Create a hierarchical, multi-Region IPAM architecture on AWS by using Terraform
Donny Schreiber, Amazon Web Services
Summary
IP address management (IPAM) is a critical component of network management, and it becomes increasingly complex as organizations scale their cloud infrastructure. Without proper IPAM, organizations risk IP address conflicts, wasted address space, and complex troubleshooting that can lead to outages and application downtime. This pattern demonstrates how to implement a comprehensive IPAM solution for AWS enterprise environments by using HashiCorp Terraform. It helps organizations to create a hierarchical, multi-Region IPAM architecture that facilitates centralized IP address management across all AWS accounts in an AWS organization.
This pattern helps you implement Amazon VPC IP Address Manager with a sophisticated four-tier pool hierarchy: top-level pool, Regional pools, business unit pools, and environment-specific pools. This structure supports proper IP address governance while enabling delegation of IP management to appropriate teams within the organization. The solution uses AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) to seamlessly share IP Address Manager pools across the organization. AWS RAM centralizes and standardizes IPAM specifications, which teams can build upon across all managed accounts.
This pattern can help you achieve the following:
Automate IP address allocation across AWS Regions, business units, and environments.
Enforce organizational network policies through programmatic validation.
Scale network infrastructure efficiently as business requirements evolve.
Reduce operational overhead through centralized management of IP address spaces.
Accelerate cloud-native workload deployments with self-service CIDR range allocation.
Prevent address conflicts through policy-based controls and validation.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
One or more AWS accounts, managed as an organization in AWS Organizations.
A network hub or network management account that will serve as the IP Address Manager delegated administrator.
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), installed and configured.
Terraform version 1.5.0 or later, installed
. AWS Provider for Terraform, configured
. Permissions to manage IP Address Manager, AWS RAM, and virtual private clouds (VPCs), configured in AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Limitations
IP Address Manager is subject to service quotas. The default service quota for pools is 50 per scope. Running this deployment for 6 Regions, 2 business units, and 4 environments would create 67 pools. Therefore, a quota increase might be necessary.
Modifying or deleting IP Address Manager pools after resources have been allocated can cause dependency issues. You must release the allocation before you can delete the pool.
In IP Address Manager, resource monitoring can experience a slight delay in reflecting resource changes. This delay can be approximately 20 minutes.
IP Address Manager cannot automatically enforce IP address uniqueness across different scopes.
Custom tags must adhere to AWS tagging best practices. For example, each key must be unique and cannot begin with
aws:.There are considerations and limitations when integrating IP Address Manager with accounts outside of your organization.
Architecture
Target architecture
IP Address Manager configuration and pool hierarchy
The following diagram shows the logical constructs of the target architecture. A scope is the highest-level container in IP Address Manager. Each scope represents the IP address space for a single network. The pools are collections of contiguous IP address ranges (or CIDR ranges) within the scope. Pools help you organize your IP addresses according to your routing and security needs. This diagram shows four hierarchical levels of pools: a top-level pool, Regional pools, business unit pools, and environment pools.
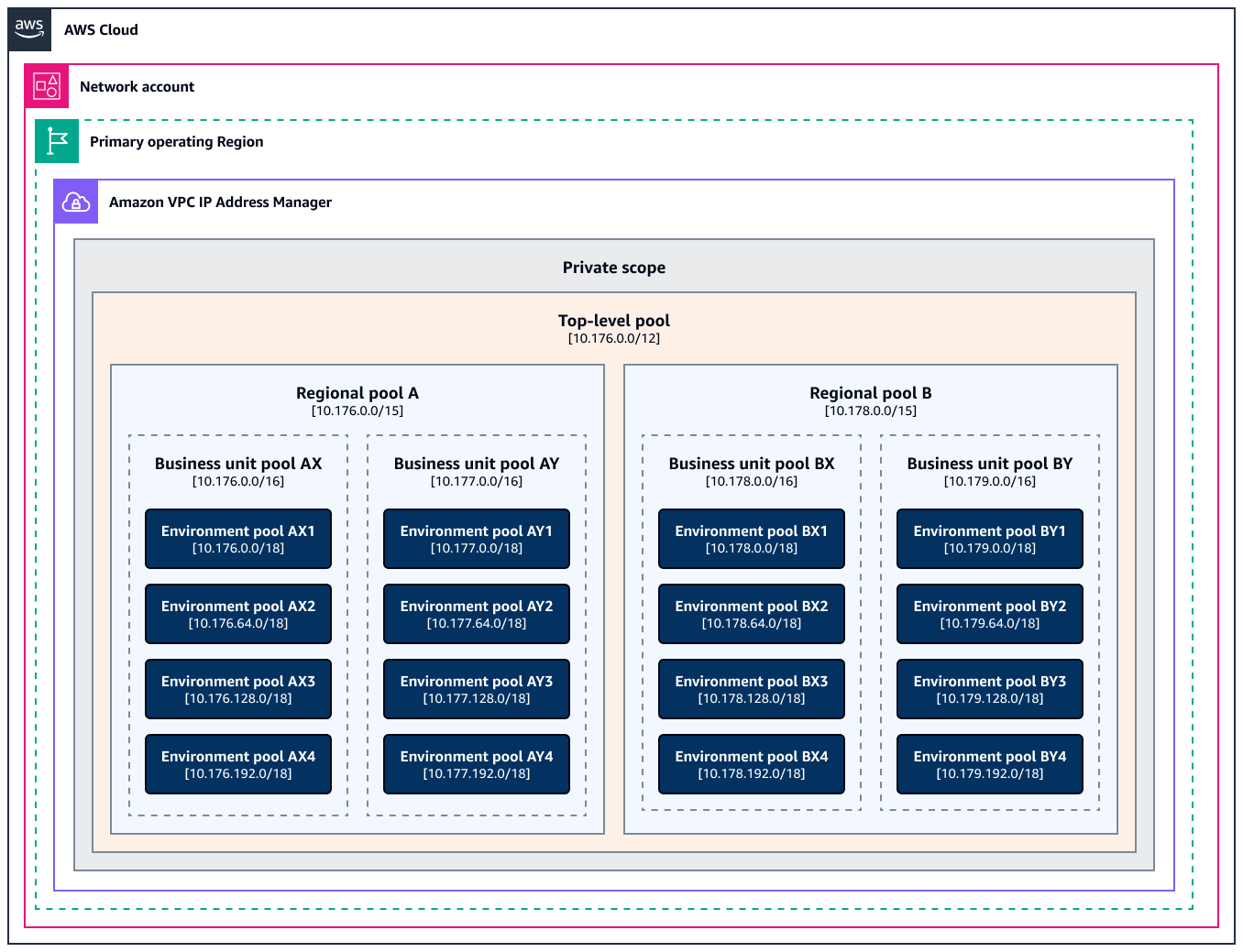
This solution establishes a clear hierarchy of IP Address Manager pools:
The top-level pool encompasses the entire organizational IP address space, such as
10.176.0.0/12.The Regional pools are for Region-specific allocations, such as
10.176.0.0/15forus-east-1.The business unit pools are domain-specific allocations within each AWS Region. For example, the finance business unit in the
us-east-1Region might have10.176.0.0/16.The environment pools are purpose-specific allocations for different environments. For example, the finance business unit in the
us-east-1Region might have10.176.0.0/18for a production environment.
This deployment topology distributes IP Address Manager resources geographically while maintaining centralized control. The following are its features:
IP Address Manager is deployed in a single primary AWS Region.
Additional Regions are registered as operating regions, where IP Address Manager can manage resources.
Each operating region receives a dedicated address pool from the top-level pool.
Resources in all operating regions are centrally managed through IP Address Manager in the primary Region.
Each Regional pool has a locale property tied to its Region to help you properly allocate resources.
Advanced CIDR range validation
This solution is designed to prevent deployment of invalid configurations. When you deploy the pools through Terraform, the following are validated during the Terraform plan phase:
Validates that all environment CIDR ranges are contained within their parent business unit CIDR ranges
Confirms that all business unit CIDR ranges are contained within their parent regional CIDR ranges
Verifies that all Regional CIDR ranges are contained within the top-level CIDR ranges
Checks for overlapping CIDR ranges within the same hierarchy level
Validates proper mapping of environments to their respective business units
CIDR range allocation
The following diagram shows an example of how developers or administrators can create new VPCs and allocate IP addresses from the pool levels.

The diagram shows the following workflow:
Through the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or through infrastructure as code (IaC), a developer or administrator requests the next available CIDR range in the
AY3environment pool.IP Address Manager allocates the next available CIDR range in that pool to the
AY3-4VPC. This CIDR range can no longer be used.
Automation and scale
This solution is designed for scalability as follows:
Regional expansion – Add new Regions by extending the Terraform configuration with additional Regional pool entries.
Business unit growth – Support new business units by adding them to the BU configuration map.
Environment flexibility – Configure different environment types, such as development or production, based on organizational needs.
Multi-account support – Share pools across all accounts in your organization through AWS RAM.
Automated VPC provisioning – Integrate with VPC provisioning workflows to automate CIDR range allocation.
The hierarchical structure also allows for different scales of delegation and control, such as the following:
Network administrators might manage the top-level and Regional pools.
Business unit IT teams might have delegated control of their respective pools.
Application teams might consume IP addresses from their designated environment pools.
Note
You can also integrate this solution with AWS Control Tower Account Factory for Terraform (AFT). For more information, see Integration with AFT in the Additional information section of this pattern.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon CloudWatch helps you monitor the metrics of your AWS resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time.
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) is an open source tool that helps you interact with AWS services through commands in your command-line shell.
AWS Organizations is an account management service that helps you consolidate multiple AWS accounts into an organization that you create and centrally manage.
AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) helps you securely share your resources across AWS accounts to reduce operational overhead and provide visibility and auditability.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) helps you launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS. IP Address Manager is a feature of Amazon VPC. It helps you plan, track, and monitor IP addresses for your AWS workloads.
Other tools
HashiCorp Terraform
is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that helps you use code to provision and manage cloud infrastructure and resources.
Code repository
The code for this pattern is available in the Sample Terraform Implementation for Hierarchical IPAM on AWS
Root module – Deployment orchestration and input variables.
IPAM module – Core implementation of the architecture described in this pattern.
Tags module – Standardized tagging for all resources.
Best practices
Consider the following best practices for network planning:
Plan first – Thoroughly plan your IP address space before deployment. For more information, see Plan for IP address provisioning.
Avoid overlapping CIDR ranges – Make sure that CIDR ranges at each level do not overlap.
Reserve buffer space – Always allocate larger CIDR ranges than immediately needed to accommodate growth.
Document IP address allocation – Maintain documentation of your IP address allocation strategy.
Consider the following deployment best practices:
Start with non-production – Deploy in non-production environments first.
Use Terraform state management – Implement remote state storage and locking. For more information, see State storage and locking
in the Terraform documentation. Implement version control – Version control all Terraform code.
Implement CI/CD integration – Use continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines for repeatable deployments.
Consider the following operational best practices:
Enable auto-import – Configure an IP Address Manager pool to automatically discover and import existing resources. Follow the instructions in Edit an IPAM pool to turn on auto-import.
Monitor IP address utilization – Set up alarms for IP address utilization thresholds. For more information, see Monitor IPAM with Amazon CloudWatch.
Audit regularly – Periodically audit IP address usage and compliance. For more information, see Tracking IP address usage in IPAM.
Clean up unused allocations – Release IP address allocations when resources are decommissioned. For more information, see Deprovision CIDRs from a pool.
Consider the following security best practices:
Implement least privilege – Use IAM roles with the minimum required permissions. For more information, see Security best practices in IAM and Identity and access management in IPAM.
Use service control policies – Implement service control policies (SCPs) to enforce IP Address Manager usage in your organization. For more information, see Enforce IPAM use for VPC creation with SCPs.
Control resource sharing – Carefully manage the scope of IP Address Manager resource sharing in AWS RAM. For more information, see Share an IPAM pool using AWS RAM.
Enforce tagging – Implement mandatory tagging for all resources related to IP Address Manager. For more information, see Tagging strategy in the Additional information section.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Enable AWS Organizations features. | Make sure that AWS Organizations has all features enabled. For instructions, see Enabling all features for an organization with AWS Organizations in the AWS Organizations documentation. | AWS administrator |
Enable resource sharing in AWS RAM. | Using the AWS CLI, enter the following command to enable AWS RAM resource sharing for your organization:
For more information, see Enable resource sharing within AWS Organizations in the AWS RAM documentation. | AWS administrator |
Designate an administrator for IP Address Manager. | From the organization’s management account, using the AWS CLI, enter the following command, where
NoteTypically, a network or network hub account is used as the delegated administrator for IP Address Manager. For more information, see Integrate IPAM with accounts in an AWS Organization in the IP Address Manager documentation. | AWS administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Define the network architecture. | Define and document your network architecture, including the CIDR ranges for Regions, business units, and environments. For more information, see Plan for IP address provisioning in the IP Address Manager documentation. | Network engineer |
Clone the repository. |
| DevOps engineer |
Configure the variables. |
| Network engineer, Terraform |
Deploy the IP Address Manager resources. |
| Terraform |
Validate the deployment. |
| General AWS, Network engineer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create a VPC. | Follow the steps in Create a VPC in the Amazon VPC documentation. When you reach the step to choose a CIDR range for the VPC, allocate the next available from one of your Regional, business unit, and environment pools. | General AWS, Network administrator, Network engineer |
Validate the CIDR range allocation. |
| General AWS, Network administrator, Network engineer |
Monitor IP Address Manager. | Configure monitoring and alarms related to the allocation of IP Address Manager resources. For more information and instructions, see Monitor IPAM with Amazon CloudWatch and Monitor CIDR usage by resource in the IP Address Manager documentation. | General AWS |
Enforce use of IP Address Manager. | Create a service control policy (SCP) in AWS Organizations that requires members in your organization to use IP Address Manager when they create a VPC. For instructions, see Enforce IPAM use for VPC creation with SCPs in the IP Address Manager documentation. | General AWS, AWS administrator |
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
Terraform fails with IP Address Manager resource not found | Make sure that the IP Address Manager administrator account is properly delegated and that your AWS Provider is authenticated to that account. |
CIDR range allocation fails | Check that the requested CIDR range fits within the available range of the IP Address Manager pool and doesn't overlap with existing allocations. |
AWS RAM sharing issues | Verify that resource sharing is enabled for your AWS Organization. Verify that the correct principal, the organization Amazon Resource Name (ARN), is used in the AWS RAM share. |
Pool hierarchy validation errors | Make sure that the child pool CIDR ranges are properly contained within their parent pool CIDR ranges and don't overlap with sibling pools. |
IP Address Manager quota limit exceeded | Request a quota increase for IP Address Manager pools. For more information, see Requesting a quota increase in the Service Quotas User Guide. |
Related resources
AWS service documentation
AWS blog posts
Videos and tutorials
Additional information
Integration with AFT
You can integrate this solution with AWS Control Tower Account Factory for Terraform (AFT) to make sure that newly provisioned accounts automatically receive proper network configurations. By deploying this IPAM solution in your network hub account, new accounts created through AFT can reference the shared IP Address Manager pools when you create VPCs.
The following code sample demonstrates AFT integration in an account customization by using AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store:
# Get the IP Address Manager pool ID from Parameter Store data "aws_ssm_parameter" "dev_ipam_pool_id" { name = "/org/network/ipam/finance/dev/pool-id" } # Create a VPC using the IP Address Manager pool resource "aws_vpc" "this" { ipv4_ipam_pool_id = data.aws_ssm_parameter.dev_ipam_pool_id.value ipv4_netmask_length = 24 tags = { Name = "aft-account-vpc" } }
Tagging strategy
The solution implements a comprehensive tagging strategy to facilitate resource management. The following code sample demonstrates how it is used:
# Example tag configuration module "tags" { source = "./modules/tags" # Required tags product_name = "enterprise-network" feature_name = "ipam" org_id = "finance" business_unit = "network-operations" owner = "network-team" environment = "prod" repo = "https://github.com/myorg/ipam-terraform" branch = "main" cost_center = "123456" dr_tier = "tier1" # Optional tags optional_tags = { "project" = "network-modernization" "stack_role" = "infrastructure" } }
These tags are automatically applied to all IP Address Manager resources. This facilitates consistent governance, cost allocation, and resource management.