Le traduzioni sono generate tramite traduzione automatica. In caso di conflitto tra il contenuto di una traduzione e la versione originale in Inglese, quest'ultima prevarrà.
Trasferimenti sicuri di file utilizzando Transfer Family, Amazon Cognito e GuardDuty
Manoj Kumar, Amazon Web Services
Riepilogo
Questa soluzione consente di trasferire file in modo sicuro tramite un server SFTP utilizzando. AWS Transfer Family Include funzionalità di scansione antimalware automatizzata tramite Malware Protection for S3, una funzionalità di Amazon GuardDuty. È progettato per le organizzazioni che devono scambiare file in modo sicuro con parti esterne e verificare che tutti i file in arrivo vengano scansionati alla ricerca di malware prima di essere elaborati.
I modelli Infrastructure as Code (IaC) forniti con questo modello consentono di implementare quanto segue:
Un server SFTP sicuro con autenticazione Amazon Cognito tramite AWS Lambda
Bucket Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) per i caricamenti e i file in entrata sottoposti a scansione alla ricerca di malware
Un'architettura basata su cloud privato virtuale (VPC) con sottoreti pubbliche e private su più zone di disponibilità
Controllo degli accessi basato su IP per il traffico in ingresso e in uscita, con elenchi di autorizzazioni e negazioni configurabili
Scansione antimalware automatizzata tramite GuardDuty
Routing intelligente dei file basato sui risultati della scansione tramite Amazon EventBridge e Lambda
Notifiche in tempo reale per incidenti di sicurezza tramite Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS)
Crittografia per bucket Amazon S3 e variabili di ambiente Lambda tramite () AWS Key Management Service AWS KMS
Endpoint Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) per l'accesso senza esposizione a Internet
Registrazione completa tramite l'integrazione con Amazon CloudWatch
Prerequisiti e limitazioni
Prerequisiti
Un attivo Account AWS
Autorizzazioni in AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) per eseguire le azioni descritte in questo modello, inclusa la distribuzione di AWS CloudFormation modelli che forniscono ruoli IAM
GuardDuty, abilitato nell'account di destinazione
Protezione da malware per S3, abilitata nell'account di destinazione
Le quote di servizio consentono di creare quanto segue nell'account di destinazione:
Un VPC
Una sottorete privata
Una sottorete pubblica
Tre indirizzi IP elastici
Limiti di concorrenza Lambda sufficienti
Un indirizzo e-mail valido per le notifiche relative alla sicurezza
(Facoltativo) Un elenco di indirizzi IP o intervalli CIDR che desideri consentire o negare
(Facoltativo) AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), installato e configurato
Limitazioni
La protezione da malware per S3 è soggetta a quote, come la dimensione massima dei file. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Quotas in Malware Protection for S3 e Supportabilità delle funzionalità di Amazon S3 nella documentazione. GuardDuty
Questa soluzione utilizza solo l'autenticazione con nome utente e password di Amazon Cognito. I metodi di autenticazione basati su certificati o altri metodi di autenticazione non sono supportati in questo modello. Per impostazione predefinita, questa soluzione non configura l'autenticazione a più fattori (MFA).
La soluzione implementa il controllo degli accessi basato su IP solo tramite gruppi di sicurezza.
Architecture
Il seguente diagramma di architettura mostra le risorse distribuite secondo questo schema. Questa soluzione utilizza Amazon Cognito per l'autenticazione e l'autorizzazione degli utenti. Per il caricamento dei file viene utilizzato un server AWS Transfer Family SFTP. I file vengono archiviati in bucket Amazon S3 e Amazon GuardDuty esegue la scansione dei file alla ricerca di malware. Amazon SNS invia una notifica e-mail se viene rilevato un malware.
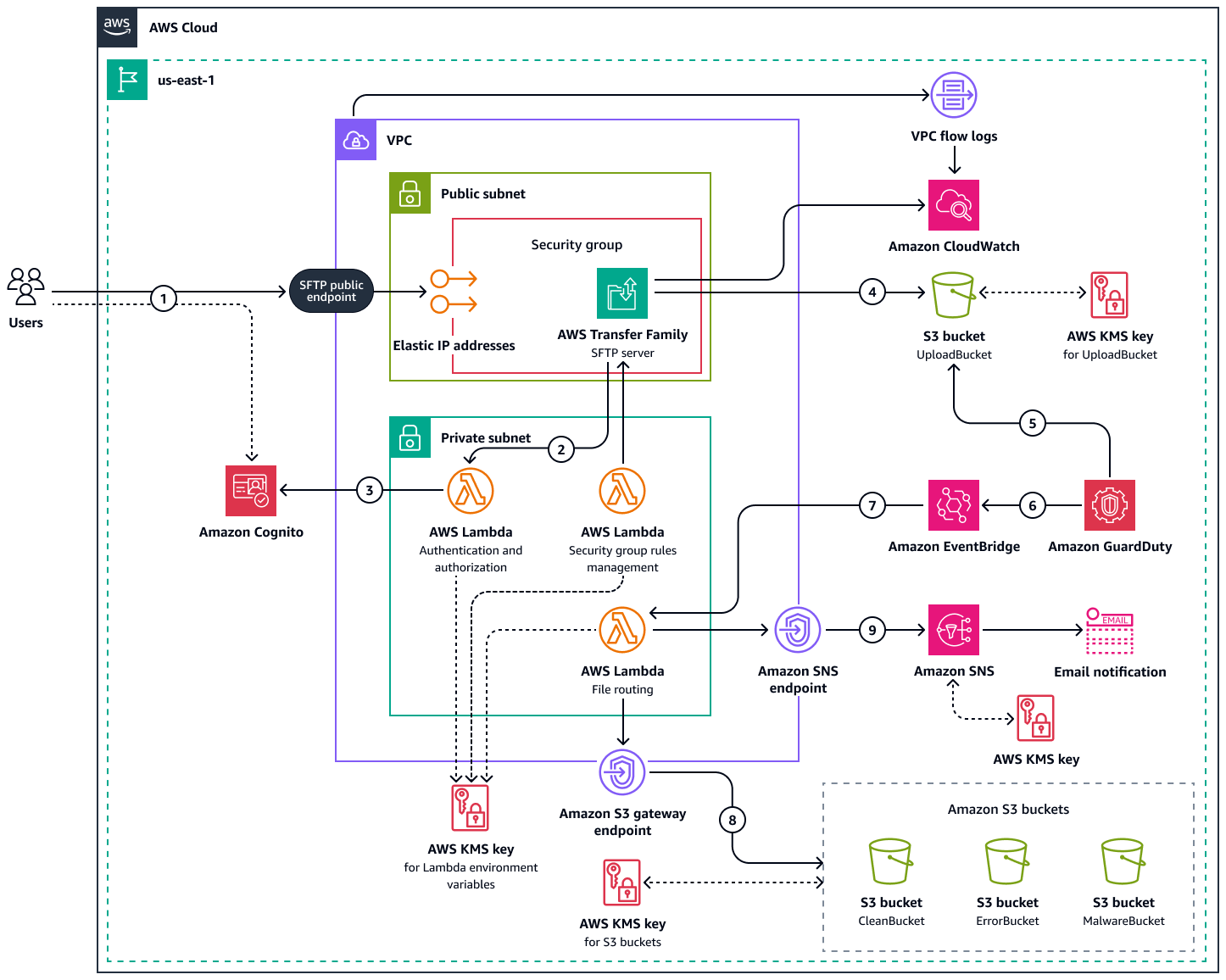
Il diagramma mostra il flusso di lavoro seguente:
Un utente si connette all'endpoint del server SFTP in. AWS Transfer Family Questo avvia il processo di autenticazione con il pool di utenti di Amazon Cognito.
Una funzione Lambda avvia il processo di autenticazione e autorizzazione e convalida le credenziali dell'utente con Amazon Cognito.
La funzione Lambda restituisce il
UploadBucketbucket Amazon S3 come directory home. L'utente assume il ruolo IAM per il server Transfer Family e la funzione Lambda notifica all'utente che è stato autenticato correttamente.L'utente carica un file sul server SFTP Transfer Family. Il file viene archiviato nel
UploadBucketbucket Amazon S3.GuardDuty esegue la scansione del file alla ricerca di malware. I potenziali risultati della scansione sono
NO_THREATS_FOUND,THREATS_FOUND,UNSUPPORTEDACCESS_DENIED, eFAILED. Per risultati di esempio, consulta il risultato della scansione degli oggetti S3 nella GuardDuty documentazione.Una EventBridge regola rileva l'evento del risultato della scansione.
EventBridge avvia la funzione Lambda per il routing dei file.
La funzione Lambda elabora l'evento e filtra i file in base ai risultati della scansione come segue:
I file con un risultato di
NO_THREATS_FOUNDscansione vengono inviati al bucketCleanBucketAmazon S3.I file con un risultato di
THREATS_FOUNDscansione vengono inviati al bucketMalwareBucketAmazon S3.I file con un risultato di
UNSUPPORTEDscansione vengono inviati al bucketErrorBucketAmazon S3.I file con un risultato di
ACCESS_DENIEDscansione vengono inviati al bucketErrorBucketAmazon S3.I file con un risultato di
FAILEDscansione vengono inviati al bucketErrorBucketAmazon S3.
Tutti i file sono crittografati con un. AWS KMS key
Se un file è stato inviato al bucket
MalwareBucketAmazon S3, la funzione Lambda avvia un argomento Amazon SNS. L'argomento Amazon SNS invia una notifica e-mail a un indirizzo e-mail che configuri.
Tools (Strumenti)
Servizi AWS
Amazon ti CloudWatch aiuta a monitorare i parametri delle tue AWS risorse e delle applicazioni su cui esegui AWS in tempo reale.
Amazon Cognito fornisce autenticazione, autorizzazione e gestione degli utenti per app Web e mobili.
Amazon EventBridge è un servizio di bus eventi senza server che ti aiuta a connettere le tue applicazioni con dati in tempo reale provenienti da una varietà di fonti. Ad esempio, AWS Lambda funzioni, endpoint di invocazione HTTP che utilizzano destinazioni API o bus di eventi in altro modo. Account AWS
Amazon GuardDuty è un servizio di monitoraggio continuo della sicurezza che analizza ed elabora i log per identificare attività impreviste e potenzialmente non autorizzate nel tuo ambiente. AWS
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) ti aiuta a creare e controllare chiavi crittografiche per proteggere i tuoi dati.
AWS Lambda è un servizio di calcolo che consente di eseguire il codice senza gestire i server o effettuarne il provisioning. Esegue il codice solo quando necessario e si ridimensiona automaticamente, quindi paghi solo per il tempo di elaborazione che utilizzi.
Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) ti aiuta a coordinare e gestire lo scambio di messaggi tra editori e clienti, inclusi server Web e indirizzi e-mail.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) è un servizio di archiviazione degli oggetti basato sul cloud che consente di archiviare, proteggere e recuperare qualsiasi quantità di dati.
AWS Transfer Familyti aiuta a trasferire file da e verso i servizi di AWS storage tramite i protocolli SFTP, FTPS o FTP.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) ti aiuta a lanciare AWS risorse in una rete virtuale che hai definito. Questa rete virtuale è simile a una comune rete da gestire all'interno del proprio data center, ma con i vantaggi dell'infrastruttura scalabile di AWS.
Repository di codice
Il codice di questo pattern è disponibile nel repository GitHub AWS Transfer Family and GuardDuty Malware Scanning Solution
Best practice
Il CloudFormation modello fornito è progettato per incorporare molte AWS best practice, come le autorizzazioni con privilegi minimi per i ruoli e le policy IAM, la crittografia a riposo e in transito e la rotazione automatica delle chiavi. Per gli ambienti di produzione, valuta la possibilità di implementare i seguenti consigli aggiuntivi:
Abilita l'autenticazione a più fattori per gli utenti di Amazon Cognito
Implementa AWS Shieldla protezione da denial of service (S) DDo distribuita
Configurazione AWS Configper il monitoraggio continuo della conformità
AWS CloudTrailImplementa per una registrazione completa delle API
Configura Amazon GuardDuty per il rilevamento delle minacce oltre alla scansione dei malware
Implementa AWS Security Hub CSPMper la gestione centralizzata della sicurezza
Utilizzalo Gestione dei segreti AWSper la gestione delle credenziali
Implementa il monitoraggio del traffico di rete con Traffic Mirroring
Configura Amazon Macie per il rilevamento e la protezione dei dati sensibili in Amazon S3
Implementa valutazioni di sicurezza e test di penetrazione regolari
Stabilisci un piano formale di risposta agli incidenti
Implementa l'applicazione di patch automatizzate per tutti i componenti
Conduci corsi di formazione periodici sulla sicurezza per gli amministratori
Configurazione AWS Organizationsper la gestione della sicurezza su più account
Epiche
| Operazione | Description | Competenze richieste |
|---|---|---|
Clonare il repository. | Immettete il seguente comando per clonare l'AWS Transfer Family archivio della soluzione di scansione GuardDuty antimalware
| Sviluppatore di app, ingegnere DevOps |
Crea lo CloudFormation stack. |
| Amministratore del cloud, ingegnere DevOps |
| Operazione | Description | Competenze richieste |
|---|---|---|
Attiva la protezione da malware. |
| Amministratore cloud, amministratore AWS |
Aggiungi utenti al pool di utenti. | Aggiungi uno o più utenti al pool di utenti di Amazon Cognito. Per istruzioni, consulta Gestire gli utenti nel tuo pool di utenti nella documentazione di Amazon Cognito. | Amministratore cloud, amministratore AWS |
| Operazione | Description | Competenze richieste |
|---|---|---|
Connect all'endpoint del server SFTP. |
| Sviluppatore di app, amministratore cloud, architetto cloud, DevOps ingegnere |
risoluzione dei problemi
| Problema | Soluzione |
|---|---|
L'autenticazione dell'utente non riesce |
Per un elenco di AWS CLI comandi che possono aiutarti a eseguire queste procedure di risoluzione dei problemi, vedi Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi nella sezione Informazioni aggiuntive. |
L'autenticazione SFTP non riesce |
Per un elenco di AWS CLI comandi che possono aiutarti a eseguire questi passaggi di risoluzione dei problemi, consulta Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi nella sezione Informazioni aggiuntive. |
Accesso al caricamento dei file negato |
Per un elenco di AWS CLI comandi che possono aiutarti a eseguire questi passaggi di risoluzione dei problemi, consulta Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi nella sezione Informazioni aggiuntive. |
Nessuna scansione antimalware |
Per un elenco di AWS CLI comandi che possono aiutarti a eseguire questi passaggi di risoluzione dei problemi, consulta Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi nella sezione Informazioni aggiuntive. |
Errori della funzione Lambda |
Per un elenco di AWS CLI comandi che possono aiutarti a eseguire queste procedure di risoluzione dei problemi, vedi Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi nella sezione Informazioni aggiuntive. |
Risorse correlate
App web Transfer Family (documentazione Transfer Family)
Informazioni aggiuntive
Comandi utili per la risoluzione dei problemi
Controlla lo stato di uno CloudFormation stack:
aws cloudformation describe-stacks \ --stack-name <STACK_NAME>
Elenca tutti gli utenti in un pool di utenti Amazon Cognito:
aws cognito-idp list-users \ --user-pool-id <USER_POOL_ID>
Visualizza i log per le funzioni Lambda:
aws logs describe-log-groups \ --log-group-name-prefix /aws/lambda/
Controlla lo stato di: GuardDuty
aws guardduty list-detectors
Controlla le regole del gruppo di sicurezza:
aws ec2 describe-security-groups \ --group-ids <SECURITY_GROUP_ID> \ --output table
Controlla lo stato del AWS Transfer Family server:
aws transfer describe-server \ --server-id <SERVER_ID>
Elenca tutti i file in un bucket Amazon S3:
aws s3 ls s3://<BUCKET_NAME>/ \ --recursive
Controlla lo stato di una EventBridge regola:
aws events describe-rule \ --name <RULE_NAME>