Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Bearbeiten Sie die Konfiguration des Identitätsanbieters
Sie können den Identitätsanbietertyp Ihres Servers von einem beliebigen Typ auf einen beliebigen anderen Typ ändern. Die verfügbaren Identitätsanbietertypen sind:
-
Dienst verwaltet — Benutzeranmeldeinformationen innerhalb des Dienstes speichern
-
AWS Directory Service — Verwenden Sie AWS Managed Microsoft AD oder AWS Directory Service für Entra ID Domain Services
-
Benutzerdefiniert — Verwenden Sie die Lambda-Funktion oder Amazon API Gateway zur Integration mit Ihrem bestehenden Identitätsanbieter
Wenn Sie die Typen von Identitätsanbietern ändern, müssen Sie je nach Umstellung spezifische Informationen angeben. In den folgenden Abschnitten werden die erforderlichen Informationen für jede Art von Änderung beschrieben.
Wichtig
Überlegungen beim Wechsel des Identitätsanbieters:
-
Benutzermigration — Beim Ändern der Identitätsanbietertypen werden bestehende Benutzerkonfigurationen nicht automatisch migriert. Sie müssen Benutzer im neuen Identitätsanbietersystem einrichten.
-
Testen — Testen Sie die neue Identitätsanbieter-Konfiguration gründlich, bevor Sie die Änderung in Produktionsumgebungen vornehmen.
-
Berechtigungen — Stellen Sie sicher, dass der neue Identitätsanbieter über die erforderlichen IAM-Berechtigungen und -Rollen verfügt, bevor Sie die Änderung vornehmen.
Umstellung auf einen vom Service verwalteten Identitätsanbieter
Wenn Sie von einem anderen Identitätsanbietertyp zu einem vom Service verwalteten Anbieter wechseln, müssen Sie:
-
Wählen Sie als Identitätsanbietertyp „Service managed“ aus
-
Erstellen Sie neue Benutzer direkt AWS Transfer Family nach Abschluss der Änderung, da vorhandene Benutzerkonfigurationen von anderen Identitätsanbietern nicht übertragen werden
Beispiel: Wenn Sie von einem benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter zu einem vom Dienst verwalteten Identitätsanbieter wechseln, müssen Sie alle Benutzerkonten und die zugehörigen Berechtigungen innerhalb des AWS Transfer Family Dienstes neu erstellen.
Wechsel zum AWS Directory Service
Wenn Sie von einem anderen Identitätsanbietertyp zu AWS Directory Service wechseln, müssen Sie Folgendes angeben:
-
Verzeichnis — Wählen Sie ein vorhandenes AWS Managed Microsoft AD- oder AWS Directory Service for Entra ID Domain Services-Verzeichnis aus
-
Zugriff — Wählen Sie aus, ob der Zugriff auf eine bestimmte Gruppe beschränkt oder allen Benutzern im Verzeichnis der Zugriff gewährt werden soll
-
Zugriffsrolle — Eine IAM-Rolle, die AWS Transfer Family den Zugriff auf Ihr Verzeichnis ermöglicht
Beispiel: Wenn Sie von service-managed zu AWS Directory Service wechseln, würden Sie Ihr vorhandenes d-1234567890 Verzeichnis auswählen, den Zugriff auf die TransferUsers Gruppe einschränken und die TransferDirectoryAccessRole IAM-Rolle angeben.
Zum benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter wechseln
Wenn Sie von einem anderen Identitätsanbietertyp zu einem benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter wechseln, müssen Sie zwischen Lambda-Funktion oder Amazon API Gateway wählen und die erforderliche Konfiguration angeben:
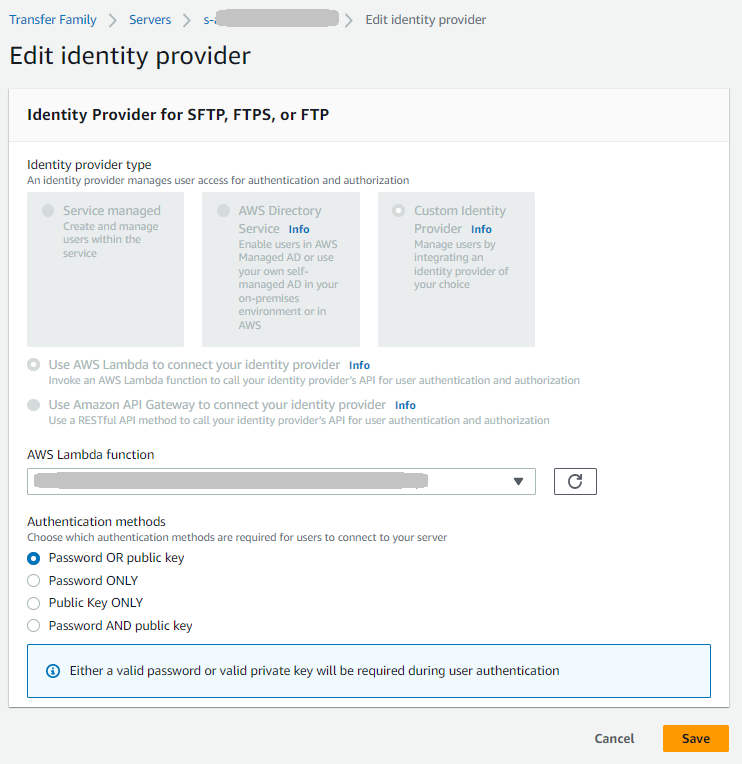
Lambda-Funktion verwenden
Geben Sie für die Lambda-Funktionsintegration Folgendes an:
-
Funktion — Wählen Sie eine vorhandene Lambda-Funktion aus, die die Authentifizierung abwickelt
-
Authentifizierungsmethode (für das SFTP-Protokoll) — Wählen Sie ein Passwort, einen öffentlichen Schlüssel oder beides
Beispiel: Wenn Sie von AWS Directory Service zu einem benutzerdefinierten Lambda-Identitätsanbieter wechseln, würden Sie Ihre TransferCustomAuth Funktion auswählen und Password als Authentifizierungsmethode wählen.
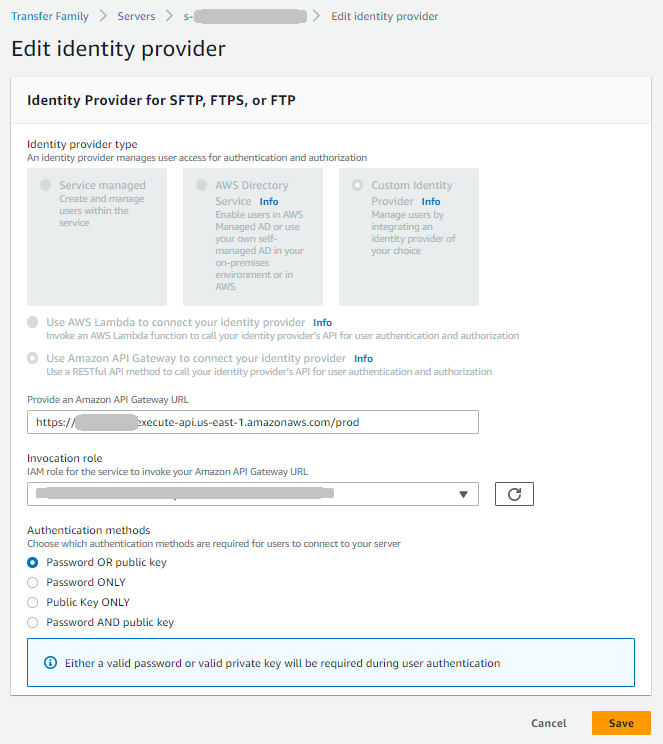
Amazon API Gateway verwenden
Geben Sie für die Amazon API Gateway Gateway-Integration Folgendes an:
-
API-Gateway-URL — Die Aufruf-URL Ihres API-Gateway-Endpunkts
-
Aufruf-Rolle — Eine IAM-Rolle, mit der AWS Transfer Family Sie Ihr API Gateway aufrufen können
-
Authentifizierungsmethode (für das SFTP-Protokoll) — Wählen Sie ein Passwort, einen öffentlichen Schlüssel oder beides
Beispiel: Wenn Sie von service-managed zu API Gateway wechseln, geben Sie die URL anhttps://abcdef123.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod, geben die TransferApiGatewayInvocationRole IAM-Rolle an und wählen Public Key als Authentifizierungsmethode.
Wechsel von Amazon API Gateway zur Lambda-Funktion
Ein gängiger Übergang ist der Wechsel von Amazon API Gateway zur Lambda-Funktion für die Integration benutzerdefinierter Identitätsanbieter. Diese Änderung ermöglicht es Ihnen, Ihre Architektur zu vereinfachen und gleichzeitig dieselbe Authentifizierungslogik beizubehalten.
Die wichtigsten Überlegungen zu diesem Übergang:
-
Gleiche Funktion, unterschiedliche Berechtigungen — Sie können dieselbe Lambda-Funktion sowohl für API Gateway als auch für die direkte Lambda-Integration verwenden, aber die Ressourcenrichtlinie muss aktualisiert werden.
-
Anforderungen an die Ressourcenrichtlinie — Beim Wechsel zur direkten Lambda-Integration muss die Ressourcenrichtlinie der Funktion zusätzlich zu die
transfer.amazonaws.com.rproxy.govskope.caBerechtigung zum Aufrufen der Funktion gewähren.apigateway.amazonaws.com
Um diese Änderung vorzunehmen
-
Aktualisieren Sie die Ressourcenrichtlinie Ihrer Lambda-Funktion, damit
transfer.amazonaws.com.rproxy.govskope.cadie Funktion aufgerufen werden kann. -
Ändern Sie in der AWS Transfer Family Konsole den Identitätsanbieter von API Gateway zu Lambda-Funktion.
-
Wählen Sie Ihre bestehende Lambda-Funktion aus.
-
Testen Sie die Konfiguration, um sicherzustellen, dass die Authentifizierung korrekt funktioniert.
Beispiel für eine Ressourcenrichtlinie für die direkte Lambda-Integration:
-
{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement": [{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": [ "transfer.amazonaws.com", "apigateway.amazonaws.com" ] }, "Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction", "Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:function-name" }] }
Benutzererhaltung bei Übergängen zum Identitätsanbieter
Beim Wechsel zwischen Identitätsanbietertypen werden bestehende Benutzerkonfigurationen in bestimmten Szenarien beibehalten, um bei Problemen ein effizientes Rollback zu ermöglichen:
-
Vom Dienst verwalteter zum benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter und zurück — Wenn Sie von einem vom Dienst verwalteten zu einem benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter und dann zurück zu einem vom Dienst verwalteten Identitätsanbieter wechseln, bleiben alle Benutzer in ihrer letzten bekannten Konfiguration erhalten.
-
AWS Directory Service zu einem benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter und zurück — Wenn Sie von AWS Directory Service einem benutzerdefinierten Identitätsanbieter und dann zurück zu wechseln AWS Directory Service, werden alle Definitionen für Gruppen mit delegiertem Zugriff in ihrer letzten bekannten Konfiguration beibehalten.
Dieses Beibehaltungsverhalten ermöglicht es Ihnen, benutzerdefinierte Identitätsanbieter-Konfigurationen sicher zu testen und zu Ihrer vorherigen Konfiguration zurückzukehren, ohne die Benutzerzugriffskonfigurationen zu verlieren.
Wichtige Überlegungen beim Wechsel des Identitätsanbieters
-
Benutzermigration — Beim Ändern der Identitätsanbietertypen werden bestehende Benutzerkonfigurationen nicht automatisch migriert. Sie müssen Benutzer im neuen Identitätsanbietersystem einrichten.
-
Testen — Testen Sie die neue Identitätsanbieter-Konfiguration gründlich, bevor Sie die Änderung in Produktionsumgebungen vornehmen.
-
Berechtigungen — Stellen Sie sicher, dass der neue Identitätsanbieter über die erforderlichen IAM-Berechtigungen und -Rollen verfügt, bevor Sie die Änderung vornehmen.