Primary backups to logically air-gapped vaults
Overview
The logically air-gapped vault primary backup feature offers you the option to specify a logically air-gapped vault as a primary backup destination within the same account, for both scheduled and on-demand backup jobs. This eliminates the need to maintain separate copies in both a standard backup vault and a logically air-gapped vault, reducing costs and simplifying workflows while preserving the security benefits of logical air-gapping.
You can assign a logically air-gapped vault as the primary target in backup plans, organization-wide policies, or on-demand backups. Previously, to back up to a logically air-gapped vault, you first had to create a backup in a backup vault and then copy it to a logically air-gapped vault. With this feature, depending on the resource type, AWS Backup can create backups directly in your logically air-gapped vault or automatically manage temporary backups that are copied to your logically air-gapped vault and then deleted.
The behavior depends on two factors:
-
Whether the resource type is supported by logically air-gapped vault.
-
Whether the resource type supports full AWS Backup management.
Warning
We recommend integrating your logically air-gapped vaults with Multi-party approval (MPA) if you adopt this capability. This enables recovery of backups in the vault even if the vault-owning account is inaccessible.
There is no new pricing for this feature. You are only charged for backups stored in logically air-gapped vaults and for temporary snapshots (during their retention period in the system)
for applicable resources at prevailing rates. See AWS Backup pricing
Topics
How it works
You can onboard to this feature by updating your existing backup plan or creating a new one and adding a logically air-gapped vault ARN (field name: TargetLogicallyAirGappedBackupVaultArn)
as a primary backup target. You can perform this operation either through the AWS Backup console or through AWS Backup CLI commands.
"TargetLogicallyAirGappedBackupVaultArn": "arn:aws:backup:us-east-1:123456789012:backup-vault:AirGappedVault",
When you specify both a backup vault and a logically air-gapped vault as targets for your backup jobs, AWS Backup determines the appropriate workflow based on the resource type and encryption configuration.
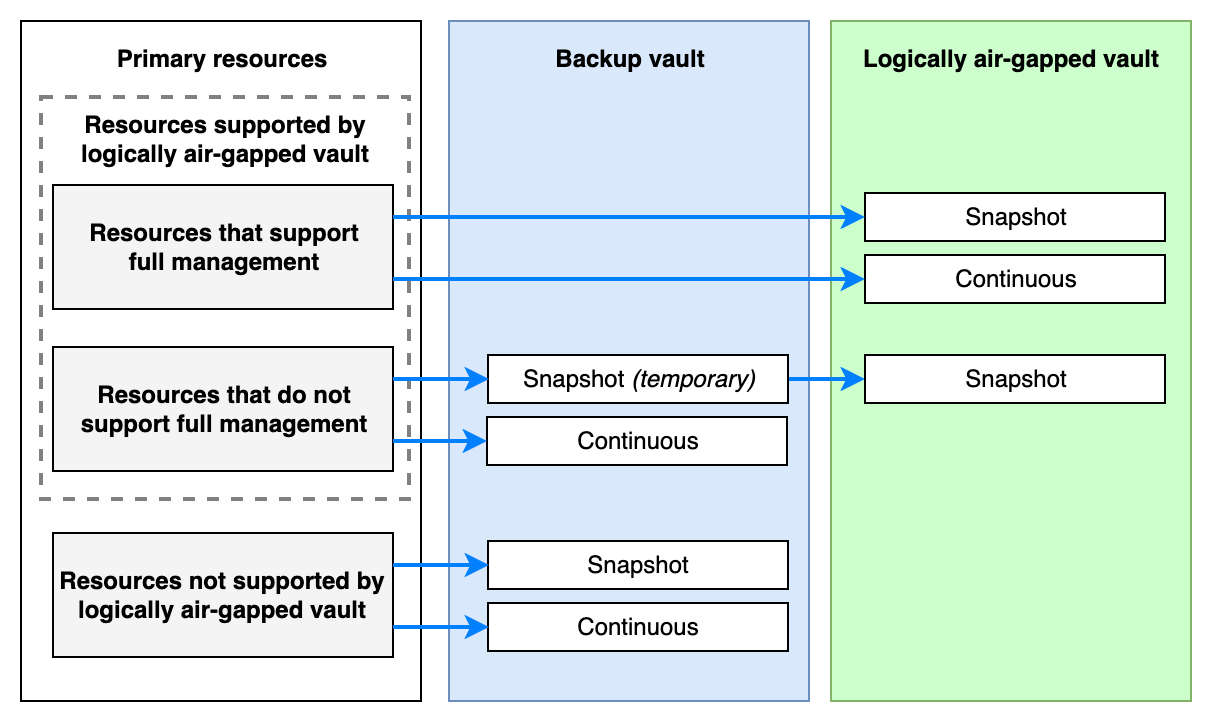
Supported resources for primary backup to logically air-gapped vaults
To view the full list of supported resources for logically air-gapped vaults, see AWS Backup feature availability. All resources that support logically air-gapped vaults follow the principle of maintaining only one copy of your backup, rather than storing two separate copies, when this feature is used.
Warning
Resources not currently supported for this feature may have their support enabled in the future. When that occurs, your newly supported resource will automatically start backing up in the logically air-gapped vault using the workflow shown above.
Considerations and limitations:
-
Same account and Region only – Your logically air-gapped vault must be in the same AWS account and Region as your resources to use this feature. You cannot create backups directly cross-account or cross-Region. We recommend backing up to a logically air-gapped vault in the same Region to enable faster recovery without requiring a copy. If you require a copy of your data in a second Region for Disaster Recovery (DR), we recommend either cross-Region replication of your primary resources for quick failover or cross-Region recovery point copies to a locked backup vault.
-
Constraints with using AWS managed keys – Resources not supporting full AWS Backup management and encrypted with AWS managed keys (for example,
aws/ebs,aws/rds) cannot be copied to logically air-gapped vaults. These resources must be encrypted with a customer managed KMS key or be unencrypted. Resources supporting full AWS Backup management do not have this constraint. -
Backup frequency and concurrent copies – For resources not supporting full AWS Backup management, ensure your backup frequency allows sufficient time for copies to complete. If backups are scheduled more frequently than copies can finish, copy jobs will queue and may eventually fail. For guidance on concurrent copy limits, see quotas.
-
Lifecycle compatibility – The retention period specified in your backup plan must be compatible with the minimum and maximum retention periods configured for your logically air-gapped vault.
-
Locked backup vaults – If your target backup vault has a vault lock enabled, temporary recovery points cannot be deleted manually and will be retained until either the copy completes or the retention period expires.
-
Restore testing, indexing, and scanning – Restore testing, recovery point indexing, and malware scanning will ignore temporary recovery points with a
DELETE_AFTER_COPYlifecycle. Recovery point indexing does not support recovery points in logically air-gapped vault. Malware scanning does not support scheduled scans of copied recovery points, which includes automatic copies taken as part of primary backups to logically air-gapped vault.
Resources supporting full AWS Backup management
Some resource types, such as Amazon EFS, Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB with AWS Backup advanced features etc., that support full AWS Backup management, can back up directly to your logically air-gapped vault. No recovery point is created in your backup vault, and no copy operation is required. Any scheduled copy actions in your backup plan use the recovery point in your logically air-gapped vault as the source.
Resources that support continuous backup, such as Amazon S3, can also perform continuous backup directly to a logically air-gapped vault.
For a list of resource types supporting full AWS Backup management and logically air-gapped vaults, see Feature availability by resource in the columns labeled "Full management" and "Logically air-gapped vault".
Resource not supporting full AWS Backup management
Resources such as Amazon EBS/EC2, Amazon Aurora, and Amazon FSx cannot back up directly to logically air-gapped vaults. For these resource types, AWS Backup creates a temporary recovery point in your backup vault and then automatically copies it to your logically air-gapped vault.
The temporary recovery point has a special lifecycle setting called DELETE_AFTER_COPY. Once the copy to your logically air-gapped vault completes successfully,
AWS Backup automatically deletes the temporary recovery point. All other scheduled copy actions in your backup plan start in parallel with the copy to your logically air-gapped vault and do not impact your current copy experience.
If the copy to your logically air-gapped vault fails, the temporary recovery point is retained in your backup vault according to the retention period you specified.
This helps you ensure that you always have a usable recovery point after a backup job completes. If the recovery point is later manually copied to the logically air-gapped vault,
it is automatically cleaned up according to the DELETE_AFTER_COPY rule.
Warning
Resources encrypted with AWS managed keys (for example, aws/ebs) are not supported for copy to logically air-gapped vaults.
These resources must be encrypted with an AWS Key Management Service customer managed key or be unencrypted. Resources supporting full AWS Backup management do not have this constraint.
Delete after copy lifecycle
Temporary recovery points have a new lifecycle attribute called DeleteAfterEvent with a value of DELETE_AFTER_COPY. This attribute indicates that
the recovery point will be deleted automatically after all copy jobs are complete, or after the retention period you specified, whichever comes first.
A temporary recovery point is deleted when all the following conditions are true:
-
All automatic and scheduled copy jobs have finished.
-
There is a completed copy job to your target logically air-gapped vault with a retention period at least as long as the source recovery point.
If you need to prevent manual deletion of the temporary recovery point while copies are ongoing, consider using a locked backup vault as your target backup vault.
Continuous backup for Resource not supporting full AWS Backup management
For resources such as Amazon Aurora, if you enable continuous backup, AWS Backup creates a continuous recovery point in your backup vault and takes a temporary snapshot that is copied to your logically air-gapped vault. The temporary snapshot should be automatically deleted after the copy is completed, regardless of whether the copy succeeds or fails, because you retain a continuous recovery point in your backup vault.
If you do not want to create a continuous recovery point for Amazon Aurora in your backup vault, but do want a continuous recovery point for Amazon S3 in your logically air-gapped vault,
then you can disable continuous backup (EnableContinuousBackup) setting in the current plan and enable S3 continuous from a different plan.
You can learn more about Aurora backup storage in Understanding Amazon Aurora backup storage usage.
Unsupported resources
If a resource type is not supported by logically air-gapped vaults, or if a non-fully managed resource is encrypted with an AWS managed key, AWS Backup creates the backup in your backup vault only. No copy to your logically air-gapped vault is attempted. The backup job completes successfully with a message indicating why the backup did not go to your logically air-gapped vault.
Cost considerations
-
This feature does not incur new charges. You only pay for the storage in your vaults.
-
For resources supporting full AWS Backup management, maintaining backups only in your logically air-gapped vault can result in significant cost savings compared to maintaining two backup copies in both a backup vault and a logically air-gapped vault.
-
For resources not supporting full AWS Backup management, you are charged for both the temporary recovery point in your backup vault and the recovery points in your logically air-gapped vault.
-
You can still achieve significant cost savings from retention of just a single backup copy, but these savings can vary based on your backup frequency and change rate.
-
Lower backup frequencies generally produce greater savings because temporary recovery points occupy storage for a shorter percentage of your billing period.
-
Some resources have minimum billing durations, which increase costs for temporary recovery points.
-
-
Disable Tags or ACLs metadata retrieval in your backup configuration if you do not use these S3 features. This reduces API calls and associated charges for metadata checks during copy operations.
Configure logically air-gapped vault primary backup
You can configure logically air-gapped vault primary backup through the AWS Backup console, the AWS CLI, AWS CloudFormation, or AWS Organizations backup policies.
Configure a Backup plan
Configure on-demand backup
Monitor logically air-gapped vault primary backup
You can monitor the status of your backups and copy jobs using the AWS Backup console, AWS CLI, or Amazon EventBridge events.
Monitor for Backup Jobs
Monitor backup job status
(DescribeBackupJob)
to ensure your resources remain protected. A failed backup job indicates no recovery point was created.
-
Verify recovery point creation location - When a backup job completes successfully, you have a recovery point in either your target backup vault or your target logically air-gapped vault. Check the
BackupVaultArnfield to determine where the recovery point was created. -
Verify job status - If a resource is not supported by logically air-gapped vaults, the backup job completes with a
MessageCategoryofLOGICALLY_AIR_GAPPED_BACKUP_VAULT_NOT_SUPPORTEDand a status message explaining why the backup was created in your backup vault instead. -
Verify temporary recovery point type - To check if a recovery point is temporary, look for the
RecoveryPointLifecycle.DeleteAfterEventfield with a value ofDELETE_AFTER_COPY.
Monitor for Copy Jobs
Monitor copy jobs
(ListCopyJobs)
to your logically air-gapped vault for failures. A failed copy job means your recovery point remains in your standard backup vault without logically air-gapped vault protection.
-
Verify copy job status - You can monitor copy job status using the existing
Copy Job State ChangeEventBridge event. Optionally, filter on the destination vault (destinationBackupVaultArn) to focus on logically air-gapped vault copies. -
Verify copies for a source recovery point - Use the
ListCopyJobsAPI with the newBySourceRecoveryPointArnfilter to find all copy jobs associated with a specific recovery point, including both automatic copies to your logically air-gapped vault and scheduled copies to other destinations. -
Verify deletion of temporary recovery point - Track completion of temporary recovery point deletion. If the copy job state is
RUNNING, the recovery point has not yet been deleted. If the copy to your logically air-gapped vault hasFAILED, the recovery point will be retained per your specified retention period.
Note
Copy job records expire and are removed 30 days after they finish. After this period, you cannot use ListCopyJobs to determine historical copy status.
Monitor for Recovery point
Monitor for EXPIRED recovery points
(ListRecoveryPointsByBackupVault),
which may indicate AWS Backup could not delete them (possibly due to missing permissions).
EXPIRED recovery points can have cost implications.
-
Verify recovery point state - Use the existing Recovery Point State Change EventBridge event to monitor expirations.
-
Verify deletion of temporary recovery point - If a recovery point with
DeleteAfterEvent: DELETE_AFTER_COPYhas not been deleted, use theListCopyJobsAPI to determine the reason, as mentioned above.
Onboarding and migration
If you currently use copy actions to copy backups to a logically air-gapped vault, you can migrate to logically air-gapped vault primary backup to reduce costs. You can also migrate your existing Amazon S3 continuous backups from a backup vault to a logically air-gapped vault. This guide explains the prerequisites and steps required to migrate to the logically air-gapped vault primary backup feature.
Prerequisites and Best Practices
Before you can effectively use logically air-gapped vault primary backup feature, there are prerequisites and recommended best practices.
Prerequisites
Currently, a logically air-gapped vault as a primary backup target supports only backups within the same AWS account and AWS Region as your backup resources. Logically air-gapped vault backups are inherently stored in separate service accounts, providing cross-account / cross-Org isolation without requiring copies to a separate accounts. If you need cross-Region backups, continue using the logically air-gapped vault as a copy destination. Before migrating to this feature, ensure you meet the following requirements:
-
Region and account requirements
-
Your logically air-gapped vault must be in the same AWS account and Region as your resources
-
-
Resource compatibility
-
Verify that your resources are supported by logically air-gapped vaults in Feature availability by resource.
-
Check if your resources support full AWS Backup management or not. The experience of creating air-gapped backups differs between these two types of resources, even though the outcome is similar for both.
-
-
Encryption requirements
-
Resources that do not support full AWS Backup management must be either unencrypted or encrypted with Customer Managed Keys (CMKs). AWS Managed Key (AMK) encrypted resources are not supported by logically air-gapped vault.
-
Best Practices
-
Start with a pilot migration of non-critical resources.
-
Review and adjust backup frequencies based on copy job performance.
-
Implement comprehensive monitoring before full migration.
-
Regularly verify recovery point creation in intended vaults.
Planning Your Migration
-
Review existing backup plans and policies.
-
Identify which resources support full AWS Backup management and which do not.
-
Resources supporting full AWS Backup management (e.g., EFS, S3) - can backup directly to logically air-gapped vault
-
Resources not supporting full AWS Backup management (e.g., EC2, EBS, FSx) - require temporary backup in backup vault before being copied to Logically air-gapped vault
-
-
Review your current backup volume and frequency and ensure your configuration aligns with concurrent copy limits for all resources not supporting full AWS Backup management.
-
Skip this step If you already copy to a logically air-gapped vault at the same frequency as your standard vault backups.
-
Consider adjusting backup frequency, if needed, to prevent copy job queuing.
-
If copy job queuing occurs, you will still have a usable recovery point in your standard backup vault while awaiting completion of the copy to your logically air-gapped vault. However, that recovery point will not provide the protection level that Logically air-gapped vault offers.
-
Resources supporting full AWS Backup management migration path
For fully managed resources, you can back up directly to your logically air-gapped vault without requiring copy operations.
For snapshot-based backups
This process applies to all snapshot scenarios, regardless of whether your backup vault is locked. When migrating an existing backup plan or using an existing backup vault (primary) and logically air-gapped vault (copy) in a new backup plan:
-
Maintain your existing backup vault or add it as a backup target (
TargetBackupVaultName). This vault will not store any backups but must be provided for backwards compatibility. -
Update your backup plan to include the logically air-gapped vault (
TargetLogicallyAirGappedBackupVaultArn), existing in the same account, as a primary target. -
Review any existing copy action to another logically air-gapped vault to determine if it is still needed. You can also move this vault as a primary target in Step 2 if it is in the same account.
For Amazon S3 continuous backups
Logically air-gapped vault as a primary backup target supports continuous backup for Amazon S3. However, you can maintain only one active continuous recovery point per resource in a single vault. If you have an existing active Amazon S3 continuous recovery point, you must disassociate or delete it before creating a new one in a different vault. Adding a logically air-gapped vault target (from the same account) to your backup plan, with an existing active Amazon S3 continuous recovery point, will cause the continuous backup job to fail.
To migrate your Amazon S3 continuous recovery point to your logically air-gapped vault from an unlocked backup vault:
-
Update your backup plan to add a copy action to your logically air-gapped vault. This will reduce your cost to generate the initial backup in your logically air-gapped vault. Skip this step if you are already copying to your local logically air-gapped vault.
-
Verify that at least one snapshot copy completes successfully in your logically air-gapped vault before proceeding.
-
Disassociate existing Amazon S3 continuous recovery point. Call the DisassociateRecoveryPoint API to change the recovery point status from AVAILABLE to STOPPED. This action preserves your existing backup data while stopping new data from being added.
-
Update backup plan to add logically air-gapped vault (
TargetLogicallyAirGappedBackupVaultArn) as a backup target. -
Remove any previous copy actions in the plan.
-
On the next backup plan execution, a new continuous recovery point will be created in your logically air-gapped vault. This recovery point will be incremental, based on the copied snapshot from Step 1.
To migrate your Amazon S3 continuous recovery point to your logically air-gapped vault from a locked backup vault:
-
Update your backup plan to add a copy action to your logically air-gapped vault. This will reduce your cost to generate the initial backup in your logically air-gapped vault. Skip this step if you are already copying to your local logically air-gapped vault.
-
Verify that at least one snapshot copy completes successfully in your logically air-gapped vault before proceeding. Ensure the copied snapshot has a retention period long enough to remain available until you complete all the steps.
-
Add the logically air-gapped vault as a primary target and remove any copy action.
-
This step is required because locked vaults do not support disassociation of continuous recovery points.
-
Your existing continuous recovery point in the locked backup vault will continue accumulating data until it expires according to its lifecycle.
-
New continuous backup jobs will fail because only one active continuous recovery point can exist per resource. Since these jobs are failing, no copy actions will execute.
-
-
Wait for the existing continuous recovery point to expire. After expiration, a new continuous recovery point will be created in the logically air-gapped vault. This recovery point will be incremental based on the copied snapshot from step 1, provided the snapshot still exists in your logically air-gapped vault.
-
Any data accumulated in your standard vault will be lost upon expiration. Only data backed up after the new recovery point creation in the Logically air-gapped vault will be retained.
Resources not supporting full AWS Backup management migration path
Non-fully managed resources require a copy operation to the logically air-gapped vault. The process creates a temporary recovery point (billable) in your standard backup vault, which is automatically copied to your logically air-gapped vault and then deleted after the copy is completed. When you update your backup plan to include a logically air-gapped vault target:
-
Backup jobs will create a recovery point in your backup vault. This has a lifecycle dictated by
DELETE_AFTER_COPYevent. -
A copy job automatically initiates transferring the recovery point to your logically air-gapped vault.
-
After the copy is completed successfully, the temporary recovery point in your vault is deleted.
-
If the copy fails, the temporary recovery point is retained for a maximum duration according to your specified retention period, ensuring you have a usable recovery point.
Troubleshooting
Backup or copy job fails with lifecycle incompatibility error
Error for backup jobs: Backup job failed because the lifecycle is outside the valid range for backup vault.
Error for copy jobs: Copy job failed. The retention specified in the job is not within the range specified for the target Backup Vault.
Possible cause: Backup jobs or copy jobs fail because the retention period is incompatible with the logically air-gapped vault's minimum or maximum retention settings.
Resolution: Update your backup plan to specify a retention period that falls within the minimum and maximum retention periods configured for your logically air-gapped vault.
Continuous backup jobs fail with "already has continuous backup enabled"
Error: Bucket {bucket_name} already has continuous backup enabled for another vault Backup job failed.
Possible cause: Continuous backup jobs fail because there is already a continuous recovery point for the resource in another vault.
Resolution: Each resource can have only one continuous recovery point. If your backup vault is unlocked, disassociate the existing continuous recovery point using the disassociate-recovery-point command. If your backup vault is locked, wait until the existing continuous recovery point expires according to its lifecycle.
Backup job completes with "Completed with issues" - Unsupported resource type
Message: Backup job completed successfully to the target backup vault. This resource type is not supported by logically air-gapped backup vault.
Possible cause: Backup jobs for unsupported non-fully managed resources show "Completed with issues" with a message indicating that the resource is not supported.
Resolution: Resource types that are not supported will only backup to backup vault. If you want to retain these backups in your backup vault, no action is required. If you prefer not to mix unsupported resources with your logically air-gapped vault, you can:
-
Remove the resource or logically air-gapped vault target from your backup plan for these resources and continue backing up to your backup vault only. You can subsequently add the resource as part of a different plan.
Backup job completes with "Completed with issues" - Unsupported encryption key
Message: Backup job completed successfully to the target backup vault. This resource is encrypted with an AWS managed key and cannot be copied to a logically air-gapped backup vault.
Possible cause: Backup jobs for unsupported non-fully managed resources show "Completed with issues" with a message indicating that the resource is encrypted with an AWS managed key.
Resolution: Non-fully managed resources encrypted with AWS managed keys cannot be copied to logically air-gapped vaults. If you want to retain these backups in your backup vault, no action is required. If you prefer not to mix unsupported resources with your logically air-gapped vault, you can:
-
Re-encrypt your resources with a customer managed KMS key, or
-
Remove the resource or logically air-gapped vault target from your backup plan for these resources and continue backing up to your backup vault only. You can subsequently add the resource as part of a different plan.
Recovery points remain in EXPIRED state
Possible cause: Temporary recovery points transition to EXPIRED state but are not deleted.
Resolution: AWS Backup may lack permissions to delete the recovery points. Verify that your backup role has the necessary IAM permissions. You may need to manually delete expired recovery points.
Copy jobs are queued or failing due to high backup frequency
Possible cause: Copy jobs to logically air-gapped vaults are queuing or failing because backups are scheduled more frequently than copies can complete.
Resolution: Reduce your backup frequency or adjust your backup schedule to allow more time between backups. See the AWS Backup quotas documentation for information about concurrent copy limits.