End of support notice: On October 7th, 2026, AWS will discontinue support for AWS IoT Greengrass Version 1. After October 7th, 2026, you will no longer be able to access the AWS IoT Greengrass V1 resources. For more information, please visit Migrate from AWS IoT Greengrass Version 1.
Test on-demand Lambda functions
An on-demand Lambda function is similar in functionality to a cloud-based AWS Lambda function. Multiple invocations of an on-demand Lambda function can run in parallel. An invocation of the Lambda function creates a separate container to process invocations or reuses an existing container, if resources permit. Any variables or preprocessing that are defined outside of the function handler are not retained when containers are created.
-
On the group configuration page, choose the Lambda functions tab.
-
Under My Lambda functions, choose the Greengrass_HelloWorld_Counter Lambda function.
-
On the Greengrass_HelloWorld_Counter details page, choose Edit.
-
For Pinned, choose False, and then choose Save.
-
On the group configuration page, choose Deploy.
-
After your deployment is complete, return to the AWS IoT console home page and choose Test.
-
Configure the following fields:
-
For Subscription topic, enter
hello/world/counter. -
For Quality of Service, choose 0.
-
For MQTT payload display, choose Display payloads as strings.

-
-
Choose Subscribe.
Note
You should not see any messages after you subscribe.
-
To test the on-demand lifecycle, invoke the function by publishing a message to the
hello/world/counter/triggertopic. You can use the default message.-
Choose Publish three times quickly, within five seconds of each press of the button.
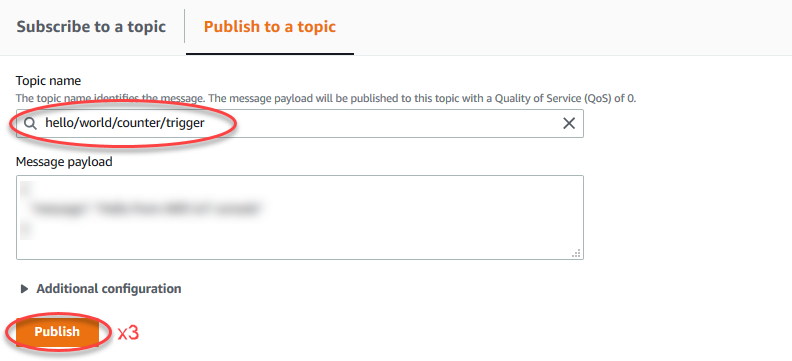
Each publish invokes the function handler and creates a container for each invocation. The invocation count is not incremented for the three times you triggered the function because each on-demand Lambda function has its own container/sandbox.

-
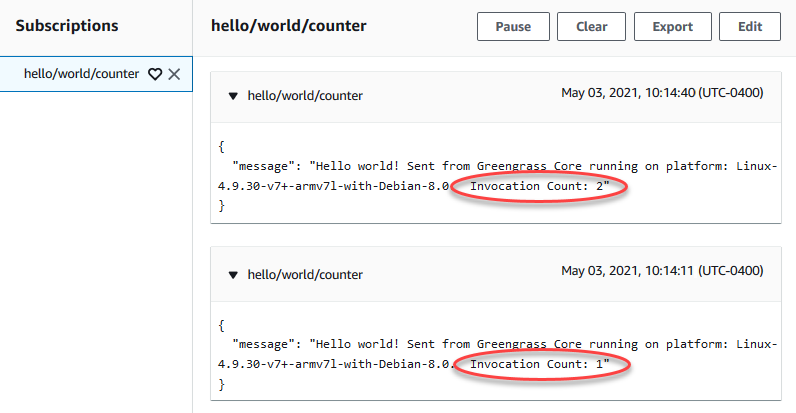
After approximately 30 seconds, choose Publish to topic. The invocation count should be incremented to 2. This shows that a container created from an earlier invocation is being reused, and that preprocessing variables outside of the function handler were stored.
-
You should now understand the two types of Lambda functions that can run on the AWS IoT Greengrass core. The next module, Module 4, shows you how local IoT devices can interact in an AWS IoT Greengrass group.