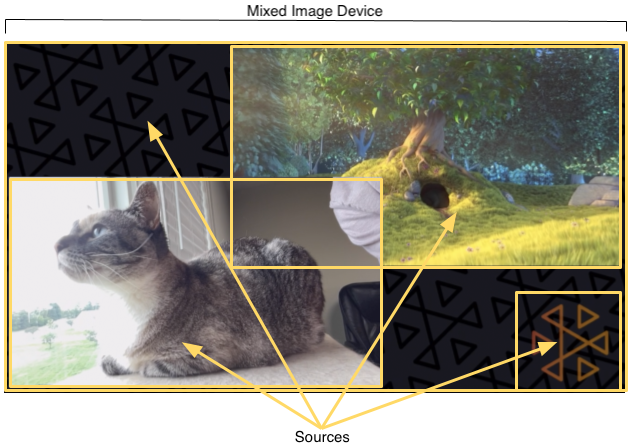
Source |
A container that defines a visual element’s position on screen and an audio track’s properties in the audio mix. A mixed device can be configured with zero or more sources. Sources are given a configuration that affects how the source’s media are used. The image above shows four image sources:
|
Source Configuration |
A configuration object for the source going into a mixed device. The full configuration objects are described below.. |
Transition |
To move a slot to a new position or change some of its
properties, use
|
Mixed Audio Device
Configuration
MixedAudioDeviceConfiguration on Android
IVSMixedAudioDeviceConfiguration on iOS
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Integer |
Number of output channels from the audio mixer. Valid values: 1, 2. 1 is mono audio; 2, stereo audio. Default: 2. |
Source Configuration
MixedAudioDeviceSourceConfiguration on Android
IVSMixedAudioDeviceSourceConfiguration on iOS
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Float |
Audio gain. This is a multiplier, so any value above 1 increases the gain; any value below 1, decreases it. Valid values: 0-2. Default: 1. |
Mixed Image Device
Configuration
MixedImageDeviceConfiguration on Android
IVSMixedImageDeviceConfiguration on iOS
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Vec2 |
Size of the video canvas. |
|
Integer |
Number of target frames per second for the mixed device. On average, this value should be met, but the system may drop frames under certain circumstances (e.g., high CPU or GPU load). |
|
Boolean |
This enables blending using the |
Source Configuration
MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration on Android
IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration on iOS
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Float |
Alpha of the slot. This is multiplicative with any alpha values in the image. Valid values: 0-1. 0 is fully transparent and 1 is fully opaque. Default: 1. |
|
AspectMode | Aspect-ratio mode for any image rendered in the slot. Valid values:
Default: |
|
Vec4 |
Fill color to be used with |
|
Vec2 |
Slot position (in pixels), relative to the top-left corner of the canvas. The origin of the slot also is top-left. |
|
Vec2 |
Size of the slot, in pixels. Setting this value also sets
|
|
Float |
Relative ordering of slots. Slots with higher
|
Creating and Configuring a Mixed Image Device

Here, we create a scene similar to the one at the beginning of this guide, with three on-screen elements:
-
Bottom-left slot for a camera.
-
Bottom-right slot for a logo overlay.
-
Top-right slot for a movie.
Note that the origin for the canvas is the top-left corner and this is the same for the slots. Hence, positioning a slot at (0, 0) puts it in the top-left corner with the entire slot visible.
iOS
let deviceDiscovery = IVSDeviceDiscovery() let mixedImageConfig = IVSMixedImageDeviceConfiguration() mixedImageConfig.size = CGSize(width: 1280, height: 720) try mixedImageConfig.setTargetFramerate(60) mixedImageConfig.isTransparencyEnabled = true let mixedImageDevice = deviceDiscovery.createMixedImageDevice(with: mixedImageConfig) // Bottom Left let cameraConfig = IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration() cameraConfig.size = CGSize(width: 320, height: 180) cameraConfig.position = CGPoint(x: 20, y: mixedImageConfig.size.height - cameraConfig.size.height - 20) cameraConfig.zIndex = 2 let camera = deviceDiscovery.listLocalDevices().first(where: { $0 is IVSCamera }) as? IVSCamera let cameraSource = IVSMixedImageDeviceSource(configuration: cameraConfig, device: camera) mixedImageDevice.add(cameraSource) // Top Right let streamConfig = IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration() streamConfig.size = CGSize(width: 640, height: 320) streamConfig.position = CGPoint(x: mixedImageConfig.size.width - streamConfig.size.width - 20, y: 20) streamConfig.zIndex = 1 let streamDevice = deviceDiscovery.createImageSource(withName: "stream") let streamSource = IVSMixedImageDeviceSource(configuration: streamConfig, device: streamDevice) mixedImageDevice.add(streamSource) // Bottom Right let logoConfig = IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration() logoConfig.size = CGSize(width: 320, height: 180) logoConfig.position = CGPoint(x: mixedImageConfig.size.width - logoConfig.size.width - 20, y: mixedImageConfig.size.height - logoConfig.size.height - 20) logoConfig.zIndex = 3 let logoDevice = deviceDiscovery.createImageSource(withName: "logo") let logoSource = IVSMixedImageDeviceSource(configuration: logoConfig, device: logoDevice) mixedImageDevice.add(logoSource)
Android
val deviceDiscovery = DeviceDiscovery(this /* context */) val mixedImageConfig = MixedImageDeviceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(1280f, 720f)) setTargetFramerate(60) setEnableTransparency(true) } val mixedImageDevice = deviceDiscovery.createMixedImageDevice(mixedImageConfig) // Bottom Left val cameraConfig = MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(320f, 180f)) setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(20f, mixedImageConfig.size.y - size.y - 20)) setZIndex(2) } val camera = deviceDiscovery.listLocalDevices().firstNotNullOf { it as? CameraSource } val cameraSource = MixedImageDeviceSource(cameraConfig, camera) mixedImageDevice.addSource(cameraSource) // Top Right val streamConfig = MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(640f, 320f)) setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(mixedImageConfig.size.x - size.x - 20, 20f)) setZIndex(1) } val streamDevice = deviceDiscovery.createImageInputSource(streamConfig.size) val streamSource = MixedImageDeviceSource(streamConfig, streamDevice) mixedImageDevice.addSource(streamSource) // Bottom Right val logoConfig = MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(320f, 180f)) setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(mixedImageConfig.size.x - size.x - 20, mixedImageConfig.size.y - size.y - 20)) setZIndex(1) } val logoDevice = deviceDiscovery.createImageInputSource(logoConfig.size) val logoSource = MixedImageDeviceSource(logoConfig, logoDevice) mixedImageDevice.addSource(logoSource)
Removing Sources
To remove a source, call MixedDevice.remove with the Source
object you want to remove.
Animations with Transitions
The transition method replaces a source’s configuration with a new configuration. This replacement can be animated over time by setting a duration higher than 0, in seconds.
Which Properties Can Be Animated?
Not all properties in the slot structure can be animated. Any properties based on Float types can be animated; other properties take effect at either the start or end of the animation.
| Name | Can It Be Animated? | Impact Point |
|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Interpolated |
|
Yes |
Interpolated |
|
No |
End |
|
Yes |
Interpolated |
|
Yes |
Interpolated |
|
Yes |
Interpolated |
Note: The |
Yes |
Unknown |
Simple Examples
Below are examples of a full-screen camera takeover using the configuration defined above in Creating and Configuring a Mixed Image Device. This is animated over 0.5 seconds.
iOS
// Continuing the example from above, modifying the existing cameraConfig object. cameraConfig.size = CGSize(width: 1280, height: 720) cameraConfig.position = CGPoint.zero cameraSource.transition(to: cameraConfig, duration: 0.5) { completed in if completed { print("Animation completed") } else { print("Animation interrupted") } }
Android
// Continuing the example from above, modifying the existing cameraConfig object. cameraConfig.setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(1280f, 720f)) cameraConfig.setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(0f, 0f)) cameraSource.transitionToConfiguration(cameraConfig, 500) { completed -> if (completed) { print("Animation completed") } else { print("Animation interrupted") } }
Mirroring the Broadcast
| To mirror an attached image device in the broadcast in this direction … | Use a negative value for … |
|---|---|
Horizontally |
The width of the slot |
Vertically |
The height of the slot |
Both horizontally and vertically |
Both the width and height of the slot |
The position will need to be adjusted by the same value, to put the slot in the correct position when mirrored.
Below are examples for mirroring the broadcast horizontally and vertically.
iOS
Horizontal mirroring:
let cameraSource = IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration() cameraSource.size = CGSize(width: -320, height: 720) // Add 320 to position x since our width is -320 cameraSource.position = CGPoint(x: 320, y: 0)
Vertical mirroring:
let cameraSource = IVSMixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration() cameraSource.size = CGSize(width: 320, height: -720) // Add 720 to position y since our height is -720 cameraSource.position = CGPoint(x: 0, y: 720)
Android
Horizontal mirroring:
val cameraConfig = MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(-320f, 180f)) // Add 320f to position x since our width is -320f setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(320f, 0f)) }
Vertical mirroring:
val cameraConfig = MixedImageDeviceSourceConfiguration().apply { setSize(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(320f, -180f)) // Add 180f to position y since our height is -180f setPosition(BroadcastConfiguration.Vec2(0f, 180f)) }
Note: This mirroring is different than the setMirrored method on
ImagePreviewView (Android) and IVSImagePreviewView
(iOS). That method affects only the local preview view on the device and does not
impact the broadcast.