Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Temporäre IAM-Delegation
-Übersicht
Die vorübergehende Delegierung beschleunigt das Onboarding und vereinfacht die Verwaltung von Produkten von Amazon und AWS Partnern, die in Ihre AWS Konten integriert werden können. Anstatt mehrere AWS Dienste manuell zu konfigurieren, können Sie temporäre, eingeschränkte Berechtigungen delegieren, sodass der Produktanbieter Einrichtungsaufgaben in Ihrem Namen innerhalb von Minuten mithilfe automatisierter Bereitstellungsworkflows erledigen kann. Sie behalten die administrative Kontrolle in Bezug auf Genehmigungsanforderungen und Berechtigungsgrenzen, während die Berechtigungen von Produktanbietern nach Ablauf der genehmigten Dauer automatisch ablaufen, ohne dass eine manuelle Bereinigung erforderlich ist. Wenn das Produkt für den laufenden Betrieb dauerhaften Zugriff benötigt, kann der Anbieter mithilfe einer temporären Delegierung eine IAM-Rolle mit einer Berechtigungsgrenze erstellen, die die maximalen Berechtigungen der Rolle festlegt. Alle Aktivitäten der Produktanbieter werden AWS CloudTrail zur Einhaltung von Vorschriften und zur Sicherheitsüberwachung nachverfolgt.
Anmerkung
Temporäre Delegierungsanfragen können nur von Amazon-Produkten und qualifizierten AWS Partnern erstellt werden, die den Onboarding-Prozess für Funktionen abgeschlossen haben. Kunden überprüfen und genehmigen diese Anfragen, können sie jedoch nicht direkt erstellen. Wenn Sie ein AWS Partner sind, der die temporäre IAM-Delegierung in Ihr Produkt integrieren möchte, finden Sie Anweisungen zur Einführung und Integration im Partnerintegrationsleitfaden.
So funktioniert die temporäre Delegierung
Die vorübergehende Delegierung ermöglicht es Amazon und AWS Partnern, temporären, eingeschränkten Zugriff auf Ihr Konto zu beantragen. Nach Ihrer Zustimmung können sie delegierte Berechtigungen verwenden, um in Ihrem Namen Maßnahmen zu ergreifen. Delegierungsanfragen definieren spezifische Berechtigungen für AWS Dienste und Aktionen, die der Produktanbieter benötigt, um Ressourcen in Ihrem AWS Konto bereitzustellen oder zu konfigurieren. Diese Berechtigungen sind nur für eine begrenzte Zeit verfügbar und laufen automatisch nach der in der Anfrage angegebenen Dauer ab.
Anmerkung
Die maximale Dauer für delegierten Zugriff beträgt 12 Stunden. Root-Benutzer können jedoch nur Delegierungsanfragen mit einer Dauer von 4 Stunden oder weniger genehmigen. Wenn in einer Anfrage mehr als 4 Stunden angegeben sind, müssen Sie für die Genehmigung der Anfrage eine Identität verwenden, die kein Root-Benutzer ist. Einzelheiten finden Sie unter Betafunktion zur Simulation von Genehmigungen.
Für laufende Aufgaben, wie das Lesen aus einem Amazon S3 S3-Bucket, können Delegierungsanfragen die Erstellung einer IAM-Rolle beinhalten, die den kontinuierlichen Zugriff auf Ressourcen und Aktionen nach Ablauf des temporären Zugriffs ermöglicht. Produktanbieter müssen jeder IAM-Rolle, die durch temporäre Delegierung erstellt wurde, eine Berechtigungsgrenze zuweisen. Berechtigungsgrenzen beschränken die maximalen Berechtigungen einer Rolle, gewähren jedoch keine eigenständigen Berechtigungen. Sie können die Berechtigungsgrenze im Rahmen der Anfrage überprüfen, bevor Sie sie genehmigen. Einzelheiten finden Sie unter Grenzen der Berechtigungen.
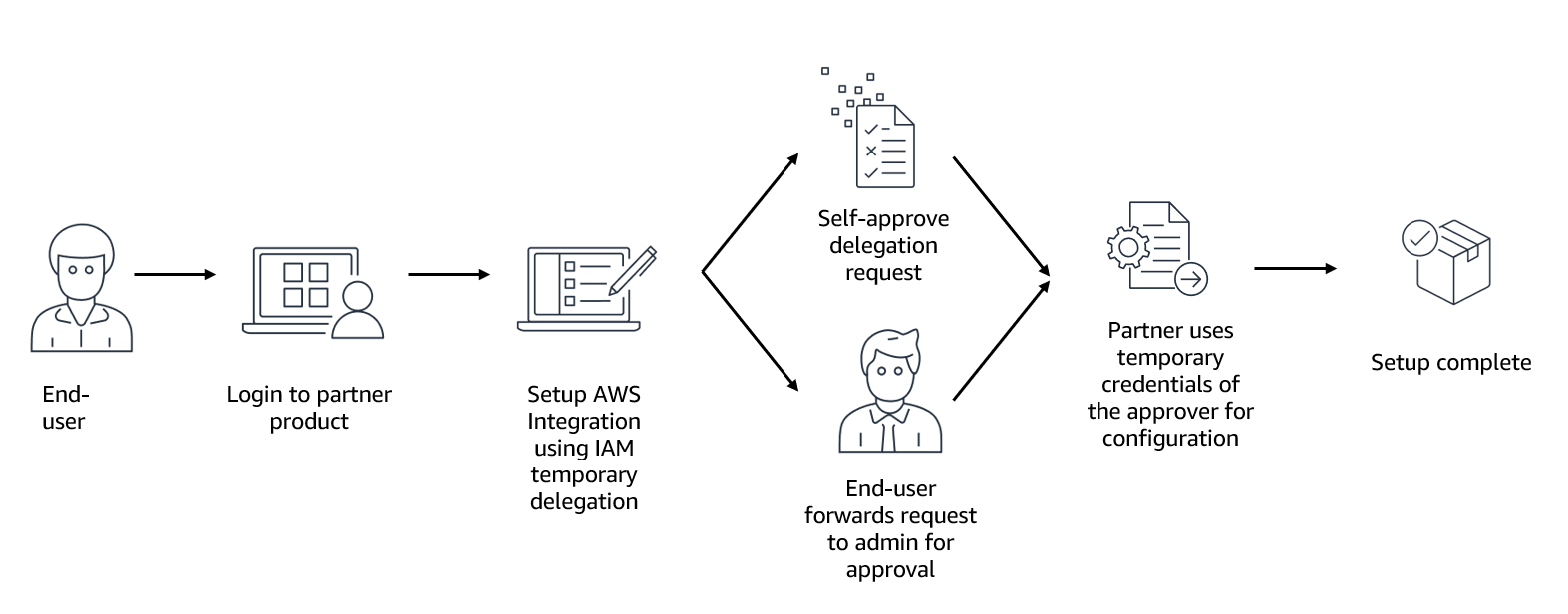
Das Verfahren funktioniert folgendermaßen:
Sie melden sich bei einem Amazon- oder AWS Partnerprodukt an, um es in Ihre AWS Umgebung zu integrieren.
Der Produktanbieter initiiert in Ihrem Namen eine Delegierungsanfrage und leitet Sie zur AWS Management Console weiter.
Sie überprüfen die angeforderten Berechtigungen und entscheiden, ob Sie die Anfrage genehmigen, ablehnen oder an Ihren Administrator weiterleiten möchten.
Sobald Sie oder Ihr Administrator die Anfrage genehmigt haben, kann der Produktanbieter die temporären Anmeldeinformationen des Genehmigers abrufen, um die erforderlichen Aufgaben auszuführen.
Der Zugriff auf den Produktanbieter läuft nach dem angegebenen Zeitraum automatisch ab. Jede IAM-Rolle, die durch die temporäre Delegierungsanfrage erstellt wurde, bleibt jedoch über diesen Zeitraum hinaus bestehen, sodass der Produktanbieter weiterhin auf Ressourcen und Aktionen für laufende Verwaltungsaufgaben zugreifen kann.
Anmerkung
Sie können Berechtigungen nur dann an einen Produktanbieter delegieren, wenn Sie über Berechtigungen für die Dienste und Aktionen verfügen, die in der temporären Delegierungsanfrage enthalten sind. Wenn Sie keinen Zugriff auf die angeforderten Dienste und Aktionen haben, erhält der Produktanbieter diese Berechtigungen nicht, wenn Sie die Anfrage genehmigen.
Wenn die Berechtigungsprüfung zeigt, dass sie wahrscheinlich erfolgreich sein wird, können Sie die temporäre Delegierungsanfrage genehmigen und mit dem Workflow fortfahren.
Wenn die Berechtigungsprüfung ergibt, dass Sie möglicherweise nicht über ausreichende Berechtigungen verfügen, leiten Sie die Anfrage zur Genehmigung an Ihren Administrator weiter. Wir empfehlen, Ihren Administrator mithilfe der von Ihnen bevorzugten Methode, z. B. per E-Mail oder Ticket, über diese Anfrage zu informieren.
Sobald Ihr Administrator die Anfrage genehmigt hat, hängt das weitere Vorgehen von der Konfiguration des Produktanbieters ab:
Wenn der Produktanbieter sofortigen Zugriff angefordert hat, erhält er automatisch temporäre Berechtigungen, und die Zugriffsdauer beginnt.
Wenn der Produktanbieter die Freigabe durch den Eigentümer (ursprünglichen Empfänger) angefordert hat, müssen Sie zu der Anfrage zurückkehren, um den temporären Kontozugriff explizit freizugeben, bevor die Zugriffsdauer beginnt. Produktanbieter verwenden diese Option in der Regel, wenn sie zusätzliche Eingaben von Ihnen benötigen, z. B. Informationen zur Ressourcenauswahl oder zur Konfiguration, um die erforderliche Aufgabe abzuschließen.
Verwaltung von Berechtigungen für Delegierungsanfragen
Administratoren können IAM-Prinzipalen Berechtigungen zur Verwaltung von Delegierungsanfragen von Produktanbietern gewähren. Dies ist nützlich, wenn Sie Genehmigungsberechtigungen an bestimmte Benutzer oder Teams in Ihrer Organisation delegieren möchten oder wenn Sie kontrollieren möchten, wer bestimmte Aktionen bei Delegierungsanfragen ausführen kann.
Die folgenden IAM-Berechtigungen sind für die Verwaltung von Delegierungsanfragen verfügbar:
| Berechtigung | Description |
|---|---|
| iam: AssociateDelegationRequest | Ordnen Sie Ihrem Konto eine nicht zugewiesene Delegierungsanfrage zu AWS |
| ich bin: GetDelegationRequest | Details einer Delegierungsanfrage anzeigen |
| Ich bin: UpdateDelegationRequest | Leiten Sie eine Delegierungsanfrage zur Genehmigung an einen Administrator weiter |
| Ich bin: AcceptDelegationRequest | Genehmigen Sie eine Delegierungsanfrage |
| ich bin: SendDelegationToken | Geben Sie das Exchange-Token nach der Genehmigung an den Produktanbieter weiter |
| Ich bin: RejectDelegationRequest | Eine Delegierungsanfrage ablehnen |
| ich bin: ListDelegationRequests | Listen Sie Delegierungsanfragen für Ihr Konto auf |
Anmerkung
Standardmäßig erhalten IAM-Principals, die eine Delegierungsanfrage initiieren, automatisch Berechtigungen zur Verwaltung dieser speziellen Anfrage. Sie können sie ihrem Konto zuordnen, Anforderungsdetails einsehen, eine Anfrage ablehnen, sie zur Genehmigung an einen Administrator weiterleiten, das Exchange-Token nach Genehmigung durch den Administrator an den Produktanbieter weitergeben und Delegierungsanfragen auflisten, deren Eigentümer sie sind.